Abstract
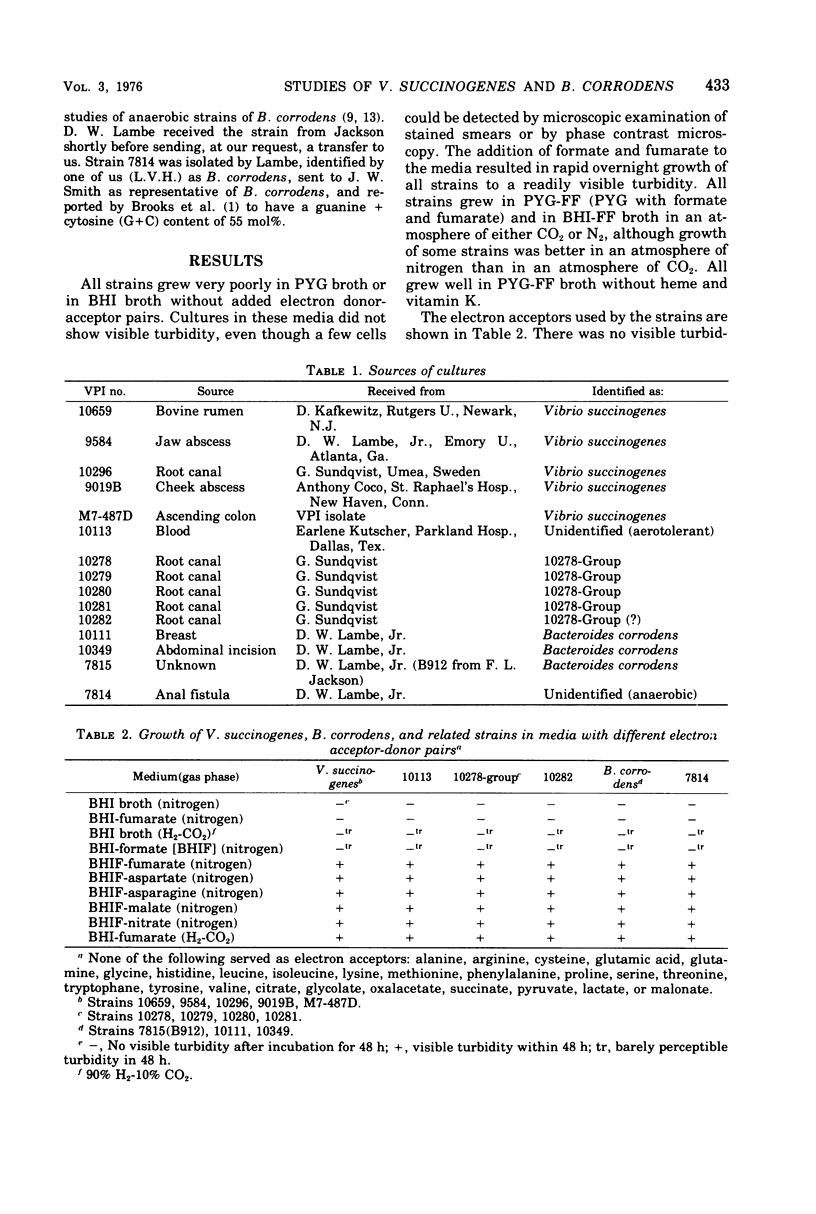
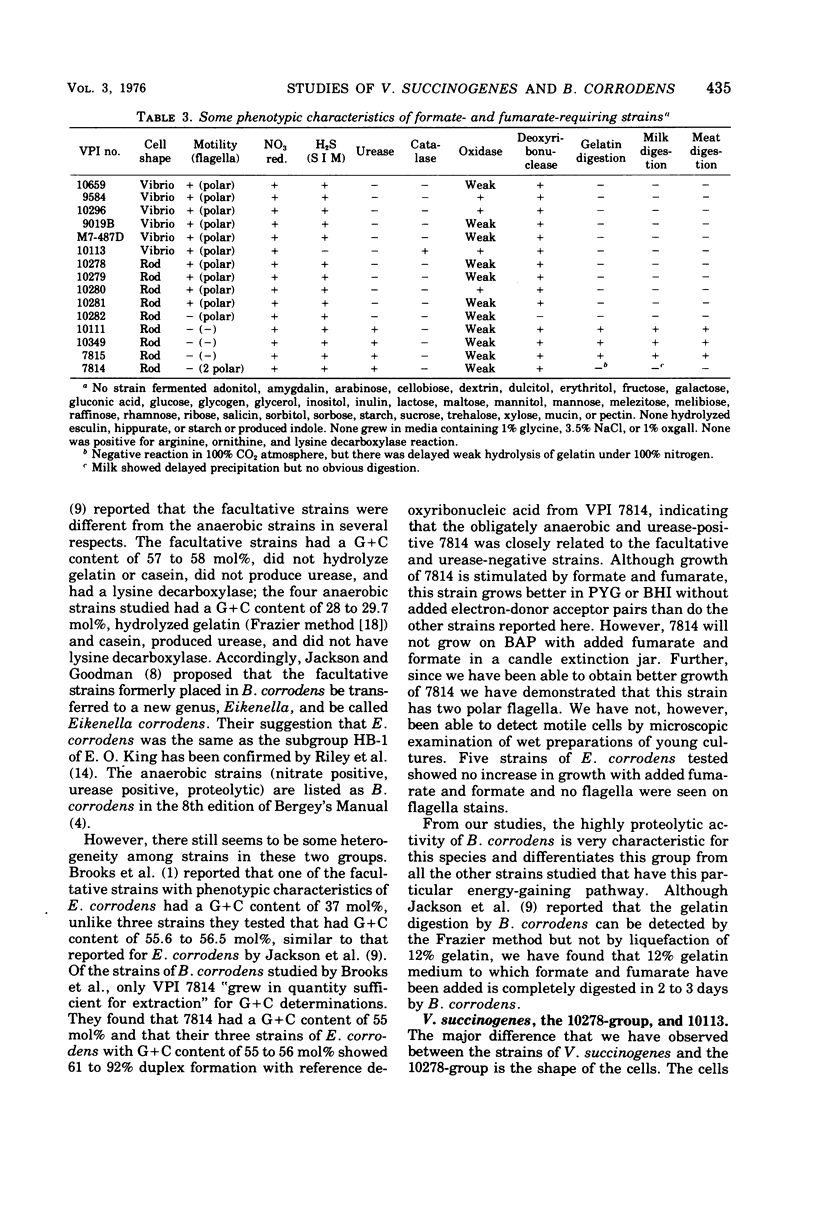
Strains of anaerobic, gram-negative bacteria, isolated from human clinical specimens and from studies of human normal flora, that have energy metabolism similar to Vibrio succinogenes are described. Included are four human isolates of V. succinogenes, five similar strains of motile straight rods, three strains of Bacteroides corrodens, and two unidentified strains. All strains studied grew poorly in usual anaerobic broth media but produced good turbidity in overnight broth cultures in media containing fromate and fumarate, indicating that all have an energy metabolism similar to V. succinogenes: they gain energy by the transfer of electrons from formate or hydrogen to fumarate.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brooks G. F., O'Donoghue J. M., Rissing J. P., Soapes K., Smith J. W. Eikenella corrodens, a recently recognized pathogen: infections in medical-surgical patients and in association with methylphenidate abuse. Medicine (Baltimore) 1974 Sep;53(5):325–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EIKEN M. Studies on an anaerobic, rodshaped, gram-negative microorganism: Bacteroides corrodens n. sp. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1958;43(4):404–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iannotti E. L., Kafkewitz D., Wolin M. J., Bryant M. P. Glucose fermentation products in Ruminococcus albus grown in continuous culture with Vibrio succinogenes: changes caused by interspecies transfer of H 2 . J Bacteriol. 1973 Jun;114(3):1231–1240. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.3.1231-1240.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson F. L., Goodman Y. E., Bel F. R., Wong P. C., Whitehouse R. L. Taxonomic status of facultative and strictly anaerobic "corroding bacilli" that have been classified as Bacteroides corrodens. J Med Microbiol. 1971 May;4(2):171–184. doi: 10.1099/00222615-4-2-171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James A. L., Robinson J. V. A comparison of the biochemical activities of Bacteroides corrodens and Eikenella corrodens with those of certain other gramnegative bacteria. J Med Microbiol. 1975 Feb;8(1):59–76. doi: 10.1099/00222615-8-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kafkewitz D., Goodman D. L-Asparaginase production by the rumen anaerobe Vibrio succinogenes. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Jan;27(1):206–209. doi: 10.1128/am.27.1.206-209.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niederman R. A., Wolin M. J. Requirement of succinate for the growth of Vibrio succinogenes. J Bacteriol. 1972 Feb;109(2):546–549. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.2.546-549.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEBALD M., VERON M. TENEUR EN BASES DE L'ADN ET CLASSIFICATION DES VIBRIONS. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1963 Nov;105:897–910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHAW C., CLARKE P. H. Biochemical classification of Proteus and Providence cultures. J Gen Microbiol. 1955 Aug;13(1):155–161. doi: 10.1099/00221287-13-1-155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLIN M. J., WOLIN E. A., JACOBS N. J. Cytochrome-producing anaerobic Vibrio succinogenes, sp. n. J Bacteriol. 1961 Jun;81:911–917. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.6.911-917.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkins T. D., Thiel T. Modified broth-disk method for testing the antibiotic susceptibility of anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Mar;3(3):350–356. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.3.350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


