Abstract
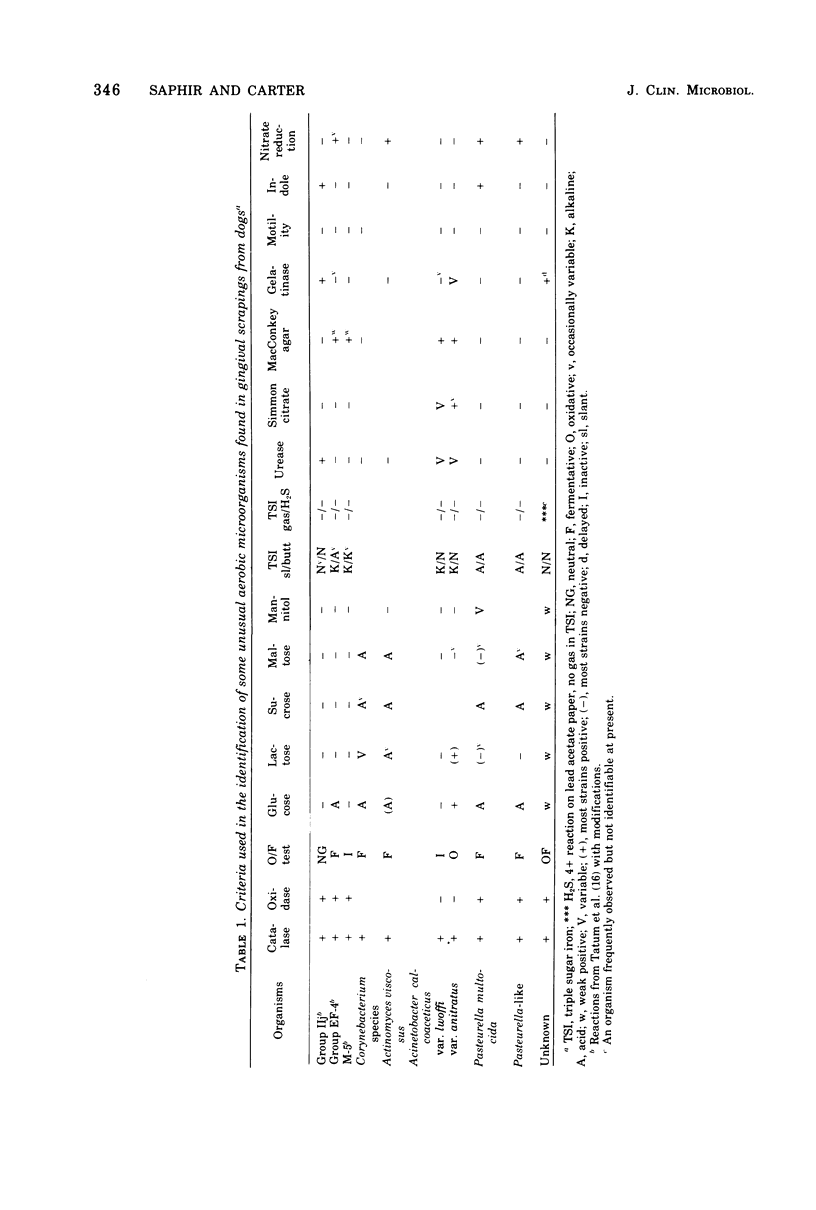
Gingival scrapings from dogs were examined to determine their aerobic bacterial flora. Of particular interest was the frequent recovery of three unclassified groups of aerobic gram-negative bacteria, IIj, EF-4, and M-5, previously associated with human dog-bite infections. Although no set pattern was found between the variability and consistency of gingival microbiota as related to age, sex, or breed of dog, a certain characteristic flora can be predicted in the healthy canine gingiva. Members of the following genera were found: Streptococcus, Staphylococcus, Actinomyces, Escherichia, Corynebacterium, Pasteurella, Caryophanon, Mycoplasma, Acinetobacter, Moraxella, Neisseria, Enterobacter, and Bacillus.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer A. W., Kirby W. M., Sherris J. C., Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 Apr;45(4):493–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter G. R. Pasteurellosis: Pasteurella multocida and Pasteurella hemolytica. Adv Vet Sci. 1967;11:321–379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davenport A. A., Carter G. R., Schirmer R. G. Canine actinomycosis due to Actinomyces viscosus: report of six cases. Vet Med Small Anim Clin. 1974 Nov;69(11):1442, 1444-7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genco R. J., Evans R. T., Ellison S. A. Dental research in microbiology with emphasis on periodontal disease. J Am Dent Assoc. 1969 May;78(5):1016–1036. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.1969.0162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell A., Jr, Jordan H. V., Georg L. K., Pine L. Odontomyces viscosus, gen. nov., spec. nov., a filamentous microorganism isolated from periodontal plaque in hamsters. Sabouraudia. 1965 Jun;4(2):65–68. doi: 10.1080/00362176685190181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbert W. T., Rosen M. N. Pasteurella multocida Infections: I. Pasteurella Multocida Infection Due to Animal Bite. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1970 Jun;60(6):1103–1108. doi: 10.2105/ajph.60.6.1103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH J. E. Studies on Pasteurella septica. I. The occurrence in the nose and tonsils of dogs. J Comp Pathol. 1955 Jul;65(3):239–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Socransky S. S., Manganiello S. D. The oral microbiota of man from birth to senility. J Periodontol. 1971 Aug;42(8):485–496. doi: 10.1902/jop.1971.42.8.485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Socransky S. S. Relationship of bacteria to the etiology of periodontal disease. J Dent Res. 1970 Mar-Apr;49(2):203–222. doi: 10.1177/00220345700490020401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]