Abstract
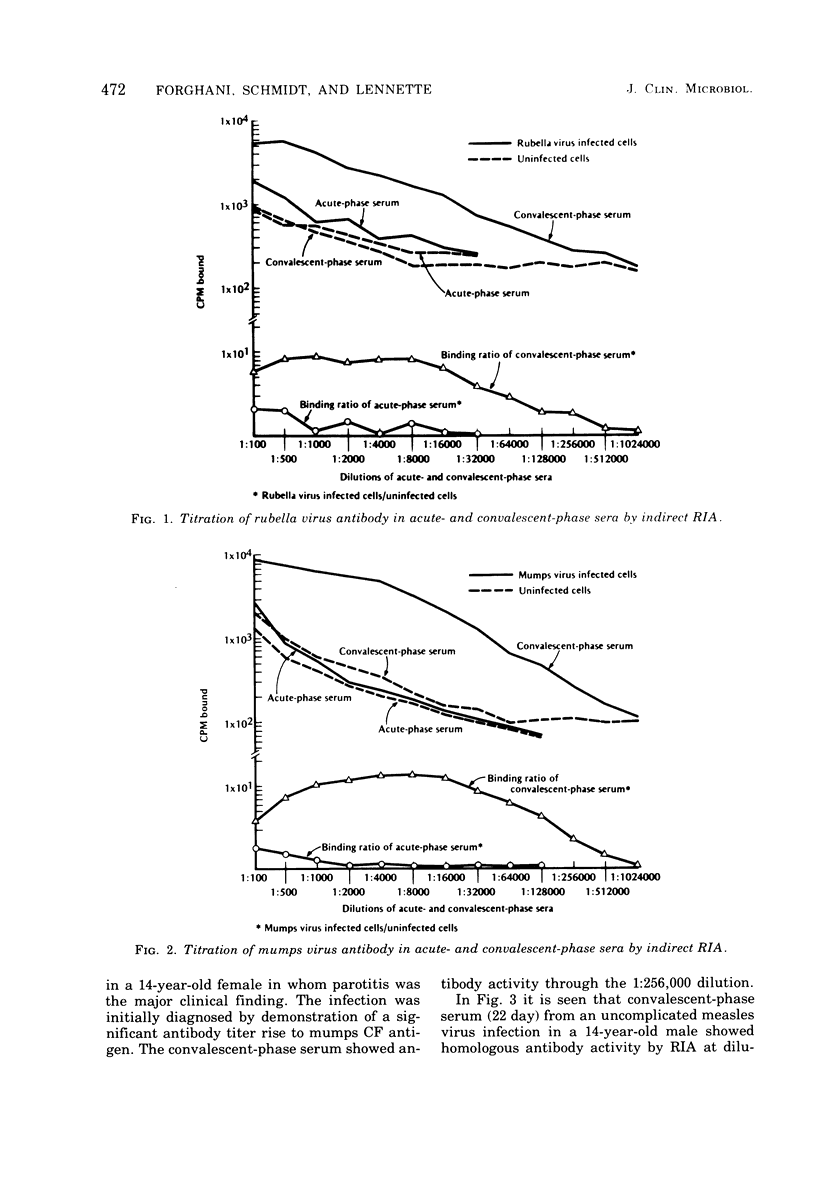
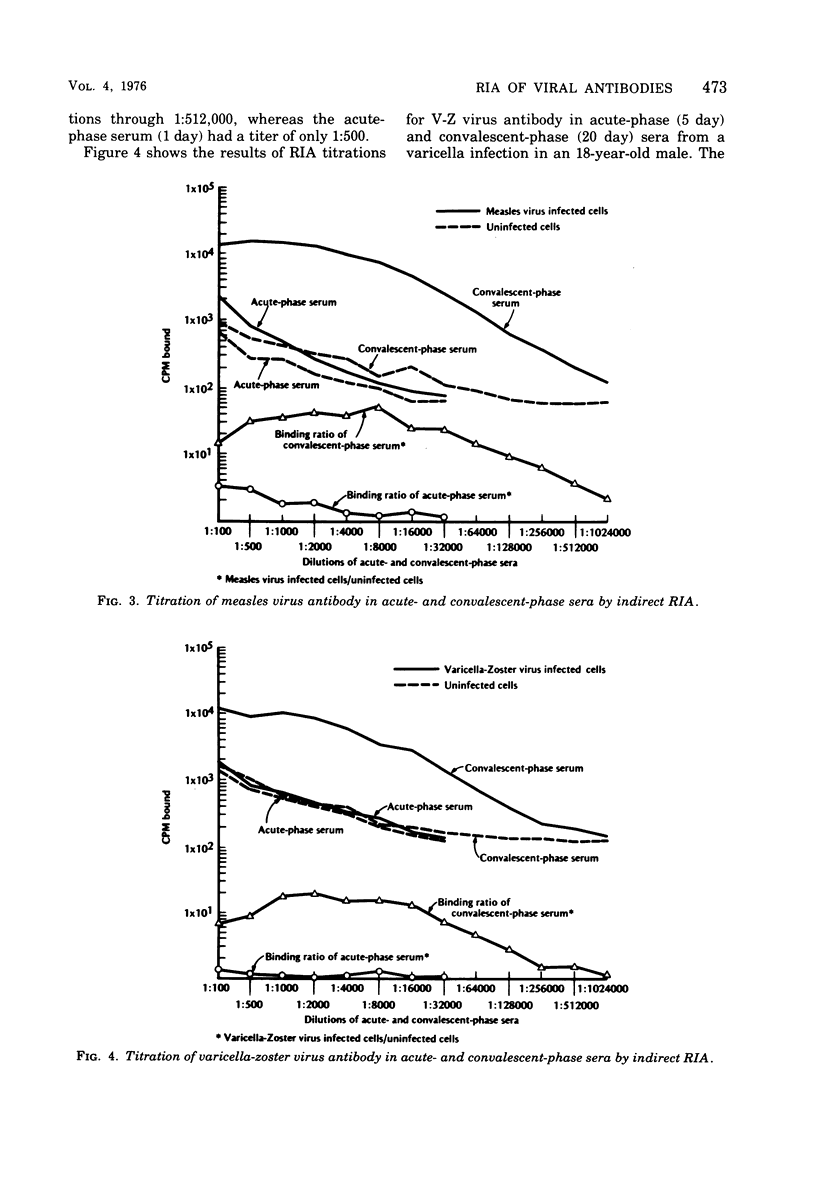
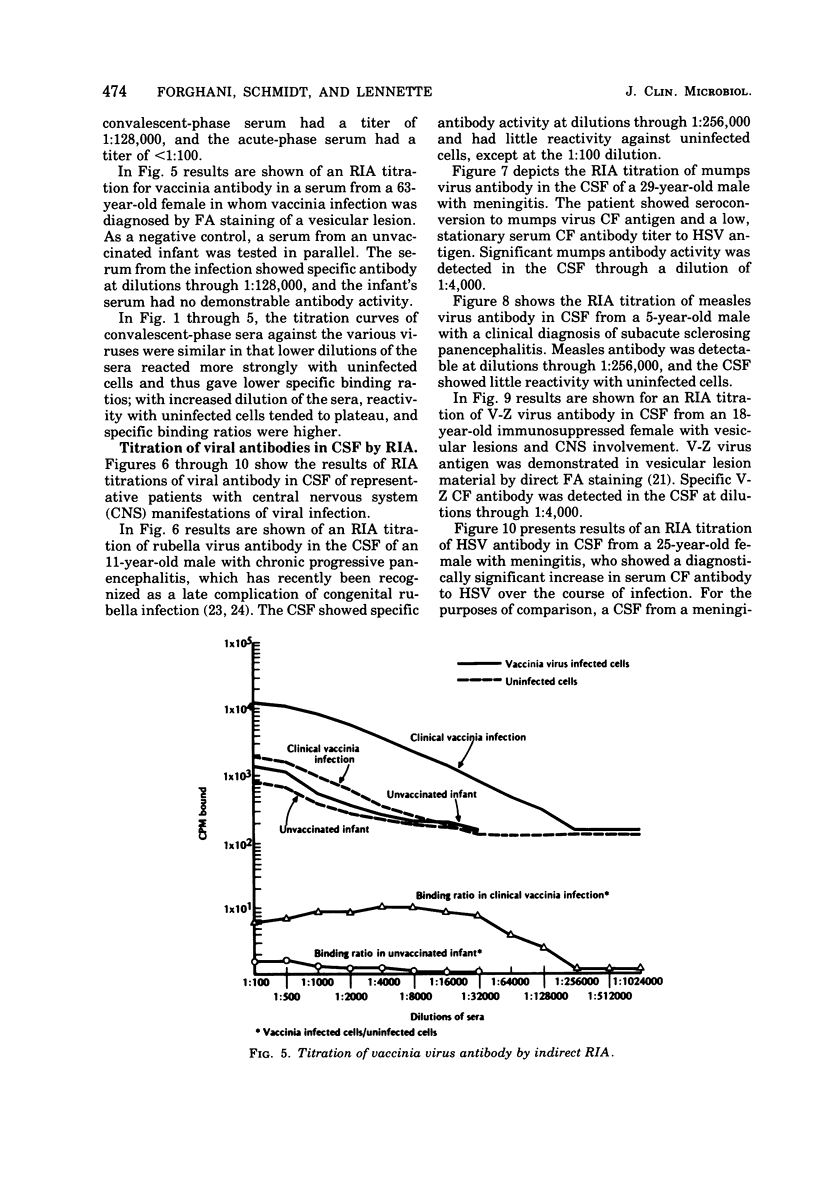
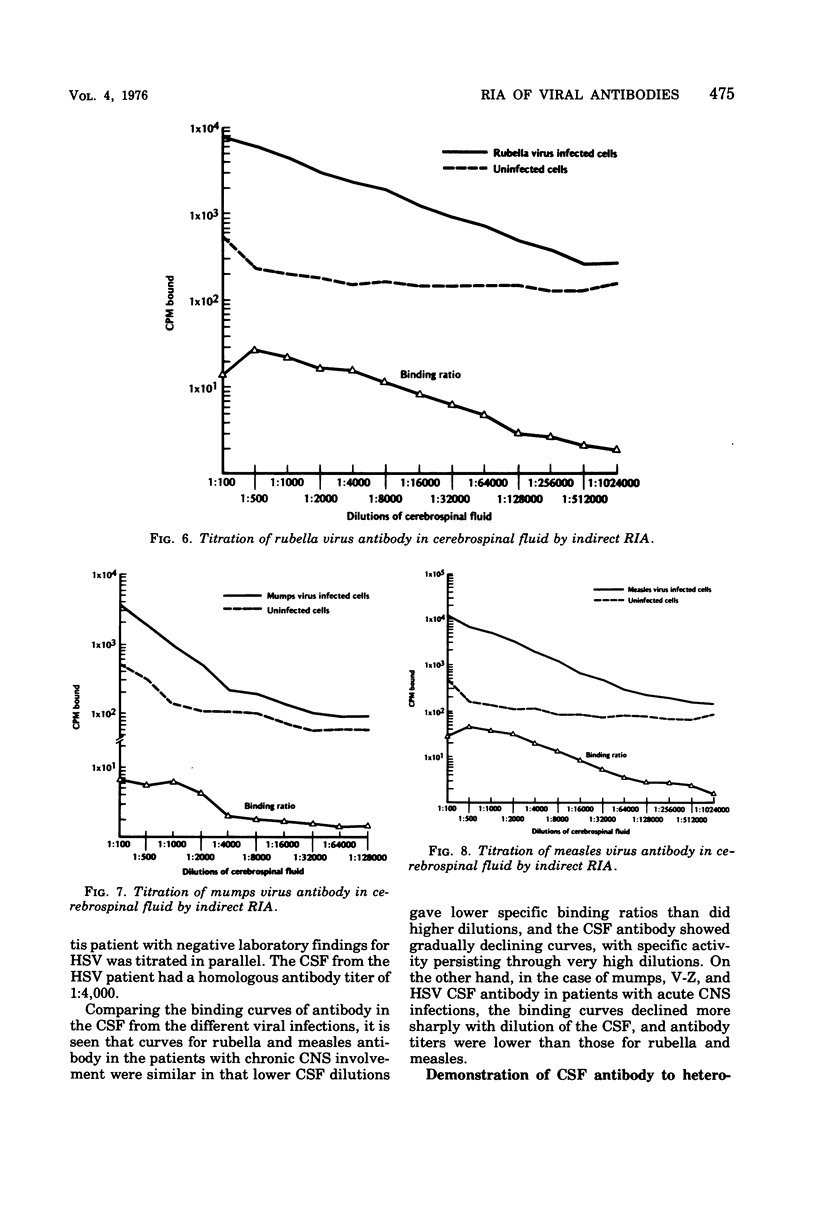
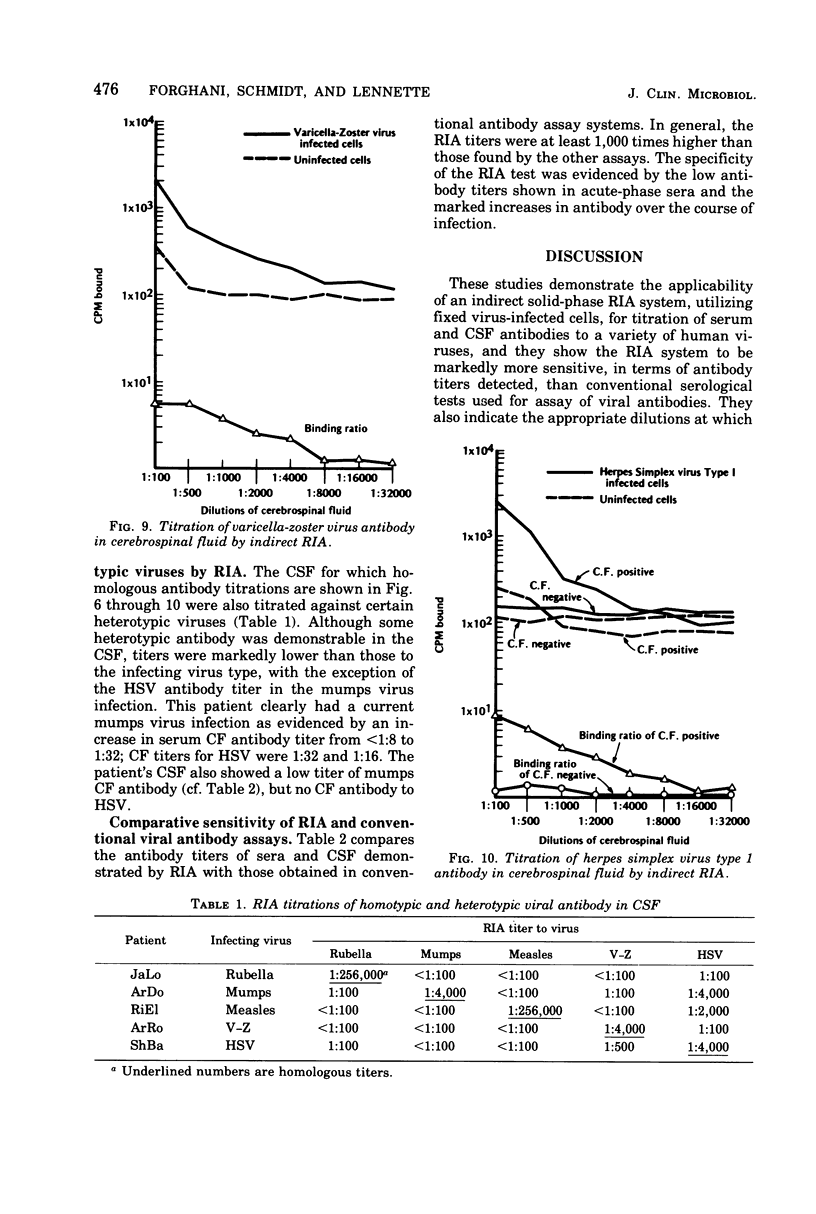
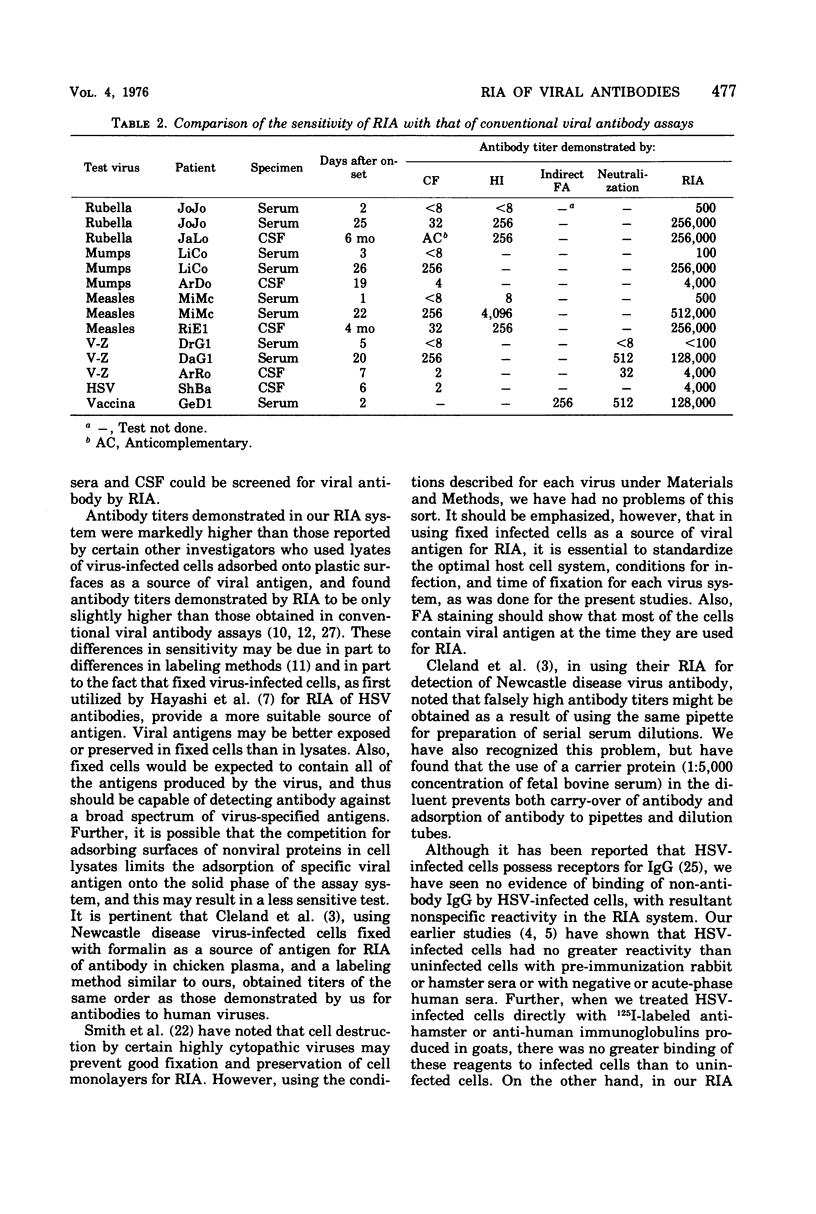
An indirect solid-phase radioimmunoassay (RIA) was applied to titration of serum and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) antibodies against a variety of viruses including rubella, mumps, measles, herpes simplex, varicella-zoster, and vaccinia. The test used fixed, virus-infected cells as a source of antigen, and conditions for optimal production of viral antigen were determined for each virus-host cell system. In acute, uncomplicated viral infections, sera taken 2 to 5 days after onset generally had low homotypic RIA titers ranging from less than 1:100 to 1:500, whereas convalescent-phase titers ranged from 1:128,000 to 1:512,000. Rubella and measles antibody titers as high as 1:256,000 were demonstrated by RIA in CSF from patients with chronic panencephalitis, whereas homologous antibody titers of 1:4,000 were detected in CSF from acute mumps, herpes simplex, and varicella-zoster virus infections with central nervous system involvement. Some heterotypic antibody was demonstrable by RIA in CSF, but, with the exception of herpes simplex antibody in a mumps virus infection, titers were markedly lower than those to the infecting virus type. RIA generally demonstrated titers at least 1,000 times higher than those obtained by conventional assays such as complement fixation, hemagglutination inhibition, neutralization, and immunofluorescent staining.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbanti-Brodano G., Oyanagi S., Katz M., Koprowski H. Presence of 2 different viral agents in brain cells of patients with subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 May;134(1):230–236. doi: 10.3181/00379727-134-34765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleland G. B., Perey D. Y., Dent P. B. Micro-radioimmunoassay for antibodies to Newcastle disease virus in the chicken. J Immunol. 1975 Jan;114(1 Pt 2):422–425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forghani B., Schmidt N. J., Lennette E. H. Antisera to human cytomegalovirus produced in hamsters: reactivity in radioimmunoassay and other antibody assay systems. Infect Immun. 1976 Nov;14(5):1184–1190. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.5.1184-1190.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forghani B., Schmidt N. J., Lennette E. H. Solid phase radioimmunoassay for identification of Herpesvirus hominis types 1 and 2 from clinical materials. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Oct;28(4):661–667. doi: 10.1128/am.28.4.661-667.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forghani B., Schmidt N. J., Lennette E. H. Solid phase radioimmunoassay for typing herpes simplex viral antibodies in human sera. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Nov;2(5):410–418. doi: 10.1128/jcm.2.5.410-418.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hierholzer J. C., Suggs M. T., Hall E. C. Standardized viral hemagglutination and hemagglutination-inhibition tests. II. Description and statistical evaluation. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Nov;18(5):824–833. doi: 10.1128/am.18.5.824-833.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson H. D., Ziegler D. W. Criteria for preparing, evaluating, and standardizing iodinated globulins for radioimmunoassay procedures. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Dec;28(6):935–942. doi: 10.1128/am.28.6.935-942.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson H. D., Ziegler D. W., Feorino P. M. Radioimmunoassay for detection of antibodies to Epstein-Barr virus in human infectious mononucleosis serum specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 May;1(5):429–433. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.5.429-433.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson H. D., Ziegler D. W. Simplified radioimmunoassay for diagnostic serology. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Nov;24(5):742–749. doi: 10.1128/am.24.5.742-749.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LENNETTE E. H., WOODIE J. D., NAKAMURA K., MAGOFFIN R. L. THE DIAGNOSIS OF RABIES BY FLUORESCENT ANTIBODY METHOD (FRA) EMPLOYING IMMUNE HAMSTER SERUM. Health Lab Sci. 1965 Jan;2:24–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander J. J., Alter H. J., Purcell R. H. Frequency of antibody to hepatitis-associated antigen as measured by a new radioimmunoassay technique. J Immunol. 1971 May;106(5):1166–1171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennette E. H., Woodie J. D., Schmidt N. J. A modified indirect immunofluorescent staining technique for the demonstration of rubella antibodies in human sera. J Lab Clin Med. 1967 Apr;69(4):689–695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling C. M., Overby L. R. Prevalence of hepatitis B virus antigen as revealed by direct radioimmune assay with 125 I-antibody. J Immunol. 1972 Oct;109(4):834–841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. A method of trace iodination of proteins for immunologic studies. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1966;29(2):185–189. doi: 10.1159/000229699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt N. J., Lennette E. H. Improved yields of cell-free varicella-zoster virus. Infect Immun. 1976 Sep;14(3):709–715. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.3.709-715.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt N. J., Lennette E. H. Neutralizing antibody responses to varicella-zoster virus. Infect Immun. 1975 Sep;12(3):606–613. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.3.606-613.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt N. J., Lennette E. H., Woodie J. D., Ho H. H. Immunofluorescent staining in the laboratory diagnosis of varicella-zoster virus infections. J Lab Clin Med. 1965 Sep;66(3):403–412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. O., Gehle W. D., McCracken A. W. Radioimmunoassay techniques for detecting naturally occurring viral antibody in human sera. J Immunol Methods. 1974 Oct;5(4):337–344. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(74)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townsend J. J., Baringer J. R., Wolinsky J. S., Malamud N., Mednick J. P., Panitch H. S., Scott R. A., Oshiro L., Cremer N. E. Progressive rubella panencephalitis. Late onset after congenital rubella. N Engl J Med. 1975 May 8;292(19):990–993. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197505082921902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil M. L., Itabashi H., Cremer N. E., Oshiro L., Lennette E. H., Carnay L. Chronic progressive panencephalitis due to rubella virus simulating subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. N Engl J Med. 1975 May 8;292(19):994–998. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197505082921903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westmoreland D., Watkins J. F. The IgG receptor induced by herpes simplex virus: studies using radioiodinated IgG. J Gen Virol. 1974 Jul;24(1):167–178. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-24-1-167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YALOW R. S., BERSON S. A. Immunoassay of endogenous plasma insulin in man. J Clin Invest. 1960 Jul;39:1157–1175. doi: 10.1172/JCI104130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler D. W., Hutchinson H. D., Koplan J. P., Nakano J. H. Detection by radioimmunoassay of antibodies in human smallpox patients and vaccinees. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Mar;1(3):311–317. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.3.311-317.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


