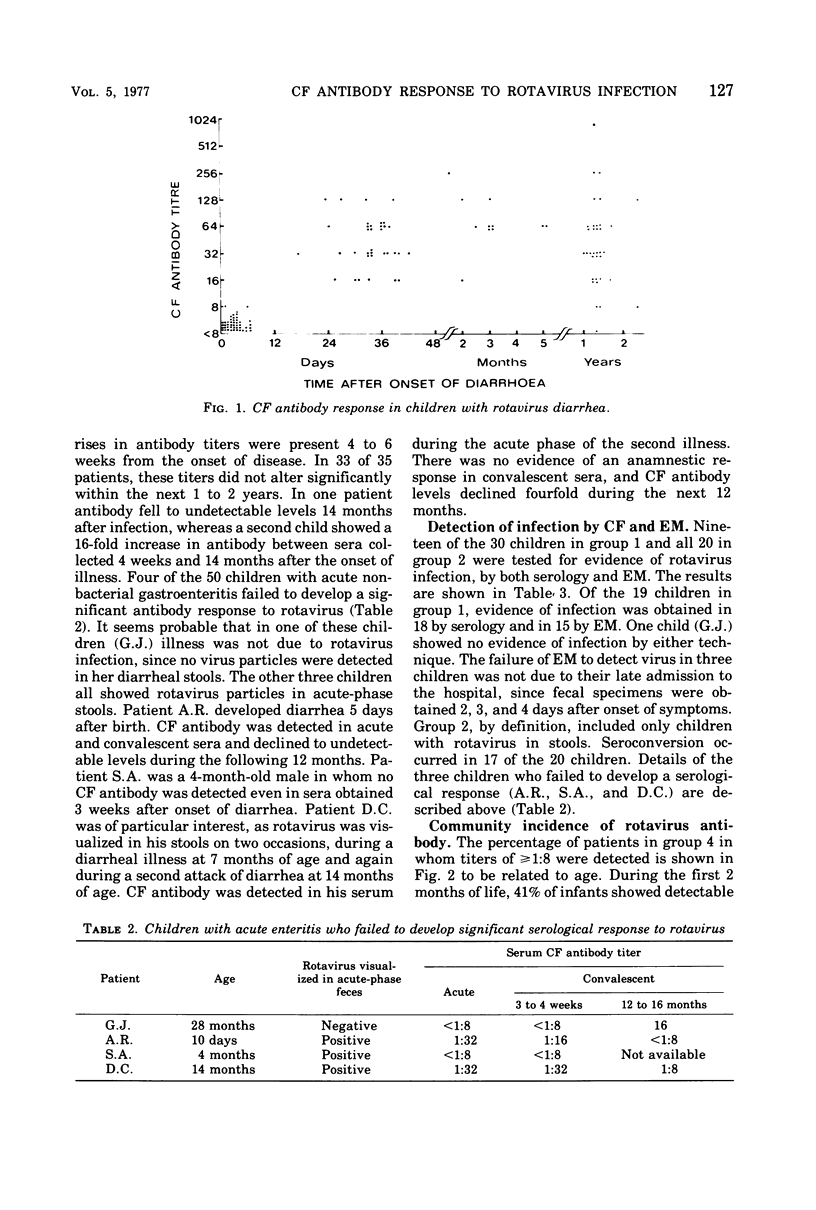
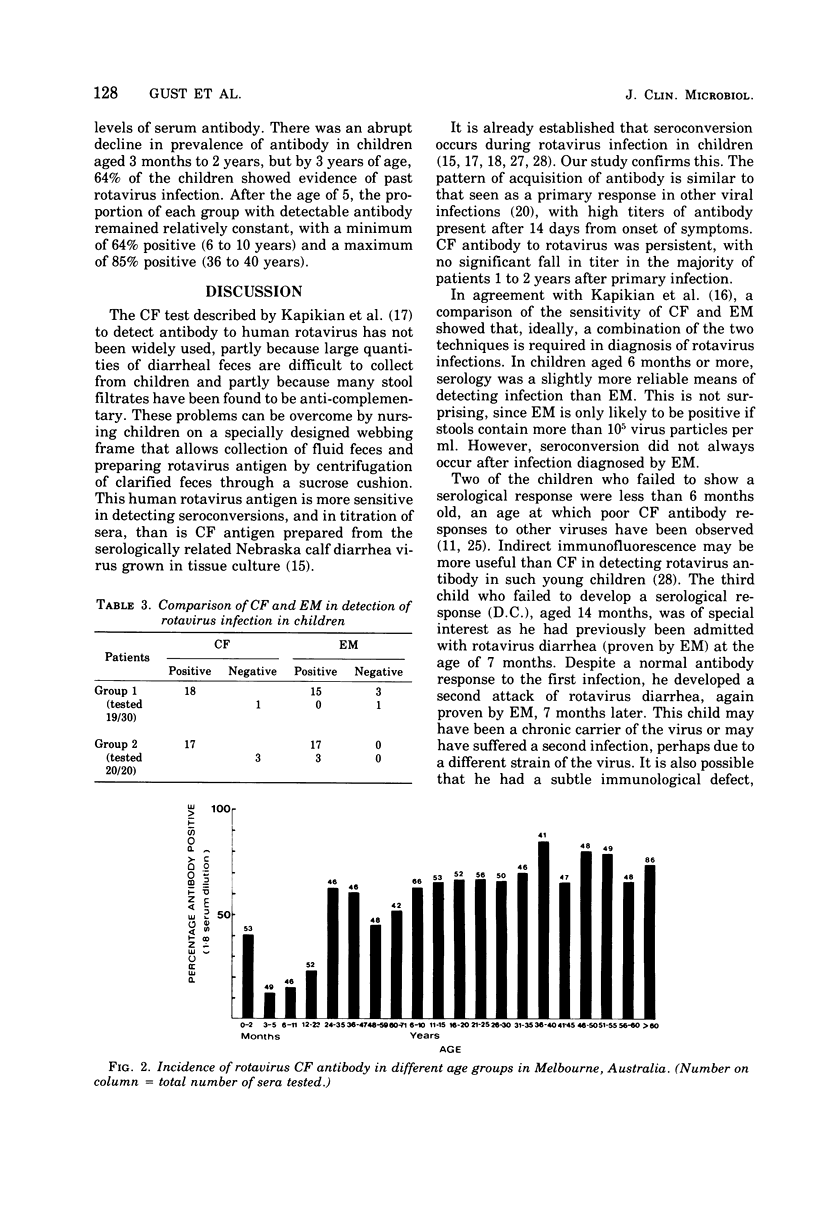
Abstract
A human rotavirus complement-fixing (CF) antigen, prepared by purification of large volumes of fluid feces collected from children with winter diarrhea, was used to study the development and persistence of antibody in children with diarrhea and the prevalence of rotavirus antibody in Melbourne. In children with diarrhea, antibody rises were detectable within 4 to 6 weeks of the onset of illness, and the titers usually remained elevated for the next 1 to 2 years. CF antibody did not develop in two children with proven rotavirus infection aged less than 6 months, an age at which poor CF responses to other viruses have also been observed. A study of CF antibody levels in the general community showed that in Melbourne, most children have been infected with human rotavirus by the age of 3 years.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRADSTREET C. M., TAYLOR C. E. Technique of complementfixation test applicable to the diagnosis of virus diseases. Mon Bull Minist Health Public Health Lab Serv. 1962 May;21:96–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop R. F., Davidson G. P., Holmes I. H., Ruck B. J. Detection of a new virus by electron microscopy of faecal extracts from children with acute gastroenteritis. Lancet. 1974 Feb 2;1(7849):149–151. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92440-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop R. F., Davidson G. P., Holmes I. H., Ruck B. J. Virus particles in epithelial cells of duodenal mucosa from children with acute non-bacterial gastroenteritis. Lancet. 1973 Dec 8;2(7841):1281–1283. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92867-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blacklow N. R., Echeverria P., Smith D. H. Serological studies with reovirus-like enteritis agent. Infect Immun. 1976 Jun;13(6):1563–1566. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.6.1563-1566.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryden A. S., Davies H. A., Hadley R. E., Flewett T. H. Rotavirus enteritis in the West Midlands during 1974. Lancet. 1975 Aug 9;2(7928):241–243. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(75)90959-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson G. P., Bishop R. F., Townley R. R., Holmes I. H. Importance of a new virus in acute sporadic enteritis in children. Lancet. 1975 Feb 1;1(7901):242–246. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91140-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson G. P., Goller I., Bishop R. F., Townley R. R., Holmes I. H., Ruck B. J. Immunofluorescence in duodenal mucosa of children with acute enteritis due to a new virus. J Clin Pathol. 1975 Apr;28(4):263–266. doi: 10.1136/jcp.28.4.263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flewett T. H., Bryden A. S., Davies H. Letter: Virus particles in gastroenteritis. Lancet. 1973 Dec 29;2(7844):1497–1497. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92760-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flewett T. H., Bryden A. S., Davies H., Woode G. N., Bridger J. C., Derrick J. M. Relation between viruses from acute gastroenteritis of children and newborn calves. Lancet. 1974 Jul 13;2(7872):61–63. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91631-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flewett T. H., Davies H., Bryden A. S., Robertson M. J. Diagnostic electron microscopy of faeces. II. Acute gastroenteritis associated with reovirus-like particles. J Clin Pathol. 1974 Aug;27(8):608–614. doi: 10.1136/jcp.27.8.608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARDNER P. S., ELDERKIN F. M., WALL A. H. SEROLOGICAL STUDY OF RESPIRATORY SYNCYTIAL VIRUS INFECTIONS IN INFANCY AND CHILDHOOD. Br Med J. 1964 Dec 19;2(5424):1570–1573. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5424.1570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gust I. D., Seeger V. J., Sandland A. M., Pringle R. C., Craig G. Letter: Acute non-bacterial gastroenteritis: collection of large quantities of stools from young children. Lancet. 1975 Nov 8;2(7941):933–933. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92178-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara M., Mukoyama J., Tsurahara T., Saito Y., Tagaya I. Letter: Duovirus in schoolchildren with gastroenteritis. Lancet. 1976 Feb 7;1(7954):311–311. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91449-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Infantile enteritis viruses: morphogenesis and morphology. J Virol. 1975 Oct;16(4):937–943. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.4.937-943.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapikian A. Z., Cline W. L., Mebus C. A., Wyatt R. G., Kalica A. R., James H. D., Jr, VanKirk D., Chanock R. M. New complement-fixation test for the human reovirus-like agent of infantile gastroenteritis. Nebraska calf diarrhea virus used as antigen. Lancet. 1975 May 10;1(7915):1056–1061. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91827-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapikian A. Z., Kim H. W., Wyatt R. G., Cline W. L., Arrobio J. O., Brandt C. D., Rodriguez W. J., Sack D. A., Chanock R. M., Parrott R. H. Human reovirus-like agent as the major pathogen associated with "winter" gastroenteritis in hospitalized infants and young children. N Engl J Med. 1976 Apr 29;294(18):965–972. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197604292941801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapikian A. Z., Kim H. W., Wyatt R. G., Rodriguez W. J., Ross S., Cline W. L., Parrott R. H., Chanock R. M. Reoviruslike agent in stools: association with infantile diarrhea and development of serologic tests. Science. 1974 Sep 20;185(4156):1049–1053. doi: 10.1126/science.185.4156.1049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konno T., Imai A., Suzuki H., Ishida N. Letter: Mercaptoethanol-sensitive antibody to reovirus-like agents in acute epidemic gastroenteritis. Lancet. 1975 Dec 27;2(7948):1312–1312. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)90654-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merigan T. C. Host defenses against viral disease. N Engl J Med. 1974 Feb 7;290(6):323–329. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197402072900608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middleton P. J., Petric M., Hewitt C. M., Szymanski M. T., Tam J. S. Counter-immunoelectro-osmophoresis for the detection of infantile gastroenteritis virus (orbi-group) antigen and antibody. J Clin Pathol. 1976 Mar;29(3):191–197. doi: 10.1136/jcp.29.3.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodger S. M., Schnagl R. D., Holmes I. H. Biochemical and biophysical characteristics of diarrhea viruses of human and calf origin. J Virol. 1975 Nov;16(5):1229–1235. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.5.1229-1235.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., Konno T. Reovirus-like particles in jejunal mucosa of a Japanese infant with acute infectious non-bacterial gastroenteritis. Tohoku J Exp Med. 1975 Mar;115(3):199–211. doi: 10.1620/tjem.115.199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tufvesson B., Johnsson T. Occurrence of reo-like calf viruses in young children with acute gastroenteritis. Diagnoses established by electron microscopy and complement fixation, using the reo-like virus as antigen. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1976 Feb;84(1):22–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zissis G., Lambert J. P., Fonteyne J., De Kegel D. Letter: Child-mother transmission of rotavirus. Lancet. 1976 Jan 10;1(7950):96–96. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)90196-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


