Abstract
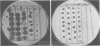
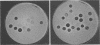
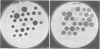
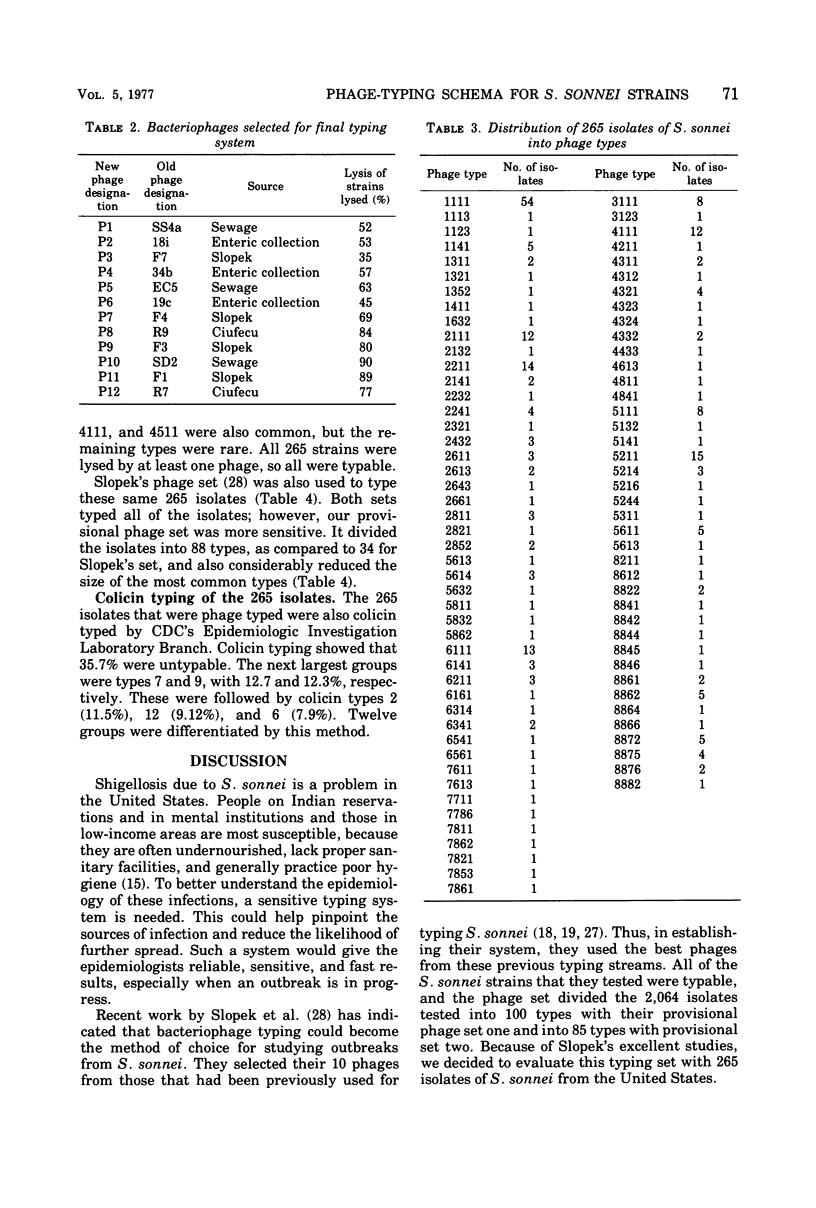
A bacteriophage-typing schema was developed for differentiating strains of Shigella sonnei. Sixty-seven bacteriophages were obtained from other collections, and 36 bacteriophages were isolated from sewage. From these 103 bacteriophages, a provisional set of 12 was chosen by computer analysis as being the most sensitive in differentiating strains of S. sonnei isolated in the United States. The provisional schema was used to type 265 strains from different geographical areas. It divided them into 87 different lysis patterns, and all 265 strains were typable. Smooth and rough colonial variants of the same strain had different lysis patterns, so the technique was standardized to type rough colonies only. Reproducibility was difficult to obtain until all conditions were carefully standardized. Changes in results were noted even on different lot numbers of Trypticase soy agar, which was defined as the standard medium. So that the medium would not be a variable, 100 pounds (ca 453.5 kg) of the same lot number was purchased. Bacteriophage typing was very useful in differentiating strains, and work should continue on establishing a standarized schema.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABBOTT J. D., SHANNON R. A method for typing Shigella sonnei, using colicine production as a marker. J Clin Pathol. 1958 Jan;11(1):71–77. doi: 10.1136/jcp.11.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANDERSON E. S., WILLIAMS R. E. Bacteriophage typing of enteric pathogens and staphylococci and its use in epidemiology. J Clin Pathol. 1956 May;9(2):94–127. doi: 10.1136/jcp.9.2.94. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoki Y. Colicin type, biochemical type and drug-resistance pattern of Shigella sonnei isolated in Japan and its neighboring countries. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 1968;16(2):303–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRUICKSHANK R. Laboratory uses of antibiotics. Br Med Bull. 1960 Jan;16:79–81. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a069797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichner E. R., Gangarosa E. J., Goldsby J. B. The current status of shigellosis in the United States. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1968 Apr;58(4):753–763. doi: 10.2105/ajph.58.4.753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elek S. D., Davies J. R., Miles R. Resistotyping of Shigella sonnei. J Med Microbiol. 1973 Aug;6(3):329–345. doi: 10.1099/00222615-6-3-329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer J. J., 3rd Epidemiological differentiation of Serratia marcescens: typing by bacteriocin production. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Feb;23(2):218–225. doi: 10.1128/am.23.2.218-225.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer J. J., 3rd Mnemonic for reporting bacteriocin and bacteriophage types. Lancet. 1970 Jul 11;1(7663):96–96. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)92663-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILLIES R. R. COLICINE PRODUCTION AS AN EPIDEMIOLOGICAL MARKER OF SHIGELLA SONNEI. J Hyg (Lond) 1964 Mar;62:1–9. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400039711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillies R. R. Fermentation studies on Shigella sonnei. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1965 Jul;90(1):345–348. doi: 10.1002/path.1700900144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gromkova R., Trifonova A. Attempts at phage typing of Shigella sonnei. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1967;204(2):212–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUDFORD C. G. Bacteriophage types of Shigella sonnei in Queensland. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1953 Dec;31(6):545–552. doi: 10.1038/icb.1953.58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- László V. G., Kerekes L. Phage and colicin typing of Shigella sonnei. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1969;16(4):309–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAYR-HARTING A. The phage typing of Shigella sonnei, and the limits of type stability. J Gen Microbiol. 1952 Nov;7(3-4):382–396. doi: 10.1099/00221287-7-3-4-382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris G. K., Wells J. G. Colicin typing of Shigella sonnei. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Feb;27(2):312–316. doi: 10.1128/am.27.2.312-316.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parisi J. T., Russell J. C., Merlo R. J. Bacteriophage typing as an epidemiological tool for urinary Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol. 1969 May;17(5):721–725. doi: 10.1128/am.17.5.721-725.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reller L. B. Colicin typing as an epidemiological tool in the investigation of outbreaks of Shigella sonnei. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Jan;21(1):21–26. doi: 10.1128/am.21.1.21-26.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slopek S., Durlakowa I., Kucharewicz-Krubkowska A., Krzywy T., Slopek A., Weber B. Phage typing of Shigella sonnei. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 1973;21(1):1–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szturm-Rubinsten S. Determination of biotype, phage type and colicinogenic character of Shigella sonnei, and its epidemiologic importance. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 1968;16(3):421–428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zierdt C. H., Schmidt P. J. Dissociation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1964 May;87(5):1003–1010. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.5.1003-1010.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]