Abstract
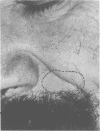
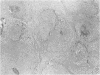
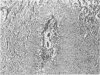
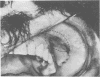
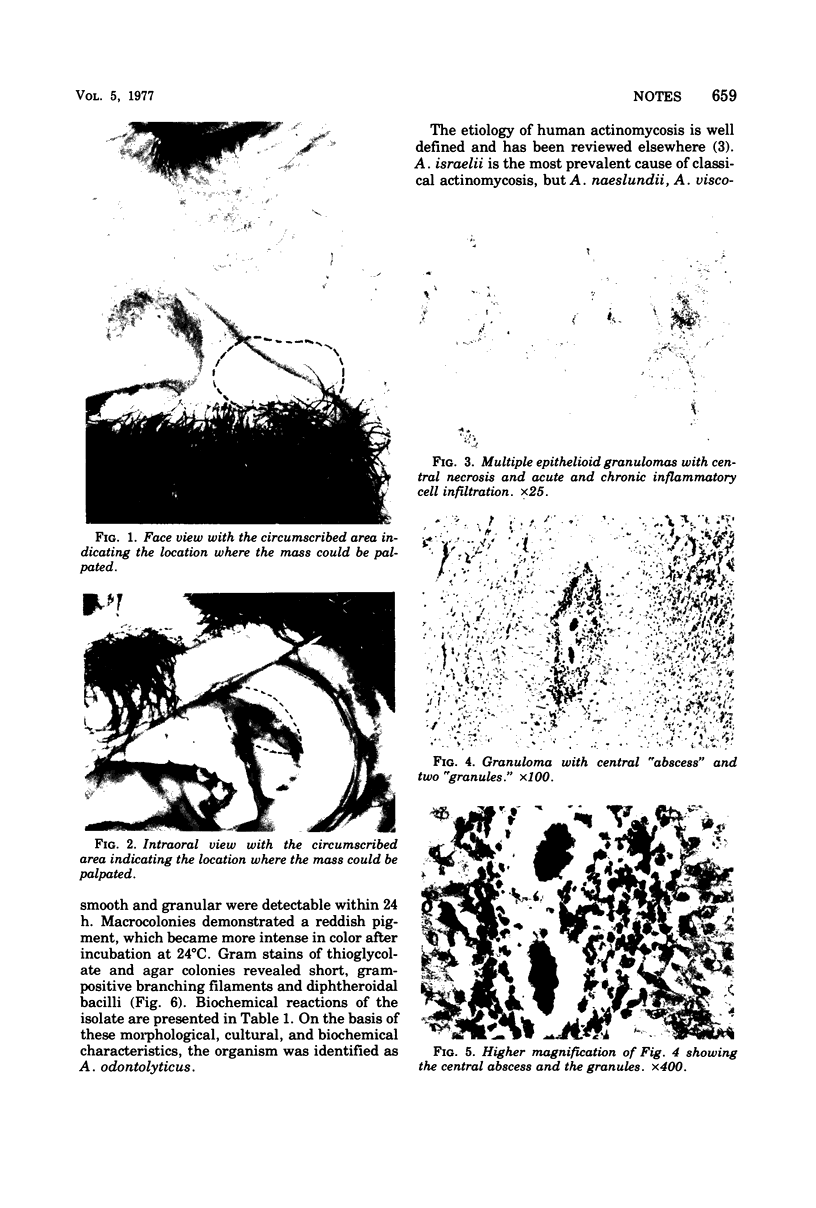
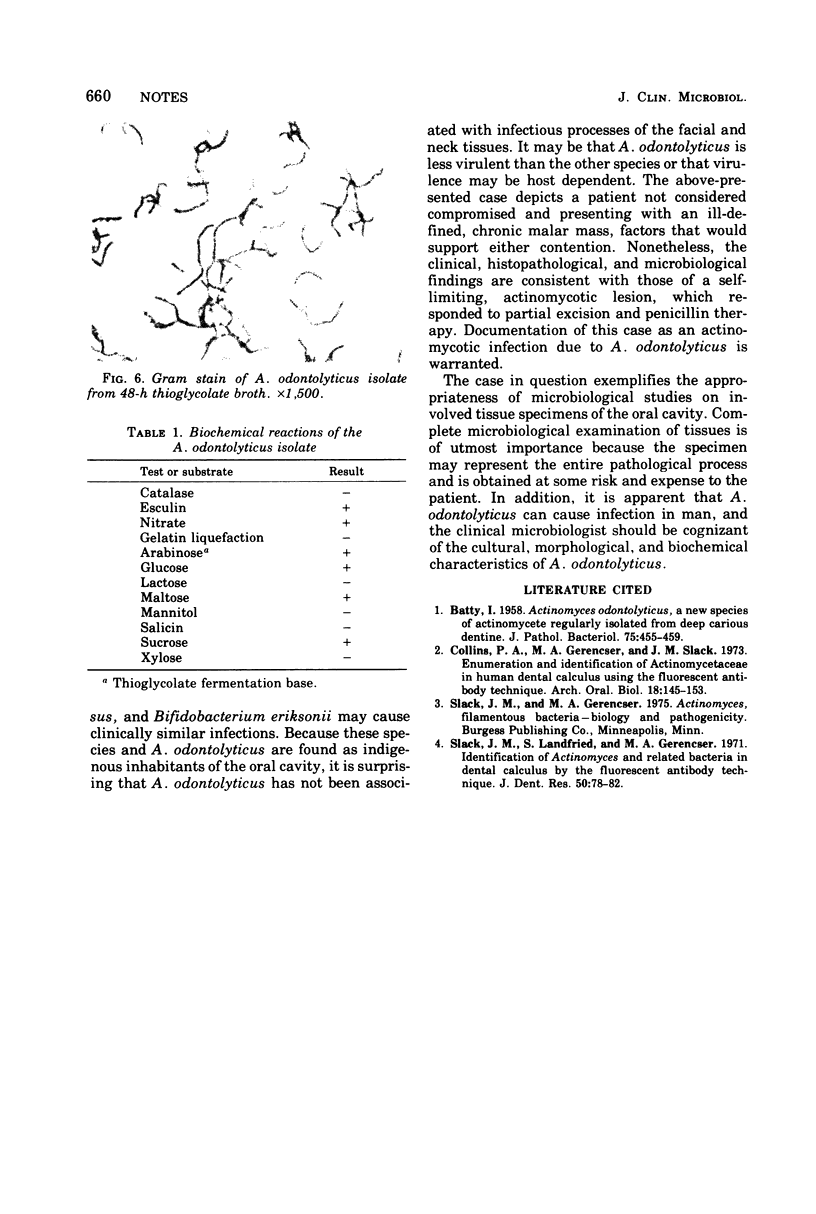
Actinomyces odontolyticus was isolated from a patient with a soft tissue mass in the malar region. The organism was identified on the basis of morphological, cultural, and biochemical characteristics. On histological examination, the tissue mass contained several granulomatous foci with small, basophilic staining areas resembling microscopic sulfur granules. This is believed to be the first reported case of actinomycosis due to A. odontolyticus.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BATTY I. Actinomyces odontolyticus, a new species of actinomycete regularly isolated from deep carious dentine. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1958 Apr;75(2):455–459. doi: 10.1002/path.1700750225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins P. A., Gerencser M. A., Slack J. M. Enumeration and identification of Actinomycetaceae in human dental calculus using the fluorescent antibody technique. Arch Oral Biol. 1973 Feb;18(2):145–153. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(73)90133-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slack J. M., Landfried S., Gerencser M. A. Identification of Actinomyces and related bacteria in dental calculus by the fluorescent antibody technique. J Dent Res. 1971 Jan-Feb;50(1):78–82. doi: 10.1177/00220345710500013501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]