Abstract
Elevated expression of p130Cas/BCAR1 (breast cancer anti estrogen resistance 1) in human breast tumors is a marker of poor prognosis and poor overall survival. Specifically, p130Cas signaling has been associated with antiestrogen resistance, for which the mechanism is currently unknown. TAM-R cells, which were established by long-term exposure of estrogen (E2)-dependent MCF-7 cells to tamoxifen, displayed elevated levels of total and activated p130Cas. Here we have investigated the effects of p130Cas inhibition on growth factor signaling in tamoxifen resistance. To inhibit p130Cas, a phosphorylated substrate domain of p130Cas, that acts as a dominant-negative (DN) p130Cas molecule by blocking signal transduction downstream of the p130Cas substrate domain, as well as knockdown by siRNA was employed. Interference with p130Cas signaling/expression induced morphological changes, which were consistent with a more epithelial-like phenotype. The phenotypic reversion was accompanied by reduced migration, attenuation of the ERK and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathways, and induction of apoptosis. Apoptosis was accompanied by downregulation of the expression of the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2. Importantly, these changes re-sensitized TAM-R cells to tamoxifen treatment by inducing cell death. Therefore, our findings suggest that targeting the product of the BCAR1 gene by a peptide which mimics the phosphorylated substrate domain may provide a new molecular avenue for treatment of antiestrogen resistant breast cancers.
Keywords: p130Cas(BCAR1), tamoxifen resistance, apoptosis, breast cancer, signal transduction, decoy mechanism
INTRODUCTION
The steroid hormone estrogen (E2) has been implicated in the proliferation of breast tumor cells and in the progression of breast cancer (Henderson et al., 1988). E2 exerts its effects through the estrogen receptor (ER), which exists in two structurally related forms, ERα and ERβ, encoded by separate genes ESR1 and ESR2, respectively. In the ‘classical’ pathway E2 diffuses into the cells and binds the ER which leads to its activation (Henderson et al., 1988). The activated ERα-E2 complex acts in the nucleus as transcriptional regulator for various genes including CCND1 (cyclin D1), BCL2, VEGFA, OXT (oxytocin) and CTSD (cathepsin D) (O’Lone et al., 2004).
ERα is clinically important in breast cancer diagnosis and treatment as it is expressed in more than 70% of breast cancers (Couse and Korach 1999). Cumulative exposure of breast epithelium to estrogen is a risk factor for the development of breast cancer (Henderson and Feigelson, 2000). Current endocrine therapies of breast cancer are based mainly on antagonizing ER function by utilizing antiestrogens such as tamoxifen and fulvestrant, or aromatase inhibitors which block estrogen synthesis (Smith and Dowsett, 2003). Tamoxifen treatment improves overall survival and decreases disease recurrence. However, the beneficial effects of existing endocrine therapies are in part counteracted by the development of resistance. Mechanisms responsible for tamoxifen resistance include mutations in the ESR1 gene resulting in enhanced sensitivity to ligand and co-activator recruitment, overexpression of co-activators such as AIB1, and downregulation of co-repressor activity (Lavinsky et al., 1998). It has been suggested that the cross talk between the ER and growth factor receptor pathways constitutes an ‘alternative’ pathway of ER action at the cell membrane, which influences the endocrine response and resistance in breast cancer (Shou et al., 2004). Upregulation of expression and/or signaling of the growth factors and their respective receptors, in particular the ERBB family proteins and the insulin growth factor receptor (IGFR), has been observed in resistant tumors and breast cancer cell lines (Guvakova and Surmacz, 1999; Knowlden et al., 2003). This enhancement of growth factor signaling is associated with an increase in phosphorylated ERK1/2 and resistance in breast cancer (Gee et al., 2001). Moreover, ERα interacts with the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt cell survival pathway in a non-nuclear ligand-dependent manner thereby suggesting that high Akt expression levels could be associated with tamoxifen resistance (Campbell et al., 2001). More recently, it was suggested that tamoxifen resistance in invasive lobular breast cancer arises from overexpression of the estrogen-related receptor γ (ERRγ), which is structurally similar to ERα (Riggins et al., 2008).
In a screen for genes involved in breast cancer antiestrogen resistance (BCAR), three independent loci BCAR1, BCAR2 and BCAR3 were identified (Bouton et al., 2001). Recently, van Agthoven and colleagues described the identification of four additional BCAR genes including AKT1, AKT2, EGFR, and GRB7 (van Agthoven et al., 2008). The first locus BCAR1 is identical to the gene encoding the p130 Crk-associated substrate (p130Cas) (Brinkman et al., 2000). High expression levels of p130Cas in primary breast tumors are associated with increased rate of relapse and with poor response to tamoxifen treatment of recurrent disease (van der Flier et al., 2000). Interestingly, high levels of p130Cas were found in invasive feline and canine mammary tumor tissues, stressing the notion that BCAR1 plays a role in breast cancer progression (Scibelli et al., 2003). p130Cas forms a signaling node downstream of activated growth factor receptors, integrins, and G-protein coupled receptors (Bouton et al., 2001). Phosphorylation on tyrosine residues situated within the p130Cas substrate domain (SD) leads to its activation, which is followed by recruitment of SH2 domain-containing molecules including Crk and Nck. Recruitment of these molecules to the p130Cas SD leads to the assembly of larger signaling complexes, which can result in the activation of the Ras-MAPK and/or Rac-DOCK180-JNK signaling cascades (Bouton et al., 2001). It has been shown that following E2 treatment, p130Cas rapidly and transiently associates with ERα in a complex containing Src kinase and the p85 subunit of PI3K, suggesting that p130Cas is involved in regulating E2-dependent cytosolic ERα signaling (Cabodi et al., 2004). It was also shown that overexpression of p130Cas in MCF-7 cells confers resistance to tamoxifen through its interaction with c-Src (Riggins et al., 2006). Moreover, transgenic mice overexpressing p130Cas in the mammary gland show extensive epithelial hyperplasia during development and delayed involution, indicating a role of p130Cas in the proliferation and survival of mammary epithelial cells (Cabodi et al., 2006). It has been suggested that overexpression of p130Cas might lead to altered regulation of progression through the cell cycle (Cabodi et al., 2004; Riggins et al., 2006).
Preventing the interaction of p130Cas with downstream signal transducers that bind to its phosphorylated SD might be a useful strategy for the development of small molecule and/or peptide inhibitors for breast cancer in which p130Cas is elevated and/or activated. We developed a dominant negative (DN) p130Cas molecule (Src*/CasSD) - composed of an attenuated c-Src kinase domain fused to the p130Cas SD (Kirsch et al., 2002). Attenuation was achieved by mutating tyrosine 416 in the c-Src kinase domain to phenylalanine. While this Src kinase mutant is inactive against exogenous substrates (Piwnica-Worms et al., 1987; Kmiecik and Shalloway, 1987), it constitutively phosphorylated the p130Cas SD in the Src*/CasSD chimera independent of upstream signals, and acted as a decoy for downstream binding partners in HEK293T cells by competing with endogenous p130Cas (Kirsch et al., 2002). Here, we assessed the effects of Src*/CasSD expression on MAPK/ERK PI3K/Akt survival pathway in MCF-7 and TAM-R cells - a tamoxifen resistant cell line derived from MCF-7 cells by long-term exposure to tamoxifen. Targeting downstream signal transducers of activated p130Cas in breast cancer cells reduced cell migration, and re-sensitized TAM-R cells to tamoxifen treatment. This re-sensitization was associated with morphological changes consistent with a more epithelial-like phenotype. These effects were correlated with changes in ERBB levels and with an attenuation of the MAPK/ERK as well as the PI3K/Akt cell survival pathway. Together these results stress the relevance of targeting the product of the BCAR1 gene, particular in tumors with elevated protein levels.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
RETROVIRAL EXPRESSION CONSTRUCTS
The Src*/CasSD, SrcKM/CasSD, Src* fragments (Kirsch et al., 2002) were amplified by PCR and subcloned into the Not I and Hpa I sites (in frame with the Myc-tag) of the constitutive retroviral expression vector pCXbsr. To generate the pCXbsr-Src*/CasSD doxycycline (Dox) inducible retroviral expression construct, the Src*/CasSD amplicon was cloned into the Hind III and EcoR I sites of the vector pC4bsrR(TO).
CELL CULTURES AND TREATMENT CONDITIONS
MCF-7 breast cancer cells were grown in RPMI-1640, 5% FBS and 4 mM glutamine, supplemented with penicillin/streptomycin and sodium pyruvate. MCF-7-derived TAM-R cells were grown in phenol-red free RPMI-1640 supplemented with antibiotics and glutamine as above and 5% charcoal-stripped FBS or in 5% FBS and 10-7 M 4-hydroxytamoxifen (Sigma). Investigation of basal expression of signaling components was carried out on cells grown in basal medium. For sensitivity assays to tamoxifen, TAM-R cells transfected with siRNA for 24 h were treated with tamoxifen for an additional 24 h. For induction of TAM-R inducible stable cells 1 μg/ml Dox was added to the medium for 8 h and subsequently the medium was supplemented with 100 nM or 1 μM tamoxifen and 10 nM E2 for another 48 h. Similarly, TAM-R stable cell lines were seeded in 5% FBS and after the overnight incubation, growth medium was supplemented with tamoxifen as above.
RETROVIRAL INFECTION AND EXPRESSION
Retroviral infection of MCF-7 and TAM-R cells was carried out as described (Min et al., 2007). Cells infected with the pCXbsr plasmids were selected with 10 μg/ml blasticidin for 4 days. For Dox inducible expression pC4bsrR(TO) based plasmids, cells were selected with 10 μg/ml blasticidin and 0.2 μg/ml G418 for about one week. Three independent pools of inducible infectants were generated.
PROTEIN ANALYSIS
Whole cells extracts (WCE) were prepared and analyzed by Western blotting (WB) and immunoprecipitation as described (Kirsch et al., 1998). Briefly, cells were incubated in RIPA buffer [50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 150 mM NaCl, 1% Nonidet P-40 (NP-40), 0.5% sodium deoxycholate, 0.1% SDS] supplemented with protease inhibitor cocktail (Roche) and phosphatase inhibitors for 30 min on ice followed by centrifugation at 16,000 × g, at 4°C for 30 min.
For immunoprecipitation of Crk, GammaBind™ G-Sepharose™ beads (Amersham Pharmacia Biotech) were preincubated with anti-Crk antibodies (BD Biosciences) at 4°C for 90 min. Cells were lysed in NP-40 buffer [1% NP-40, 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.4), 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM sodium orthovanadate, 1 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (PMSF) and 1 × complete protease inhibitors (Roche)]. Clarified cell lysates were incubated with the antibody-bead complexes at 4°C for 2 h. Immunoprecipitates were washed four times with ice-cold NP-40 buffer containing 0.1% NP-40 and then subjected to WB analysis.
ANTIBODIES
Crk (BD Biosciences), p130Cas, GSK-3β (BD, Transduction Laboratories); ERBB2, ERBB3 (Upstate); Akt, phospho-AktSer473, phospho-AktThr308, phospho-ERK1Thr202/2Thr204, EGFR, Mcl-1, phospho-GSK3Ser9, p70S6 Kinase, phospho-p70S6 KinaseThr389 (Cell Signaling); ERα (Ab-15), Nck (Labvision Corporation); Bcl-2, CrkII, ERK1, ERK2, HA (Y-11), Myc (9E10), PY-99, p130Cas (Santa Cruz); Cas B (antibody directed against the SD of p130Cas, a gift from Amy Bouton); β-Actin (Sigma); α-tubulin (Calbiochem).
FAR-WESTERN BLOT ANALYSIS
Far-Western blot analysis with purified GST-fusion proteins was conducted as described (Nollau and Mayer, 2001). Briefly, the membranes were blocked with 3% BSA/TBS-T [150 mM NaCl, 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 0.1% Tween 20] supplemented with 1 mM sodium orthovanadate and 1 mM EDTA (pH 8.8) at 4°C for 1 h. GST fusion proteins (5 μg) were preincubated with 0.5 μg of glutathione-conjugated horseradish peroxidase (Marligen Inc.) in 1× PBS (pH 7.4) on ice for 1 h, incubated with the membranes in 3% BSA/TBS-T at room temperature (RT) for 1 h, and subsequently washed in TBS-T four times for 10 min. The bound probe was detected by chemiluminescence.
PROLIFERATION ASSAY
For the CellTiter-Glo (Promega) luminescent assay cells were plated at a density of 10,000 cells/well into 96-well opague-walled culture plates in triplicate and incubated at 37°C under 5% CO2 for 6 h (baseline measurement) as well as 1 and 3 days. At the indictated times, CellTitre-Glo reagent was added and the culture plates were incubated at RT for 10 min. and the luminescence was recorded. For the acid phosphatase assay (Min et al., 2007), infected cells were plated at a density of 10,000 cells/well into 24-well culture plates in triplicate and allowed to adhere for 12 h, after which fresh medium was added and the cultures were incubated for 2 and 4 days at 37°C under 5% CO2. The color reaction was determined at OD410nm.
MIGRATION ASSAY
Cells (100,000) were suspended in RPMI-1640 supplemented with 0.05% gelatin and layered in the upper compartment of a Transwell (Costar, 8 μm pore size) and incubated at 37°C for 24 h. The lower compartment contained 500 μl RPMI-1640 supplemented with 0.05% gelatin and 5% FBS. Migration was quantified by acid phosphatase assay as above.
FLOW CYTROMETRY ANALYSIS OF CELLS
Cells were harvested, fixed overnight in 95% EtOH at -20°C overnight. Subsequently, fixed cells were re-suspended in propidium iodide (PI) solution (50 μg/ml PI, 100 μg/ml RNAse A in 1× PBS) for 20 min at 4°C, and analyzed using a FACScan (Becton Dickinson). Cells undergoing apoptosis in each sample were estimated by quantification of cell number in sub-G1 phase.
TRANSFECTION OF siRNA
Cells were seeded in 6-well plates one day before transfection (100,000 cells/well). Cells were transfected with, 80 pmol of p130Cas siRNA (sc-36141, sense strand A: 313 GUGGGCAUGUAUGAUAAGA, sense strand B: 857 CACAGGACAUCUAUGAUGU, sense strand C: 2102 GGAUGGAGGACUAUGACUA, Santa Cruz) or control siRNA (sc-37007, Santa Cruz) using Lipofectamine 2000 according to the manufacturer protocol.
RESULTS
TAMOXIFEN RESISTANT BREAST CANCER CELLS CONTAIN ELEVATED LEVELS OF p130Cas
For our studies, we utilized MCF-7 cells, and its tamoxifen resistant derivative TAM-R (Hiscox et al., 2004). Comparison of the expression of p130Cas revealed that TAM-R cells have elevated amounts of total p130Cas (Fig. 1A, left panel). Activated p130Cas was also increased as seen by the total tyrosine phosphorylation analysis of immunoprecipitated p130Cas (Figure 1a, right panel). Thus, we employed our recently established DN approach (Kirsch et al., 2002) to block signaling downstream of the phosphorylated p130Cas SD. The DN p130Cas (Src*/CasSD) composed of an attenuated Src kinase domain (Src*) fused to the CasSD was subcloned in frame with an N-terminal Myc-tag into a retroviral vector (Akagi et al., 2002). As controls we used the empty vector, Myc-tagged Src*, and Myc-tagged SrcKM/CasSD where a kinase inactive Src kinase domain (SrcKM) was fused to the CasSD (Figure 1B). All of the constructs were equally well expressed in MCF-7 and TAM-R cells, and as expected the Src*/CasSD was tyrosine phosphorylated, whereas the SrcKM/CasSD was not (Figure 1C). The expression of the Src*/CasSD was approximately 2.5 fold over endogenous p130Cas (Supplementary Figure S1). Previously, we have shown that the DN effect of the phosphorylated Src*/CasSD molecule is in part mediated by decoying downstream effector molecules from endogenous p130Cas in NIH 3T3 fibroblasts (Kirsch et al., 2002). Far-Western blot analysis was employed to test whether Crk and Nck – two well characterized downstream targets of p130Cas – are able to associate with the Src*/CasSD in breast cancer cells. As seen in Figure 1D (left panels), the GST-tagged SH2 domains of Crk and Nck bind to the phosphorylated CasSD, whereas no interaction was detected with the unphosphorylated SrcKM/CasSD. In addition, immunoprecipitation of Crk showed association with endogenous p130Cas in control cells (Figure 1D, right panel). Expression of Src*/CasSD resulted in reduced interaction of Crk with endogenous p130Cas and preferential interaction with the phosphorylated Src*/CasSD. This assay confirmed that the expressed Src*/CasSD can interact with Crk and Nck and thus act as a decoy.
Fig. 1. Tamoxifen resistant breast cancer cells contain elevated levels of p130Cas.
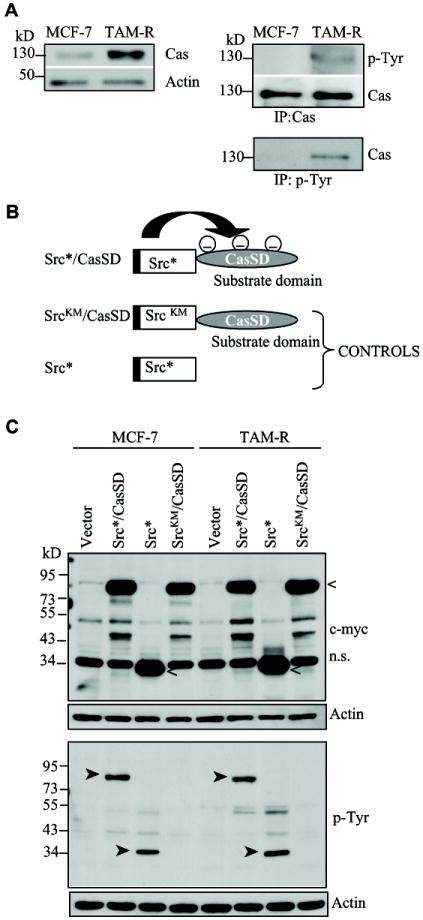

A: Whole cell extracts (WCE) (10 μg) or p130Cas (Cas) and phosphotyrosine (p-Tyr) immunoprecipitates (IP) from MCF-7 and TAM-R cells were probed with the indicated antibodies (representative of two independent experiments). B: Representation of the dominant negative (DN) p130Cas and control constructs [Src*, attenuated Src kinase domain; SrcKM, kinase inactive Src kinase domain; substrate domain (SD) of p130Cas]; the black bar at the N-terminus depicts the Myc-tag. C: MCF-7 and TAM-R stable cell populations carrying the indicated constitutive expression constructs and vector control were analyzed for protein expression (30 μg WCE) and tyrosine phosphorylation using the c-myc and p-Tyr antibodies. Equal loading was assessed by probing with actin antibodies. (<, expressed peptides; ™, phosphorylated peptides). D: The phosphorylated Src*/CasSD interacts with Crk and Nck and competes with endogenous p130Cas for binding to Crk. WCE of TAM-R Src*/CasSD and TAM-R SrcKM/CasSD cells were subjected to Far-Western blot analysis with purified GST-SH2 domains of Crk and Nck (left panels). WCE (1 mg) of TAM-R vector and TAM-R Src*/CasSD cells were immunoprecipitated with anti-Crk antibodies followed by Western blotting (WB) with Cas B (upper panel) and anti-Crk antibodies (lower panel) (representative of two independent experiments). *, marks endogenous p130Cas; <, marks the Src*/CasSD protein.
EXPRESSION OF THE Src*/CasSD IN BREAST CANCER CELLS INDUCES A MORE EPITHELIAL-LIKE PHENOTYPE
TAM-R cells underwent a partial epithelial to mesenchymal transition, displaying prominent lamellipodia (Hiscox et al., 2006a). Signaling through the p130Cas-Crk complex is important for focal adhesion kinase (FAK)-mediated migration (Klemke et al., 1998). Thus, we first compared the morphology of MCF-7 and TAM-R cells stably expressing Src*/CasSD and controls. Src*/CasSD cells rapidly adopted a different morphology, which was most prominent in TAM-R Src*/CasSD cells. These cells grew in tight clusters and were almost completely void of lamellipodia (Figure 2A). No change was seen in control cells expressing SrcKM/CasSD, Src* or empty vector. All control cell populations formed prominent lamellipodia and leading edges as indicated by arrows (Figure 2A). Epithelial cells frequently lose the expression and/or membrane localization of E-cadherin during the course of adopting a more mesenchymal phenotype. Thus we analyzed the effect of Src*/CasSD expression on E-cadherin levels and/or localization in TAM-R. WB analysis revealed no significant differences in overall protein expression (data not shown). However, immunofluorescence analysis of E-cadherin expression/localization showed increased amounds of E-cadherin at cell-cell boundaries in TAM-R Src*/CasSD, suggesting that expression of the Src*/CasSD might stabilize E-cadherin at the cell membrane. These findings are supported by detection of higher amounts of E-cadherin in the TX 100 insoluble fraction of TAM-R-Src*/CasSD (Supplementary Figs. S2A and S2B).
Fig. 2. Src*/CasSD cells display altered cell morphology and migration.
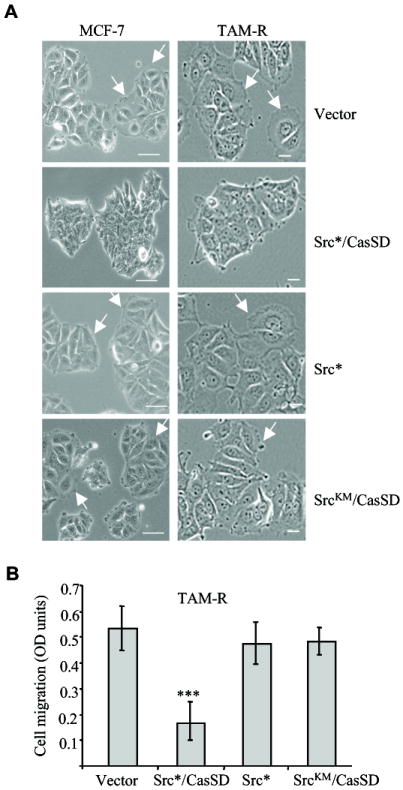
A: Phase contrast images of MCF-7 and TAM-R cells stably and constitutively expressing the indicated constructs (×20 magnification). White arrows indicate cells with lamellipodia. Scale bar 30 μm. B: TAM-R cells stably and constitutively expressing the indicated constructs were subjected to serum stimulated migration assay for 24 h. Data represent ± standard deviation of triplicate from two independent experiments. *** indicates p<0.0001 of vector versus Src*/CasSD (TAM-R cells). P values were calculated using Student’s t-test.
To determine whether the morphological changes induced by the expression of Src*/CasSD cells correlate with a reduced invasive phenotype, migration assays were performed. TAM-R Src*/CasSD, TAM-R SrcKM/CasSD, TAM-R Src*, or TAM-R vector cells were subjected to a serum-stimulated migration assay. Expression of the Src*/CasSD significantly reduced cell migration towards an FBS gradient as compared to vector control cells (Figure 2B). In contrast, the migration rate of the TAM-R SrcKM/CasSD and TAM-R Src* control cell populations was unchanged. In summary, these experiments indicate that the phosphorylated Src*/CasSD promotes a less invasive, more epithelial-like phenotype, and are consistent with the established role of p130Cas-Crk engagement in cell migration.
EXPRESSION OF Src*/CasSD REDUCES PROLIFERATION
p130Cas plays a role in signaling pathways activated by growth factor receptors, and has been shown to promote proliferation. During the course of our studies we consistently noticed reduced cell numbers in cell populations expressing the Src*/CasSD. We did not observe profound differences in plating efficiencies (Supplementary Figure S3). Thus, we determined whether interference with downstream signaling pathways of endogenous p130Cas has an effect on the proliferation of MCF-7 and TAM-R cells. Stable MCF-7 and TAM-R populations expressing the Src*/CasSD construct or vector control were seeded in equal numbers and subsequently cell numbers at days one and three post-seeding were determined. As shown in Figure 3A, the cell numbers of MCF-7 Src*/CasSD and TAM-R Src*/CasSD expressing cells were significantly reduced compared to vector control cells (p<0.03). We consistently observed a stronger effect in TAM-R cells. The cell numbers of Src* and SrcKM/CasSD expressing cells were unchanged (Figure 3A, right panel and data not shown). The enhanced sensitivity of TAM-R cells to the expression of the Src*/CasSD might reflect the adaptation of these cells to higher levels of endogenous p130Cas. In summary, signaling through endogenous p130Cas plays an important role in processes involved in cell proliferation and/or survival.
Fig. 3. Significant reduction in cell numbers of Src*/CasSD expressing cells.

A: MCF-7 and TAM-R cells stably and constitutively expressing Src*/CasSD or control vector were plated at density of 10,000 cells/well. Cell numbers in TAM-R cell populations were determined by measuring ATP at day 1 and 3 after plating (left panel). TAM-R cell populations stably and constitutively expressing Src*, Src KM/CasSD or Src*/CasSD were plated at a density of 10,000 cells/well. Cell numbers in all cell populations were determined at days 2 and 4 after plating (right panel). Results indicated are representative of three independent experiments performed in triplicate ± standard deviation. P values were calculated using Student’s t-test. *** indicates p<0.0008 and ** indicates p<0.03, vector vs. Src*/CasSD. B: Expression of Src*/CasSD influences the protein expression of EGFR, ERBB2. Serum-starved MCF-7 and TAM-R cells stably and constitutively expressing the indicated constructs were subjected to WB analyses for ERBB family proteins (50 μg WCE), and tubulin for loading (representative of three independent experiments). C: Src*Cas/SD expression attenuates ERK activation. Serum-starved MCF-7 and TAM-R Src*/CasSD and vector stable cell populations were stimulated with 10 ng/ml of epidermal growth factor (EGF). WCE (20 μg) were analyzed by WB with pERK1/2, ERK1/2 and actin antibodies. Data are representative of two independent experiments. D: Expression of Src*/CasSD influences the phosphorylation of endogenous p130Cas. WCE of TAM-R Src*/CasSD and vector control cell populations were analyzed by WB for expression of endogenous p130Cas. Arrows indicate positions of phosphorylated and unphosphorylated p130Cas (upper and lower, respectively). Densitometric analysis of three independent WBs was used to calculate the ratio of phosphorylated vs. unphosphorylated p130Cas (right panel).
ECTOPIC EXPRESSION OF THE PHOSPHORYLATED p130Cas SD DOWNREGULATES EGFR LEVELS, ERK ACTIVATION, AND REDUCES THE ACTIVATION OF ENDOGENOUS p130Cas IN TAM-R CELLS
ERBB proteins are upregulated in the TAM-R cells (Supplementary Figure S4) and have been implicated in the proliferation of these cells (Knowlden et al., 2003). Thus, we investigated whether the Src*/CasSD affects the levels of the ERBB proteins. In MCF-7 cells the ERBB levels were unchanged (Figure 3B, upper panel). In contrast, EGFR expression was prominently reduced in TAM-R Src*/CasSD cells compared to TAM-R cells expressing controls (Figure 3B, lower panel). In all TAM-R cell populations tested ERBB3 protein expression did not change noticeably while elevated levels of ERBB2 were detected in cells expressing Src*/CasSD. Next, we examined whether the difference in cell numbers was a consequence of reduced activation of downstream signaling pathways particularly the MAPK-ERK pathway. A time course analysis of ERK1/2 activation in response to EGF treatment revealed an attenuation of ERK1/2 phosphorylation in Src*/CasSD cells compared to vector control cells (Figure 3C). Consistent with the stronger reduction in cell numbers the attenuation was more pronounced in TAM-R Src*/CasSD cells compared to MCF-7 Src*/CasSD. These data suggest that the reduced cell numbers determined are in part due to attenuation of the MAPK-ERK pathway.
Next, the effect of the Src*/CasSD molecule on the levels of endogenous p130Cas was examined by WB. p130Cas levels did not change significantly, but consistently, we found a shift from the phosphorylated form of p130Cas to a lesser or unphosphorylated form (Figure 3D, left panel). A four-fold reduction in the ratio of the phosphorylated vs. unphosphorylated form was determined (Figure 3D, right panel), suggesting that expression of the Src*/CasSD not only decoys downstream molecules, but also influences the activation of endogenous p130Cas.
EXPRESSION OF Src*/CasSD INDUCES APOPTOSIS
We sought to investigate whether apoptosis contributes to the reduced cell number determined. Two procedures were used to identify apoptotic cells; flow cytometry of PI stained cells and visual counting of DAPI stained nuclei with condensed chromatin and/or fragmentation. To circumvent potential effects of adaptation, we generated a Dox-inducible HA-tagged retroviral Src*/CasSD expression plasmid. WB analysis of WCE 24 h post-induction showed that the Src*/CasSD is expressed (Figure 4A) (approximately 1.7 fold of endogenous p130Cas; Supplementary Figure S1). Induction of Src*/CasSD expression caused cells to become round and refractile, and over time an increasing number of cells detached from the substratum (data not shown). The number of cells undergoing apoptosis within the populations was determined by cell cycle analysis 72 h post-induction with Dox (Figures 4B). Approximately 10% of TAM-R Src*/CasSD cells were detected in sub-G1. This represents a 6-fold increase when compared to Dox-treated vector control cells. In addition, cells were quantified by counting the nuclei with clear signs of apoptosis. A similar fraction of cells that express Src*/CasSD underwent apoptosis compared to non-induced and vector control cells (data not shown). Thus, “de novo” expression of the Src*/CasSD in TAM-R cells induces apoptosis, which might also contribute to the reduced cell numbers determined.
Fig. 4. Expression of Src*/CasSD in TAM-R cells resulted in cell death.

A: WB analysis of inducible Src*/CasSD expression using anti-HA and actin antibodies in doxycycline- (Dox) untreated and Dox-treated (24 h) TAM-R cell populations carrying the inducible pCXbsrR(TO)Src*/CasSD expression construct and vector control (representative of at least three experiments). B: Stable TAM-R cell populations infected with inducible Src*/CasSD and vector alone were seeded in 5% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and induced with 1 μg/ml Dox for 72 h. The cells were fixed and stained with propidium iodine (PI) and subjected to flow cytometry. Apoptosis was assessed by observing the changes in sub-G1 phase of the cell cycle. Histograms are representative of three experiments performed in triplicate. The inset number indicates the percentage of cells in sub-G1 phase of the cell cycle (upper panel). TAM-R vector control was set to 1 and used to determine the fold change in cell number in sub-G1. Results are of three independent experiments (± standard deviation) performed in triplicate (lower panel). P values were calculated using Student’s t-test. C: Expression of Src*/CasSD in TAM-R cells attenuates the PI3K/Akt pathway and increases ERα levels. TAM-R stable cell populations constitutively expressing the indicated constructs were serum-starved for 24 h and stimulated with 20% FBS for 10 min. WCE (20 μg) were subjected to WB analysis with the indicated antibodies. Equal loading was assessed with actin antibodies. Data are representative of two independent experiments.
EXPRESSION OF THE Src*/CasSD ATTENUATES THE PRO-SURVIVAL PI3K/Akt PATHWAY AND INCREASES ERα LEVELS
TAM-R cells depend on the activity of Akt for proliferation and or survival (Jordan et al., 2004). Since the PI3K/Akt pathway has been linked to the regulation of programmed cell death in response to diverse stimuli, we examined the activity of Akt and downstream targets of Akt in TAM-R Src*/CasSD and control cells. Serum-starved cells were treated with 20% FBS for 10 min, and WCE were subjected to WB analysis. A profound decrease in the amount of pAktThr308/Ser473, pGSK3Ser9 and p70S6KThr389 in cell lysates expressing the Src*/CasSD molecule was seen in comparison to control cells (Figures 4C). The PI3K/Akt pathway has been implicated to alter ERα activity and/or levels. We next determined the expression levels of ERα by WB analysis and revealed an approximate 3 fold increase in ERα protein levels in Src*/CasSD cells. Thus the Src*/CasSD effectively reduces the activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway, and this attenuation may, in part, be responsible for the increase in ERα levels.
DOWNMODULATION OF p130Cas SIGNALING/EXPRESSION SENSITIZES TAM-R CELLS TO TAMOXIFEN
To elucidate whether expression of the Src*/CasSD sensitizes the TAM-R cells to tamoxifen treatment, we subjected TAM-R and MCF-7 cells constitutively expressing Src*/CasSD and vector control cells to two doses of tamoxifen (100 nM and 1 μM) for 48 h. As described above, a small fraction of untreated TAM-R Src*/CasSD cells was found in sub-G1. A dose dependent increase in the sub-G1 population of TAM-R Src*/CasSD cells was seen under both treatment conditions (Figure 5A, upper left panel). In contrast, tamoxifen treatment did not induce any change in the sub-G1 population of TAM-R vector control cells. The increase in the fraction of apoptotic cells under both treatment conditions was highly significant as the analysis of the fold change of three independent experiments revealed (p<0.0003 and p<0.0002) (Figure 5A, lower left panel). Importantly, the induction of apoptosis and sensitization to tamoxifen was specific to TAM-R Src*/CasSD cells, as no such effects were observed in MCF-7 and MCF-7 Src*/CasSD cells (Figure 5A, upper and lower right panels). Moreover, we measured the response of the Dox inducible TAM-R Src*/CasSD populations to treatment with tamoxifen. These cell populations were treated with Dox for 8 h or left untreated and subsequently exposed to 100 nM and 1 μM tamoxifen for 48 h (Figure 5B). Treatment of these cells with 100 nM and 1 μM tamoxifen similarly increased the fraction of apoptotic cells to >4% and >11%, respectively. In contrast, tamoxifen treatment had no effect on non-induced cell populations (Figure 5B). Importantly, the induction of apoptosis and sensitization to tamoxifen was specific to TAM-R Src*/CasSD cells. These data further suggest that molecules that bind to the activated p130Cas contribute to the tamoxifen resistant phenotype in breast cancer cells with high levels of endogenous p130Cas.
Fig. 5. Expression of Src*/CasSD in TAM-R cells sensitizes tamoxifen resistant cells to antiestrogen.


A: TAM-R and MCF-7 cells stably and constitutively expressing Src*/CasSD and vector cells were seeded in 5% FBS and incubated overnight. After 24 h, the cells were incubated with the indicated concentrations of tamoxifen (+Tam) and the vehicle (-Tam) for an additional 48 h. Apoptosis was assessed as above. Histograms are representative of three experiments performed in triplicate. Percentages of cells in the sub-G1 phase are indicated (upper panel). The fold changes in sub-G1 were calculated by comparing to TAM-R vector control or MCF-7 vector control (set to 1). Results are of three independent experiments (± standard deviation) performed in triplicate. P values were calculated using Student’s t-test. B: TAM-R cell populations carrying the inducible pCXbsrR(TO)Src*/CasSD expression construct and vector control were cultured in the presence and absence of 1 μg/ml Dox in phenol-red free RPMI-1640 with 5% CST for 8 h. Cultures were then supplemented with 100 nM or 1 μM tamoxifen and 10 nM E2 for 48 h. Tamoxifen induced apoptosis was determined as above. Apoptotic nuclei are recognized by their sub-G1 DNA content (left panel). Data are presented as fold changes in sub-G1 in Dox-induced groups over non-induced controls (controls set to 1, right panel). Results presented are the mean of three independent experiments ± standard deviation performed in triplicate. P values were calculated using Student’s t-test. C: Expression of Src*/CasSD in TAM-R cells downregulates Bcl-2 but not Mcl-1 expression. Serum-starved inducible TAM-R Src*/CasSD and control cell populations were treated with 1 μg/ml Dox for 8 h. Subsequently, cultures were supplemented with 100 nM tamoxifen for 48 h. WCE (20 μg) were subjected to WB analysis with the indicated antibodies. Equal loading was assessed by probing with tubulin antibodies. Data are representative of two independent experiments.
To begin to investigate the molecular mechanisms of sensitization that are involved in induction of apoptosis upon Src*/CasSD expression alone or combined with tamoxifen treatment, we determined the expression levels of the anti-apoptotic proteins Bcl-2 and Mcl-1 in inducible TAM-R cell populations (Figure 5C). These cell populations were treated with Dox for 8 h or left untreated. Induction of Src*/CasSD led to a reduction of Bcl-2 expression. The reduction was further enhanced in cell populations treated with 100 nM tamoxifen. In contrast, expression levels of Mcl-1 did not change, which suggests that attenuated Bcl-2 levels contribute to Src*/CasSD induced apoptosis and response to tamoxifen in these cells. Of note, no changes were observed in TAM-R vector cells.
In addition to the DN p130Cas approach, we utilized p130Cas siRNA to downmodulate the expression of endogenous p130Cas in TAM-R and MCF-7 cells. In these cells endogenous p130Cas was consistently reduced by greater than 90% and 70-80%, respectively (Figure 6A, upper panels). Within 24 h of treatment with p130Cas specific siRNA, a substantial fraction of the TAM-R cells population detached from the substratum, indicative of programmed cell death (Figure 6A, lower panels). This was confirmed by determining the fraction of cells in sub-G1 at 48 h of treatment. Approximately 12% of cells were detected in sub-G1 (Figure 6B). Moreover, p130Cas siRNA or control siRNA treated cells were subjected to 1 μM tamoxifen for 24 h. In p130Cas siRNA cell populations, addition of tamoxifen increased the percentage of cells in sub-G1 to >20%, while tamoxifen had no effect on control siRNA transfected cells. These results corroborate our data obtained with the Src*/CasSD cells. Furthermore, these data suggest that the increased expression and activation of p130Cas in TAM-R cells contributes to acquisition of tamoxifen resistance.
Fig. 6. Downmodulation of endogenous p130Cas induces apoptosis and sensitizes cells to tamoxifen.

A: MCF-7 and TAM-R cells were transiently transfected with 80 pmol of p130Cas siRNA as well as with control siRNA. Representative immunoblots (of three independent experiments) demonstrating the downmodulation of Cas expression at 24 h post transfection and phase contrast images of siRNA transfected cells are shown (×10 magnification). B: TAM-R cells were transiently transfected with 80 pmol of p130Cas siRNA as well as with control siRNA for 24 h and then treated with 1 μM Tamoxifen (Tam) and vehicle (ethanol) for an additional 24 h. Cells were then harvested and fixed with 70% ethanol and stained with PI. Cell populations were subjected to flow cytometry as described above. Histograms and percentage of cells in sub-G1 of one experiment are presented (upper panel). The fold changes in sub-G1 were determined by comparing the Cas siRNA treated sets to siRNA treated controls within each group (set to 1) (lower panel). Data represent three independent experiments performed in triplicate (± standard deviation). P values were calculated using Student’s t-test.
DISCUSSION
In this manuscript we demonstrate that decoying signaling molecules which bind to the p130Cas SD/blocking p130Cas signaling in breast cancer cells attenuates growth factor signaling, in particular the ERK and PI3K/Akt pathways, induces apoptosis in TAM-R cells but not in parental MCF-7 cells, and re-sensitizes TAM-R cells to tamoxifen. Apoptosis in TAM-R cell populations is associated with a reduction in Bcl-2 expression. Moreover, we show for the first time that induction of tamoxifen resistance by continued exposure of MCF-7 cells to tamoxifen substantially increased endogenous levels of p130Cas, indicating that elevated p130Cas levels contribute to tamoxifen resistance. This is in line with findings that a 7-fold overexpression of p130Cas in MCF-7 cells confers tamoxifen resistance (Riggins et al., 2006). How p130Cas levels are regulated is currently unknown. Initial experiments addressing the stability of p130Cas indicated that protein stability might not be the main regulator4. Unlike the family member HEF-1, which is rapidly and transiently induced by growth factor treatment, p130Cas is stably expressed (Law et al., 1998).
The observed increase in protein expression was accompanied by an increase in the amount of phosphorylated (activated) p130Cas. Though p130Cas is activated by upstream signals (Bouton et al., 2001), it has been demonstrated that p130Cas itself can activate its upstream kinase Src by disrupting the intramolecular binding of the SH3 domain of c-Src (Alexandropoulos and Baltimore, 1996; Burnham et al., 2000) - leading to a stabilized p130Cas-Src complex. Thus, by this mechanism p130Cas might act as a direct activator of its activating kinases in tamoxifen resistant cells. Indeed, it was recently shown that TAM-R cells have elevated Src kinase activity, which is associated with tamoxifen resistance (Hiscox et al., 2006b). Interestingly, Cowell et al. (2006) demonstrated that p130Cas phosphorylation is prominently enhanced in MCF-7 cells within 7 days of continued exposure to tamoxifen.
The majority of the tyrosine phosphorylation sites within p130Cas are situated in the central SD. This domain is crucial for recruiting the small adapter proteins Crk and Nck (Bouton et al., 2001), and for p130Cas-Crk coupled cell migration and adhesion (Huang et al., 2002; Klemke et al., 1998), a process that is important for tumor progression. Interestingly, TAM-R cells underwent a partial transition from an epithelial to a mesenchymal phenotype (Hiscox et al., 2006a), suggesting that the activated p130Cas-Crk pathway contributes to these events. Data presented here support this notion. The change in phenotype, in particular the lack of lamellipodia formation, observed by the expression of Src*/CasSD was also seen by inhibition of p130Cas expression by siRNA, and with previous reports utilizing different approaches to block p130Cas-Crk-coupling (Klemke et al., 1998). Enhanced Crk signaling mediated by ectopic expression promotes the breakdown of adherens junctions in MDCK cells (Lamorte et al., 2002). Moderate cell clustering was observed in MCF-7 Src*/CasSD cells consistent with the lower expression of endogenous p130Cas in these cells. All of these changes correlate with the reduced serum-stimulated cell migration, a further indication that the Src*/CasSD molecule acts by blocking signals through the phosphorylated SD of p130Cas. The Src*/CasSD lacks the amino-terminal SH3 domain and the carboxyl terminus containing the bipartite Src binding motif, which mediate targeting of endogenous p130Cas to the membrane (e.g. to focal adhesions or focal complexes containing FAK and Src). Lack of targeted expression of the Src*/CasSD peptide seems to account for its decoy effect, as addition of a membrane targeting sequence strongly enhances the overall cellular tyrosine phosphorylation5. While the Src*/CasSD approach was established in NIH 3T3 fibroblasts, the results presented here suggest that this chimera is a valuable experimental tool for studying p130Cas and its downstream targets in epithelial cells.
The development of antiestrogen resistance has been associated with the upregulation of alternative pathways such as the ERBB, IGFR and the non-genomic ER signaling pathway (Nicholson et al., 2005). This seems to be one of many mechanisms by which resistant cells adapt to ‘environmental’ pressure. Profound increases in the levels of EGFR, ERBB2 and ERBB3 were noticed in TAM-R cells (Knowlden et al., 2003), which are associated with increased Ras-MAPK-ERK as well as PI3K-Akt activity (Nicholson et al., 2005). In this regard, our data support the hypothesis that interference with p130Cas signaling, in particular signaling through the SD of p130Cas, can re-sensitize tamoxifen resistant cells to tamoxifen. This may be mediated in part by blocking growth factor signaling. Disruption of the p130Cas signaling node attenuated the basal and v-Crk stimulated JNK activity in NIH 3T3 cells (Kirsch et al., 2002), whereas in TAM-R breast cancer cells, the duration of ERK activation upon EGF stimulation and Akt activation were decreased. The latter was more pronounced and is consistent with the observed attenuation of GSK3β and p70S6K phosphorylation, the strong reduction of Bcl-2 expression levels, and with the findings of Cabodi and colleagues (2006) based on a p130Cas siRNA approach in a mouse breast carcinoma cell line overexpressing ERBB2.
Akt has been implicated in altering the activity of ERα by various mechanisms e.g. phosphorylation at Ser167, stability, expression, and genome wide DNA binding (Bhat-Nakshatri et al., 2004, Bhat-Nakshatri et al., 2008, Campbell et al., 2001, and Guo and Sonenshein et al., 2004). Thus upregulation of ERα levels in TAM-R Src*/CasSD cells might be due to increased stability and/or de-repressed transcriptional activity in response to reduced Akt activity, but the precise mechanism remains to be determined.
In addition, p130Cas has been implicated in adhesion-mediated survival signaling in COS-7 cells, in an osteosarcoma cell line by overexpression studies (Cho and Klemke, 2000; Weng et al., 1999), and in rabbit fibroblasts and MDCK cells via studies utilizing different approaches to block p130Cas function (Almeida et al., 2000; Chan et al., 1999). The exact molecular mechanism(s) leading to the attenuation of Akt activation is not clear. Alterations in several pathways may contribute: i) disruption of p130Cas-p85 complexes. In v-Crk transformed 3Y1 cells, a small amount of the PI3K subunit p85 is bound to the carboxyl terminus of p130Cas, which depends on the activation status of Src (Riggins et al., 2003); ii) inhibition of PI3K activity stimulation at the level of the EGFR. EGFR stimulates the production of PI3K products through heteromerization with ERBB3 and direct interaction with Gab1 (Rodrigues et al., 2000; Soltoff et al., 1994). TAM-R cells expressing the Src*/CasSD had strongly reduced EGFR levels, which may contribute to the attenuated phosphorylation of Akt and its downstream targets; iii) interference with Rac-mediated PI3K activation. Through a positive feedback loop Rac can further activate PI3K (Barber and Welch, 2006). It is feasible that blocking the p130Cas-Crk-Dock180-Rac activation pathway by uncoupling Crk from p130Cas may be partially responsible for the attenuated PI3K/Akt activities; iv) interference with growth factor receptor signaling by decoying Crk, Nck or other yet unknown binding partners. Interaction of Crk with Gab1 supports sustained Gab1 phosphorylation (Watanabe et al., 2006), which in turn may facilitate RTK-Gab1-mediated activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway. Thus decoying Crk from binding partners other than p130Cas may influence the activation of the PI3K by Gab1. Nonetheless our data support the notion that p130Cas mediates proliferative/survival signals through its SD binding molecules.
Here we demonstrate that that conversion of antiestrogen responsive breast cancer cells to antiestrogen un-responsive cells by long-term treatment with tamoxifen can be reversed by blocking p130Cas signaling. This is an important finding since in many patients tumor cells eventually circumvent the need for steroid hormones in response to long-term treatment with tamoxifen (Group, 1998). Though we observed enhanced and significant sensitization to tamoxifen in cells treated with p130Cas siRNA, decoying molecules that interact with the tyrosine phosphorylated p130Cas SD seemed to be sufficient for partial restoration of sensitivity to antiestrogen therapy. Noticeably, while MCF-7 cells respond with growth arrest to tamoxifen treatment (Wakeling et al., 1989) TAM-R Src*/CasSD cells responded with growth arrest and with an increase in apoptosis.
In conclusion, the data presented here highlight the relevance of downstream signaling molecules of the p130Cas SD in establishment and/or maintenance of tamoxifen resistance. Furthermore they suggest that targeting molecules that associate with the phosphorylated SD of endogenous p130Cas may be an effective strategy to combat antiestrogen resistance. Therefore, peptides and/or small molecules modeled after the structure of the phosphorylated CasSD might serve as potential therapeutic for treatment of breast cancer.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank Gail Sonenshein for comments and critical reading of the manuscript, Bruce Mayer and Kazuya Machida for the GST-SH2 plasmids, Stephen Farmer, Isabel Dominguez and Amy Bouton for antibodies, and Tsuyoshi Akagi for retroviral vectors. We are grateful to Celeste Rich for technical assistance with gel electrophoresis. This work has been supported by the NIH/NCI (CA106468 to K.H.K.) and the Department of Defense (W81XWH-06-1-0379 to B.-T. L. and K.H.K.)
Contract grant sponsor: NIH/NCI; Grant number: CA106468
Contract grant sponsor: Department of Defense; Grant number: W81XWH-06-1-0379
Footnotes
S.S. and K.H.K unpublished results
B.T.L. and K.H.K. unpublished results
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Journal of Cellular Biochemistry website.
References
- Akagi T, Murata K, Shishido T, Hanafusa H. v-Crk activates the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/AKT pathway by utilizing focal adhesion kinase and H-Ras. Mol Cell Biol. 2002;22:7015–23. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.20.7015-7023.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexandropoulos K, Baltimore D. Coordinate activation of c-Src by SH3- and SH2-binding sites on a novel p130Cas-related protein, Sin. Genes Dev. 1996;10:1341–55. doi: 10.1101/gad.10.11.1341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almeida EA, Ilic D, Han Q, Hauck CR, Jin F, Kawakatsu H, et al. Matrix survival signaling: from fibronectin via focal adhesion kinase to c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase. J Cell Biol. 2000;149:741–54. doi: 10.1083/jcb.149.3.741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barber MA, Welch HC. PI3K and RAC signalling in leukocyte and cancer cell migration. Bull Cancer. 2006;93:E44–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhat-Nakshatri P, Campbell RA, Patel NM, Newton TR, King AJ, marshall MS, et al. Tumour necrosis factor and PI3-kinase control oestrogen receptor alpha protein level and its transrepression function. Br J Cancer. 2004;90:853–59. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhat-Nakshatri P, Wang g, Appiah H, Luktuke N, Carroll JS, Geistlinger TR, et al. AKT alters genome-wide estrogen receptor alpha binding and impacts estrogen signaling in breast cancer. Mol Cell Biol. 2008;28:7487–503. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00799-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouton AH, Riggins RB, Bruce-Staskal PJ. Functions of the adapter protein Cas: signal convergence and the determination of cellular responses. Oncogene. 2001;20:6448–58. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkman A, van der Flier S, Kok EM, Dorssers LC. BCAR1, a human homologue of the adapter protein p130Cas, and antiestrogen resistance in breast cancer cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000;92:112–120. doi: 10.1093/jnci/92.2.112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnham MR, Bruce-Staskal PJ, Harte MT, Weidow CL, Ma A, Weed SA, et al. Regulation of c-SRC activity and function by the adapter protein CAS. Mol Cell Biol. 2000;20:5865–78. doi: 10.1128/mcb.20.16.5865-5878.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabodi S, Moro L, Baj G, Smeriglio M, Di Stefano P, Gippone S, et al. p130Cas interacts with estrogen receptor alpha and modulates non-genomic estrogen signaling in breast cancer cells. J Cell Sci. 2004;117:1603–11. doi: 10.1242/jcs.01025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell RA, Bhat-Nakshatri P, Patel NM, Constantinidou D, Ali S, Nakshatri H. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT-mediated activation of estrogen receptor alpha: a new model for anti-estrogen resistance. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:9817–24. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M010840200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan PC, Lai JF, Cheng CH, Tang MJ, Chiu CC, Chen HC. Suppression of ultraviolet irradiation-induced apoptosis by overexpression of focal adhesion kinase in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:26901–6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.38.26901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho SY, Klemke RL. Extracellular-regulated kinase activation and CAS/Crk coupling regulate cell migration and suppress apoptosis during invasion of the extracellular matrix. J Cell Biol. 2000;149:223–36. doi: 10.1083/jcb.149.1.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gee JM, Robertson JF, Ellis IO, Nicholson RI. Phosphorylation of ERK1/2 mitogen-activated protein kinase is associated with poor response to anti-hormonal therapy and decreased patient survival in clinical breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 2001;95:247–54. doi: 10.1002/1097-0215(20010720)95:4<247::aid-ijc1042>3.0.co;2-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Group EBCCTsC. Tamoxifen for early breast cancer: An overview of the randomized trials. Lancet. 1998;351:1451–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo S, Sonenshein GE. Forkhead box transcription factor FOXO3a regulates estrogen receptor alpha expression and is repressed by the Her-2/neu/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 2004;24:8681–90. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.19.8681-8690.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guvakova MA, Surmacz E. The activated insulin-like growth factor I receptor induces depolarization in breast epithelial cells characterized by actin filament disassembly and tyrosine dephosphorylation of FAK, Cas, and paxillin. Exp Cell Res. 1999;251:244–55. doi: 10.1006/excr.1999.4566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson BE, Feigelson HS. Hormonal carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis. 2000;21:427–33. doi: 10.1093/carcin/21.3.427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson BE, Ross R, Bernstein L. Estrogens as a cause of human cancer: the Richard and Hinda Rosenthal Foundation award lecture. Cancer Res. 1988;48:246–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiscox S, Jiang WG, Obermeier K, Taylor K, Morgan L, Burmi R, et al. Tamoxifen resistance in MCF7 cells promotes EMT-like behaviour and involves modulation of beta-catenin phosphorylation. Int J Cancer. 2006a;118:290–301. doi: 10.1002/ijc.21355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiscox S, Morgan L, Barrow D, Dutkowskil C, Wakeling A, Nicholson RI. Tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer cells is accompanied by an enhanced motile and invasive phenotype: inhibition by gefitinib (‘Iressa’, ZD1839) Clin Exp Metastasis. 2004;21:201–12. doi: 10.1023/b:clin.0000037697.76011.1d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiscox S, Morgan L, Green TP, Barrow D, Gee J, Nicholson RI. Elevated Src activity promotes cellular invasion and motility in tamoxifen resistant breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2006b;97:263–74. doi: 10.1007/s10549-005-9120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan NJ, Gee JM, Barrow D, Wakeling AE, Nicholson RI. Increased constitutive activity of PKB/Akt in tamoxifen resistant breast cancer MCF-7 cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2004;87:167–80. doi: 10.1023/B:BREA.0000041623.21338.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch K, Kensinger M, Hanafusa H, August A. A p130Cas tyrosine phosphorylated substrate domain decoy disrupts v-crk signaling. BMC Cell Biol. 2002;3:18. doi: 10.1186/1471-2121-3-18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch KH, Georgescu MM, Hanafusa H. Direct binding of p130(Cas) to the guanine nucleotide exchange factor C3G. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:25673–9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.40.25673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemke RL, Leng J, Molander R, Brooks PC, Vuori K, Cheresh DA. CAS/Crk coupling serves as a “molecular switch” for induction of cell migration. J Cell Biol. 1998;140:961–72. doi: 10.1083/jcb.140.4.961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowlden JM, Hutcheson IR, Jones HE, Madden T, Gee JM, Harper ME, et al. Elevated levels of epidermal growth factor receptor/c-erbB2 heterodimers mediate an autocrine growth regulatory pathway in tamoxifen-resistant MCF-7 cells. Endocrinology. 2003;144:1032–44. doi: 10.1210/en.2002-220620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamorte L, Royal I, Naujokas M, Park M. Crk adapter proteins promote an epithelial-mesenchymal-like transition and are required for HGF-mediated cell spreading and breakdown of epithelial adherens junctions. Mol Biol Cell. 2002;13:1449–61. doi: 10.1091/mbc.01-10-0477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavinsky RM, Jepsen K, Heinzel T, Torchia J, Mullen TM, Schiff R, et al. Diverse signaling pathways modulate nuclear receptor recruitment of N-CoR and SMRT complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998;95:2920–5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.6.2920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law SF, Zhang YZ, Klein-Szanto AJ, Golemis EA. Cell cycle-regulated processing of HEF1 to multiple protein forms differentially targeted to multiple subcellular compartments. Mol Cell Biol. 1998;18:3540–51. doi: 10.1128/mcb.18.6.3540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Min C, Kirsch KH, Zhao Y, Jeay S, Palamakumbura AH, Trackman PC, et al. The tumor suppressor activity of the lysyl oxidase propeptide reverses the invasive phenotype of Her-2/neu-driven breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2007;67:1105–12. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-3867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson RI, Hutcheson IR, Britton D, Knowlden JM, Jones HE, Harper ME, et al. Growth factor signalling networks in breast cancer and resistance to endocrine agents: new therapeutic strategies. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2005;93:257–62. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2004.12.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nollau P, Mayer BJ. Profiling the global tyrosine phosphorylation state by Src homology 2 domain binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98:13531–6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.241215998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggins RB, DeBerry RM, Toosarvandani MD, Bouton AH. Src-dependent association of Cas and p85 phosphatidylinositol 3’-kinase in v-crk-transformed cells. Mol Cancer Res. 2003;1:428–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggins RB, Lan JP, Klimach U, Zwart A, Cavalli LR, Haddad BR, et al. ERRgamma mediates tamoxifen resistance in novel models of invasive lobular breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2008;68:8908–17. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-2669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggins RB, Thomas KS, Ta HQ, Wen J, Davis RJ, Schuh NR, et al. Physical and functional interactions between Cas and c-Src induce tamoxifen resistance of breast cancer cells through pathways involving epidermal growth factor receptor and signal transducer and activator of transcription 5b. Cancer Res. 2006;66:7007–15. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-3952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues GA, Falasca M, Zhang Z, Ong SH, Schlessinger J. A novel positive feedback loop mediated by the docking protein Gab1 and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in epidermal growth factor receptor signaling. Mol Cell Biol. 2000;20:1448–59. doi: 10.1128/mcb.20.4.1448-1459.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shou J, Massarweh S, Osborne CK, Wakeling AE, Ali S, Weiss H, et al. Mechanisms of tamoxifen resistance: increased estrogen receptor-HER2/neu cross-talk in ER/HER2-positive breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2004;96:926–35. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djh166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith IE, Dowsett M. Aromatase inhibitors in breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:2431–42. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra023246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soltoff SP, Carraway KL, 3rd, Prigent SA, Gullick WG, Cantley LC. ErbB3 is involved in activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase by epidermal growth factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1994;14:3550–8. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.6.3550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Agthoven T, Veldscholte J, Smid M, van Agthoven TL, Vreede L, Broertjes M, et al. Functional identification of genes causing estrogen independence of human breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2008 doi: 10.1007/s10549-008-9969-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakeling AE, Newboult E, Peters SW. Effects of antioestrogens on the proliferation of MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. J Mol Endocrinol. 1989;2:225–34. doi: 10.1677/jme.0.0020225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe T, Tsuda M, Makino Y, Ichihara S, Sawa H, Minami A, et al. Adaptor molecule Crk is required for sustained phosphorylation of Grb2-associated binder 1 and hepatocyte growth factor-induced cell motility of human synovial sarcoma cell lines. Mol Cancer Res. 2006;4:499–510. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-05-0141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weng LP, Wang X, Yu Q. Transmembrane tyrosine phosphatase LAR induces apoptosis by dephosphorylating and destabilizing p130Cas. Genes Cells. 1999;4:185–96. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2443.1999.00251.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


