Abstract
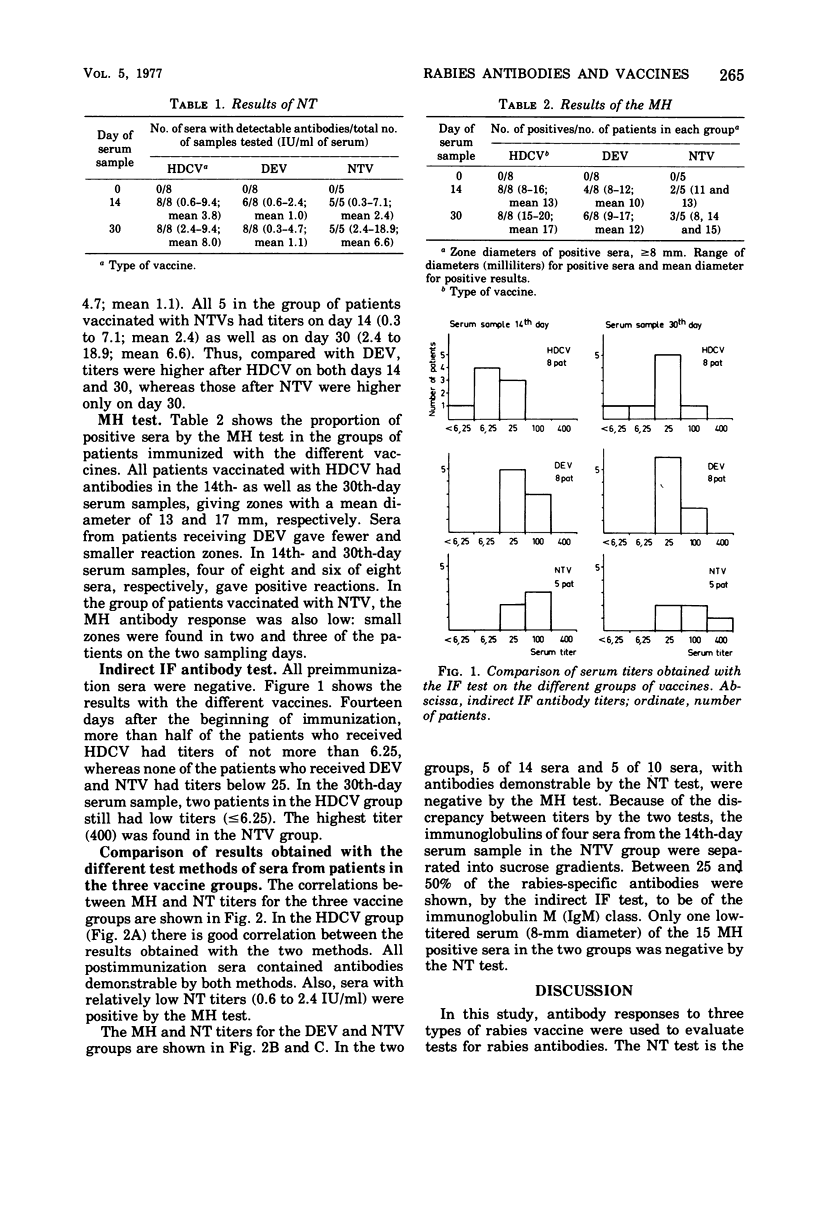
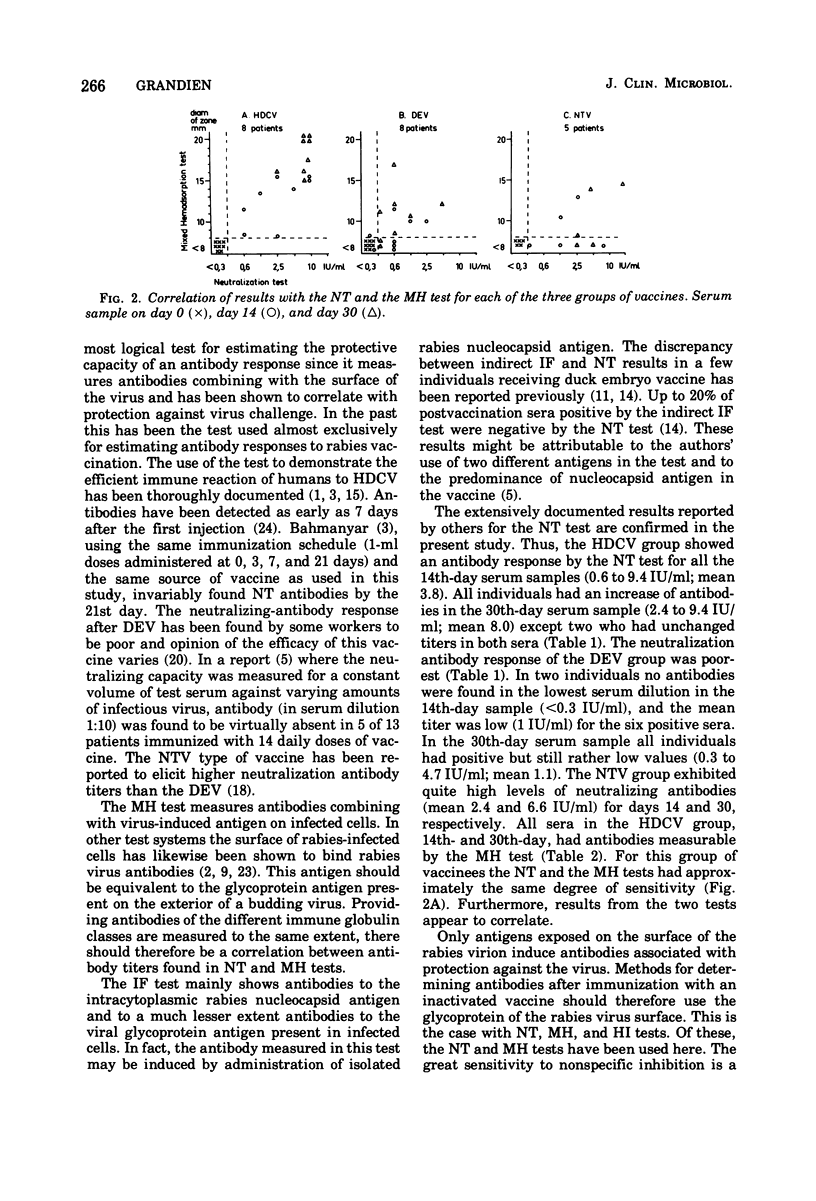
Humoral antibody response to three types of rabies vaccines were assayed by the neutralization (NT), the mixed hemadsorption (MH), and the indirect immunofluorescence (IF) tests. The NT and MH tests were used to detect antibodies combining with antigens at the surface of virions and infected cells, whereas the indirect IF test measured antibodies mainly to the rabies nucleocapsid antigen. After immunization with a human diploid cell vaccine, antibodies were detected by both the NT and the MH test in the 14th- and 30th-day serum samples from each of eight vaccinated persons. There was a good correlation between titers obtained with the two tests in this group of vaccinees. Antibodies elicited by duck embryo and nervous tissue vaccines occurred less frequently and in lower titers. In these groups of vaccinees, 5 of 14 and 5 of 10, respectively, had antibodies detectable by the NT test in the 14th- and 30th-day sera but were negative by the MH test. It is suggested that this was due to the high levels of immunoglobulin M antibodies, which are known to be elicited by daily injections of vaccine. Since antibodies of the immunoglobulin M class are considered to be less important for protection against rabies, the MH test is recommended for immunity determinations. Compared with the NT test, this test also offers the advantage of being technically more convenient because of its capacity for testing numerous sera in a single run. Antibody titers obtained by the indirect IF test in the human diploid cell vaccine group were relatively low. Titers in the duck embryo and nervous tissue vaccine groups were higher but did not correlate with the results of the NT test.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoki F. Y., Tyrrell D. A., Hill L. E. Immunogenicity and acceptability of a human diploid-cell culture rabies vaccine in volunteers. Lancet. 1975 Mar 22;1(7908):660–662. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91761-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atanasiu P., Tsiang H., Perrin P., Favre S. Les IgG anti-glycoprotéines rabiques marquées par la peroxydase et l'isothiocyanate de fluorescéine. Résultats. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1975 Jul-Aug;126B(1):69–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho H. C., Fenje P. Rabies neutralizing antibody determination in tissue culture by direct fluorescent antibody technique. J Biol Stand. 1975;3(1):101–105. doi: 10.1016/0092-1157(75)90012-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crick J., Brown F. Efficacy of rabies vaccine prepared from virus grown in duck embryo. Lancet. 1970 May 23;1(7656):1106–1107. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)92768-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debbie J. G., Andrulonis J. A., Abelseth M. K. Rabies antibody determination by immunofluorescence in tissue culture. Infect Immun. 1972 Jun;5(6):902–904. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.6.902-904.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dierks R. E., Gough P. M. Passive haemagglutination test for rabies antibodies. Monogr Ser World Health Organ. 1973;(23):147–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ESPMARK J. A., FAGRAEUS A. IDENTIFICATION OF THE SPECIES OF ORIGIN OF CELLS BY MIXED HEMADSORPTION : A MIXED ANTIGLOBULIN REACTION APPLIED TO MONOLAYER CELL CULTURES. J Immunol. 1965 Apr;94:530–537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAGRAEUS A., ESPMARK A. Use of a 'mixed haemadsorption' method in virus-infected tissue cultures. Nature. 1961 Apr 22;190:370–371. doi: 10.1038/190370a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halonen P. E., Murphy F. A., Fields B. N., Reese D. R. Hemagglutinin of rabies and some other bullet-shaped viruses. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Apr;127(4):1037–1042. doi: 10.3181/00379727-127-32864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwert E. Laboratory techniques in rabies: the complement fixation test. Monogr Ser World Health Organ. 1973;(23):124–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsh S. E. Indirect fluorescent antibody and serum neutralization response in pre-exposure prophylaxis against rabies. Ann Intern Med. 1965 Dec;63(6):955–964. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-63-6-955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plotkin S. A., Wiktor T. J., Koprowski H., Rosanoff E. I., Tint H. Immunization schedules for the new human diploid cell vaccine against rabies. Am J Epidemiol. 1976 Jan;103(1):75–80. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin R. H., Gough P., Gerlach E. H., Dierks R. E., Gregg M. B., Sikes R. K. Immunoglobulin response to rabies vaccine in man. Lancet. 1971 Sep 18;2(7725):625–628. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)80069-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedwick W. D., Wiktor T. J. Reproducible plaquing system for rabies, lymphocytic choriomeningitis,k and other ribonucleic acid viruses in BHK-21-13S agarose suspensions. J Virol. 1967 Dec;1(6):1224–1226. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.6.1224-1226.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikes R. K., Larghi O. P. Purified rabies vaccine: development and comparison of potency and safety with two human rabies vaccines. J Immunol. 1967 Sep;99(3):545–553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. S., Yager P. A., Baer G. M. A rapid tissue culture test for determining rabies neutralizing antibody. Monogr Ser World Health Organ. 1973;(23):354–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner G. S. Rabies vaccines. Br Med Bull. 1969 May;25(2):136–142. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a070682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiktor T. J., György E., Schlumberger D., Sokol F., Koprowski H. Antigenic properties of rabies virus components. J Immunol. 1973 Jan;110(1):269–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiktor T. J., Kuwert E., Koprowski H. Immune lysis of rabies virus-infected cells. J Immunol. 1968 Dec;101(6):1271–1282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiktor T. J., Plotkin S. A., Grella D. W. Human cell culture rabies vaccine. Antibody response in man. JAMA. 1973 May 21;224(8):1170–1171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


