Figure 7. The N-Terminally Extended EPK[QL9] Proteolytic Intermediate Is Bound by the Ld MHC Molecules.
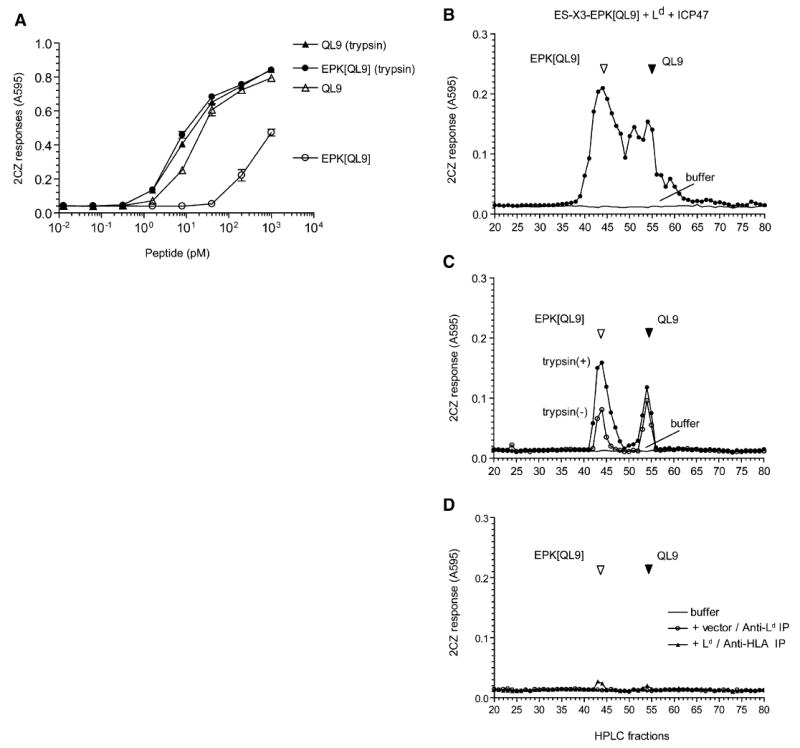
(A) Trypsin treatment of N-terminally extended QL9 precursor EPK[QL9] enhances its antigenicity. Varying concentrations of synthetic QL9 and its N-terminally extended analog EPK[QL9] peptide were tested for their ability to stimulate 2CZ T cells with Ld-L cells as APC. The peptides were tested as such or after preincubation with trypsin.
(B) The final antigenic QL9 peptide, its N-terminally extended precursors and intermediates present in the total peptide extract of COS cells transfected with ES-X3-EPK[QL9], Ld, and ICP47. The extract was fractionated by HPLC and antigenic peptides detected in the fractions by their ability to stimulate 2CZ response after trypsin treatment. HPLC fractions collected after injection of buffer alone were tested in parallel to rule out carryover between samples.
(C) The Ld MHC was immunoprecipitated from detergent lysate of COS cells transfected with the ES-X3-EPK[QL9] construct, Ld, and ICP47 cDNAs. The peptides contained in the immunoprecipitated material were fractionated by HPLC and assayed with 2CZ T cells with (closed circle) or without (open circle) trypsin treatment.
(D) As controls, the same cell lysate was immunoprecipitated with the pan HLA (W6/32) antibody (triangle), or the lysate from cells without Ld transfection was immunoprecipitated with the Ld antibody (circle). The peptide content of the immunoprecipitated material was analyzed as above. Data are representative of at least three independent experiments.
