Abstract
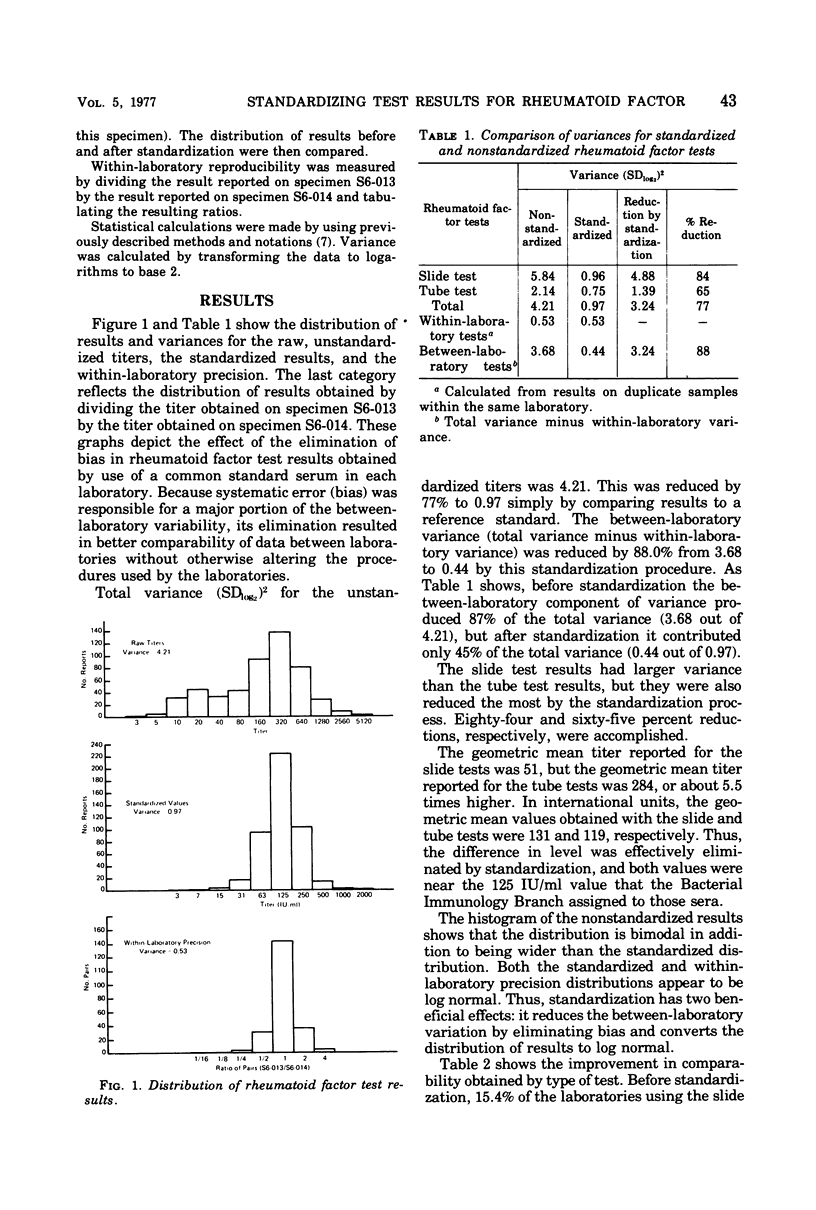
Standaridizing test results for rheumatoid factor by comparing results obtained for an unknown with results obtained for a serum reference preparation decreased variance between laboratories, as measured in the Center for Disease Control proficiency testing program, by 77%. The amount of improvement was also estimated by the type of test and by the manufacturer's product. Standardization resulted in an increase in the number of reported results that were within a twofold dilution of the median value. The percentage increased from 50.3 to 93.7% for the slide tests and from 78.1 to 91.2% fro the tube tests. Decrease in variance by manufacturer's product ranged from 94 to 27%. The study demonstrated that adopting a reference serum standard could substantially improve the comparability of rheumatoid factor test results and that proficiency testing programs can be used to estimate improvement which could be expected as a result of standardization.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson S. G., Bentzon M. W., Houba V., Krag P. International reference preparation of rheumatoid arthritis serum. Bull World Health Organ. 1970;42(2):311–318. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones W. L., Wiggins G. L. A study of rheumatoid arthritis latex kits. Am J Clin Pathol. 1973 Nov;60(5):703–706. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/60.5.703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R. N., Ehrhard H. B., Marcus S. Evaluation of tests for infectious mononucleosis through proficiency testing. Health Lab Sci. 1976 Jan;13(1):34–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


