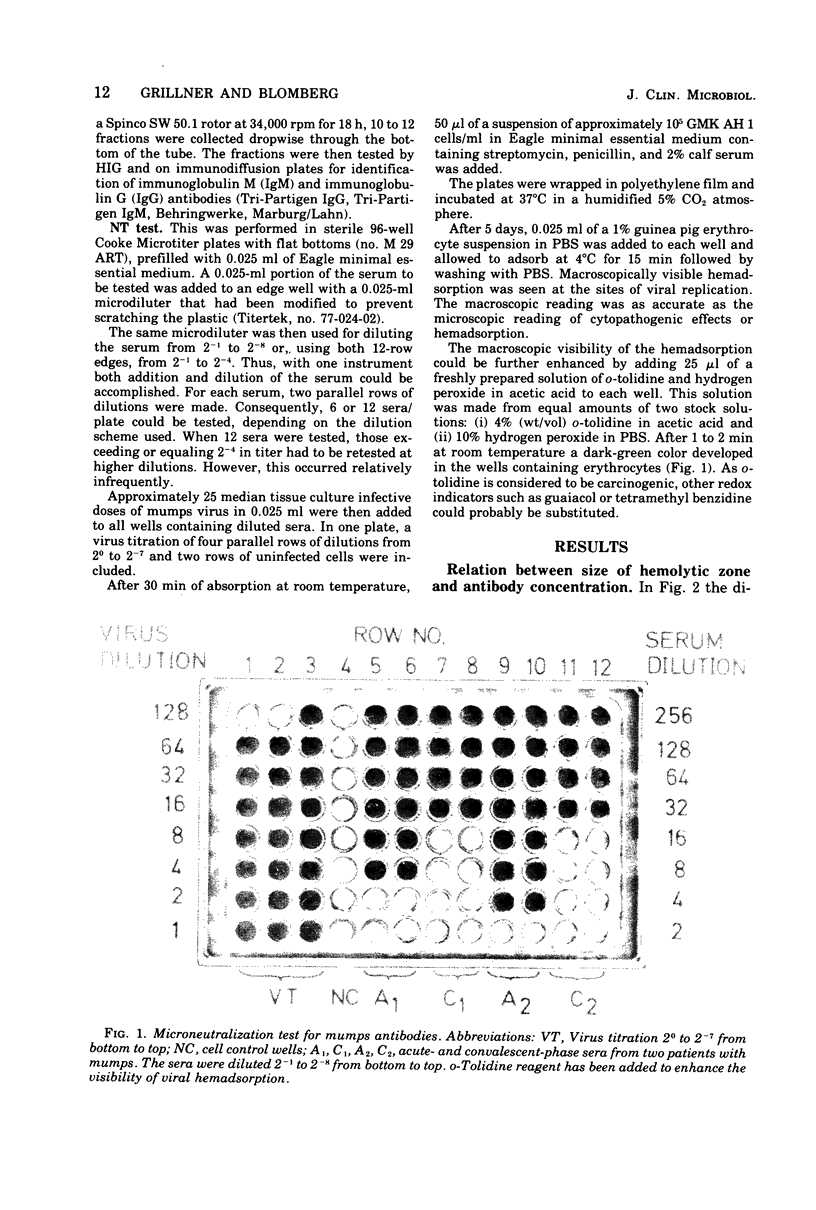
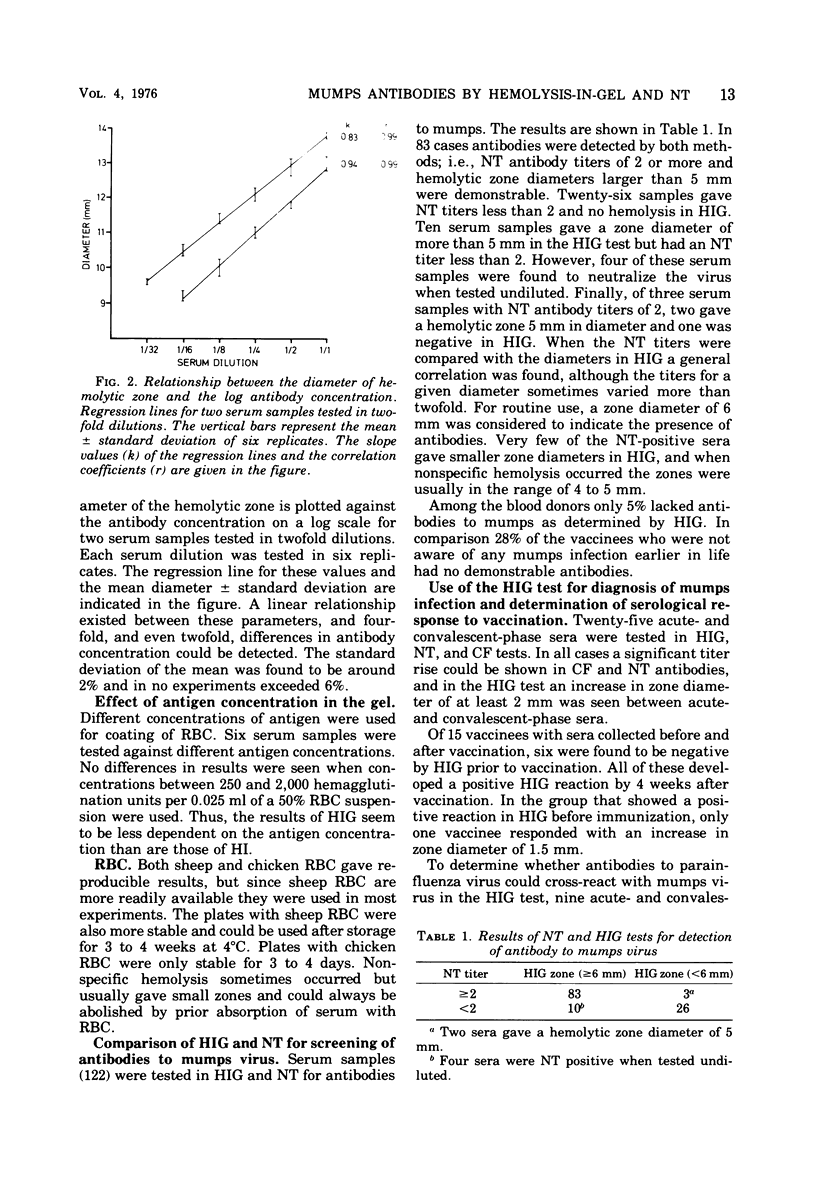
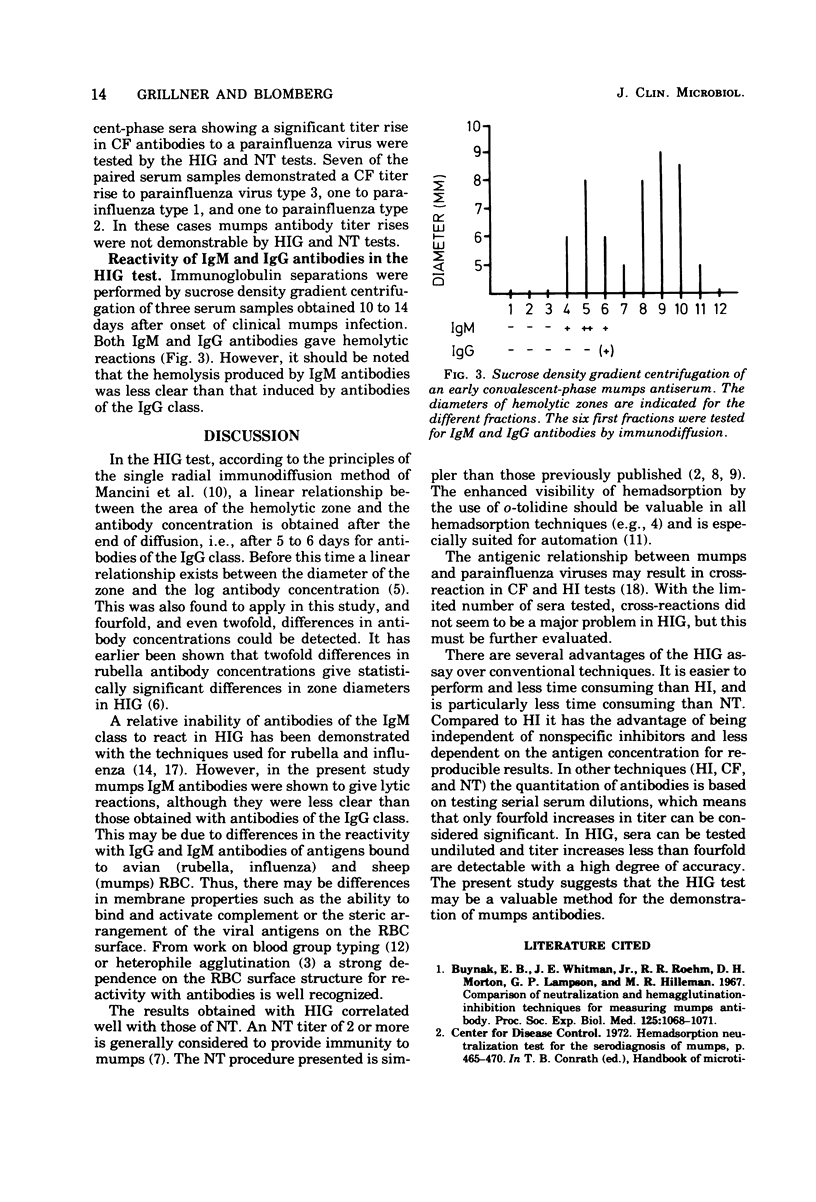
Abstract
A hemolysis-in-gel test for the demonstration of antibodies to mumps virus is described. The results were compared with those of neutralization tests using a modified microtechnique. In the neutralization test viral replication was demonstrated by the hemadsorption of guinea pig erythrocytes, the visibility of which could be further enhanced by the use of o-tolidine. Good correlation was found between the results of the two techniques. The hemolysis-in-gel test was simple to perform, rapid, sensitive, and shown to be a useful test for the demonstration of mumps antibodies.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buynak E. B., Whitman J. E., Jr, Roehm R. R., Morton D. H., Lampson G. P., Hilleman M. R. Comparison of neutralization and hemagglutination-inhibition techniques for measuring mumps antibody. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Aug-Sep;125(4):1068–1071. doi: 10.3181/00379727-125-32278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOMBS R. R. A., GLEESON-WHITE M. H., HALL J. G. Factors influencing the agglutinability of red cells. II. The agglutination of bovine red cells previously classified as "inagglutinable" by the building up of an "anti-globulin: globulin lattice" on the sensitized cells. Br J Exp Pathol. 1951 Jun;32(3):195–202. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ESPMARK A., FAGRAEUS A. Detection of antigens in tissue culture with the aid of mixed hemadsorption. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand Suppl. 1962;Suppl 154:258–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAHEY J. L., MCKELVEY E. M. QUANTITATIVE DETERMINATION OF SERUM IMMUNOGLOBULINS IN ANTIBODY-AGAR PLATES. J Immunol. 1965 Jan;94:84–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grillner L., Strannegård O. Evaluation of the hemolysis-in-gel test for the screening of rubella immunity and the demonstration of recent infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Feb;3(2):86–90. doi: 10.1128/jcm.3.2.86-90.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilleman M. R. Mumps vaccination. Mod Trends Med Virol. 1970;2(0):241–261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karchmer A. W., Friedman J. P., Casey H. L., Shope T. C., Riker J. B., Kappelman M. M., Witte J. J. Simultaneous administration of live virus vaccines. Measles, mumps, poliomyelitis, and smallpox. Am J Dis Child. 1971 May;121(5):382–388. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1971.02100160052004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny M. T., Albright K. L., Sanderson R. P. Microneutralization test for the determination of mumps antibody in vero cells. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Sep;20(3):371–373. doi: 10.1128/am.20.3.371-373.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayner R. E., McDorman D. J., Meyer B. C., Parkman P. D. Automated microtransfer technique for the assay of poliovirus- and mumps virus-neutralizing antibodies. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Dec;28(6):968–971. doi: 10.1128/am.28.6.968-971.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton J. A., Pickles M. M. The Proteolytic Enzyme Test for Detecting Incomplete Antibodies. J Clin Pathol. 1951 May;4(2):189–199. doi: 10.1136/jcp.4.2.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Probert M., Russell S. M. Measurement of parainfluenza-3 virus antibody by the single radial hemolysis technique. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Sep;2(3):157–161. doi: 10.1128/jcm.2.3.157-161.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell S. M., McCahon D., Beare A. S. A single radial haemolysis technique for the measurement of influenza antibody. J Gen Virol. 1975 Apr;27(1):1–10. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-27-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEVER J. L. Application of a microtechnique to viral serological investigations. J Immunol. 1962 Mar;88:320–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skaug K., Orstavik I., Ulstrup J. C. Application of the passive haemolysis test for the determination of rubella virus antibodies. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1975 Aug;83(4):367–372. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1975.tb00114.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strannegård O., Grillner L., Lindberg I. M. Hemolysis-in-gel test for the demonstration of antibodies to rubella virus. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Jun;1(6):491–494. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.6.491-494.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Veen J., Sonderkamp H. J. Secondary antibody response of guinea pigs to parainfluenza and mumps viruses. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1965;15(5):721–734. doi: 10.1007/BF01245218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]