Abstract
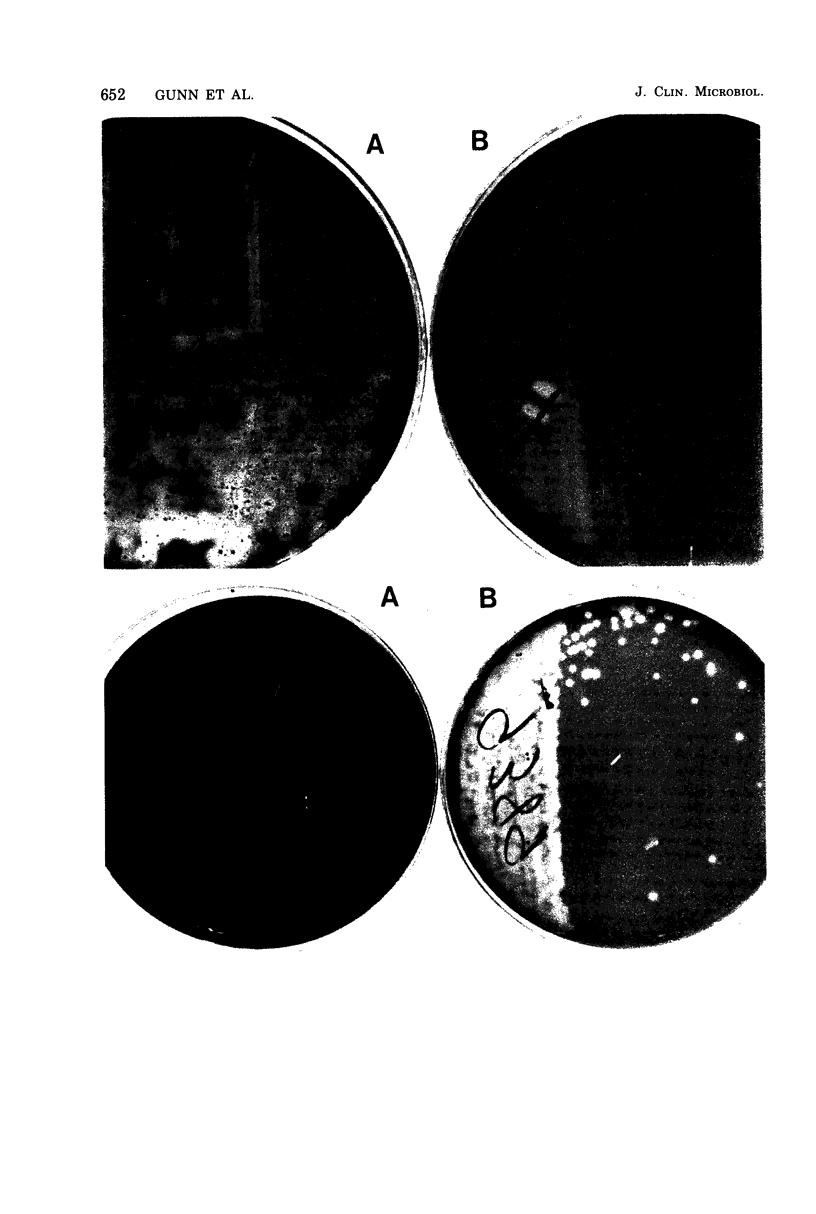
Sheep blood agar containing 23.75 microgram of sulfamethoxazole and 1.25 microgram of trimethoprim (SXT-BA) per ml was compared with conventional sheep blood agar (SBA) for isolating group A and B streptococci from throat cultures. This selective medium allowed much better recovery of group A and B streptococci and suppressed the growth of the normal flora, including "viridans" streptococci. In an initial study of 700 throat cultures, SXT-BA recovered 42% more group A and 49% more group B streptococci than did SBA. When SXT-BA was introduced into the routine microbiology laboratory and used by a number of medical technologists. SXT-BA recovered 28% more group A and 37% more group B streptococci than did SBA. In addition, the selective medium inhibited 83% of the non-group A and B streptococci that were recovered by SBA.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker C. J., Clark D. J., Barrett F. F. Selective broth medium for isolation of group B streptococci. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Dec;26(6):884–885. doi: 10.1128/am.26.6.884-885.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. J., Goroff D. K., Alpert S. L., Hayes C., McCormack W. M. Comparison of bacteriological methods for the isolation of group of B Streptococcus from vaginal cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Jul;4(1):46–48. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.1.46-48.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bill N. J., Washington J. A. Bacterial interference by Streptococcus salivarius. Am J Clin Pathol. 1975 Jul;64(1):116–120. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/64.1.116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black W. A., Van Buskirk F. Gentamicin blood agar used as a general-purpose selective medium. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Jun;25(6):905–907. doi: 10.1128/am.25.6.905-907.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowe C. C., Sanders W. E., Jr, Longley S. Bacterial interference. II. Role of the normal throat flora in prevention of colonization by group A Streptococcus. J Infect Dis. 1973 Oct;128(4):527–532. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.4.527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Facklam R. R. A review of the microbiological techniques for the isolation and identification of streptococci. CRC Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 1976 Mar;6(4):287–317. doi: 10.3109/10408367609151573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeburg P. W., Buckingham J. M. Evaluation of the Bacti-Lab streptococci culture systems for selective recovery and identification of group A streptococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Apr;3(4):443–448. doi: 10.1128/jcm.3.4.443-448.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunn B. A. SXT and Taxo A disks for presumptive identification of group A and B streptococci in throat cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Aug;4(2):192–193. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.2.192-193.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray P. R., Wold A. D., Schreck C. A., Washington JA I. I. Effects of selective media and atmosphere of incubation on the isolation of group A streptococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Jul;4(1):54–56. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.1.54-56.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamizo Y., Sato M. New selective media for the isolation of Streptococcus hemolyticus. Am J Clin Pathol. 1972 Feb;57(2):228–235. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/57.2.228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders E. Bacterial interference. I. Its occurrence among the respiratory tract flora and characterization of inhibition of group A streptococci by viridans streptococci. J Infect Dis. 1969 Dec;120(6):698–707. doi: 10.1093/infdis/120.6.698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagg J. R., Dajani A. S., Wannamaker L. W. Bacteriocins of gram-positive bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Sep;40(3):722–756. doi: 10.1128/br.40.3.722-756.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent W. F., Gibbons W. E., Gaafar H. A. Selective medium for the isolation of streptococci from clinical specimens. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Nov;22(5):942–943. doi: 10.1128/am.22.5.942-943.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]