Abstract
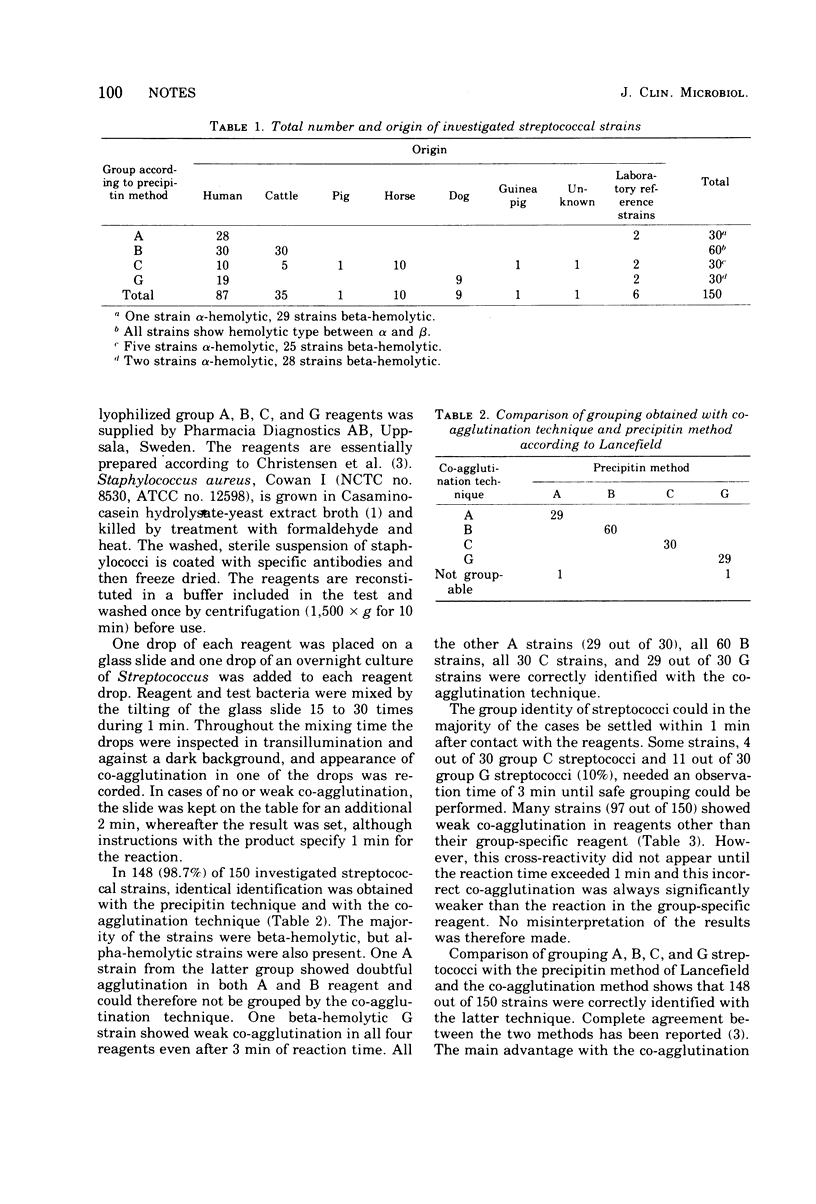
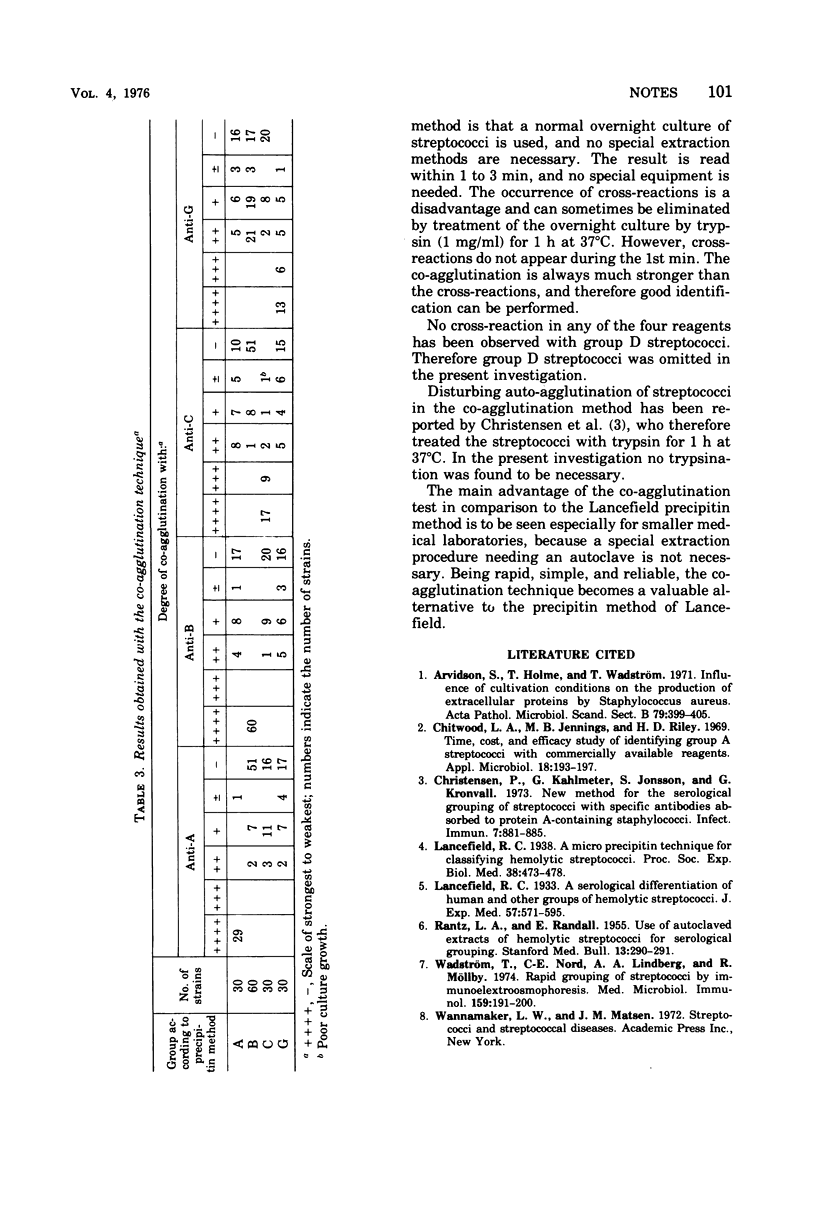
A total of 98.7% of streptococci, groups A,B,C, and G, isolated from various sources was correctly identified by the co-agglutination technique. The active components in this technique are protein A-containing staphylococci coated with antibodies specific for group A,B,C, and G streptococci. A suspension of streptococci belonging to one of these four groups co-agglutinates with the antibody-sensitized staphylococci specific for this group. The technique is extremely rapid and simple and requires no special equipment. It should therefore be a valuable alternative to other techniques used in the grouping of streptococci and is shown here to be as reliable as the Lancefield technique.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chitwood L. A., Jennings M. B., Riley H. D., Jr Time, cost, and efficacy study of identifying group A streptococci with commercially available reagents. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Aug;18(2):193–197. doi: 10.1128/am.18.2.193-197.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen P., Kahlmeter G., Jonsson S., Kronvall G. New method for the serological grouping of Streptococci with specific antibodies adsorbed to protein A-containing staphylococci. Infect Immun. 1973 Jun;7(6):881–885. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.6.881-885.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANTZ L. A., RANDALL E. Use of autoclaved extracts of hemolytic streptococci for serological grouping. Stanford Med Bull. 1955 May;13(2):290–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadström T., Nord C. E., Lindberg A. A., Möllby R. Rapid grouping of streptococci by immunoelectroosmophoresis. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1974 Mar 22;159(3):191–200. doi: 10.1007/BF02121335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



