Abstract
Clinical and bacteriological features of eight cases of Vibrio alginolyticus infections in Hawaii are presented. These isolates occurred in superficial sites, primarily related to infections caused by swimming.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barker W. H., Jr Vibrio parahaemolyticus outbreaks in the United States. Lancet. 1974 Mar 30;1(7857):551–554. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92727-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
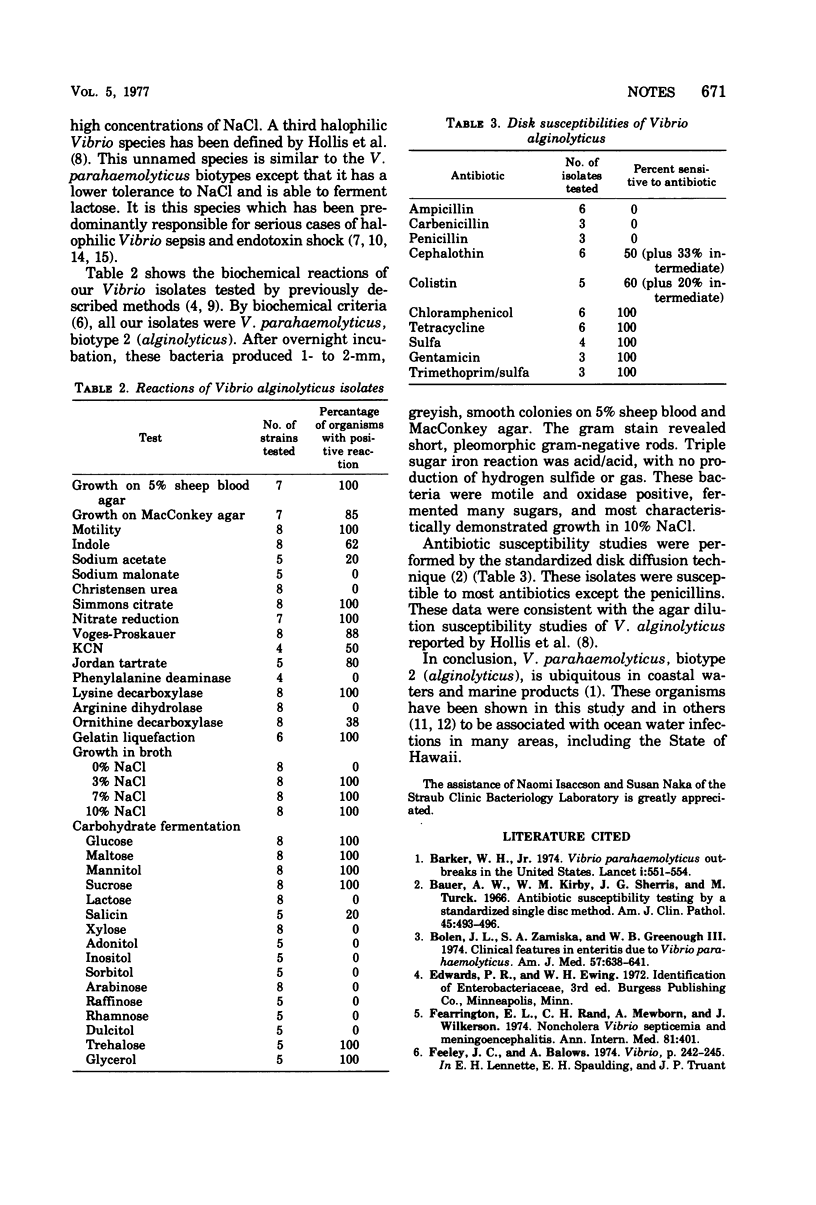
- Bauer A. W., Kirby W. M., Sherris J. C., Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 Apr;45(4):493–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolen J. L., Zamiska S. A., Greenough W. B., 3rd Clinical features in enteritis due to Vibrio parahemolyticus. Am J Med. 1974 Oct;57(4):638–641. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(74)90017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearrington E. L., Rand C. H., Jr, Mewborn A., Wilkerson J. Letter: Non-cholera vibrio septicemia and meningoencephalitis. Ann Intern Med. 1974 Sep;81(3):401–401. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-81-3-401_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez C. R., Pankey G. A. Tissue invasion by unnamed marine vibrios. JAMA. 1975 Sep 15;233(11):1173–1176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollis D. G., Weaver R. E., Baker C. N., Thornsberry C. Halophilic Vibrio species isolated from blood cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Apr;3(4):425–431. doi: 10.1128/jcm.3.4.425-431.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roland F. P. Leg gangrene and endotoxin shock due to vibrio parahaemolyticus--an infection acquired in New England coastal waters. N Engl J Med. 1970 Jun 4;282(23):1306–1306. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197006042822306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin S. J., Tilton R. C. Isolation of Vibrio alginolyticus from wound infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Dec;2(6):556–558. doi: 10.1128/jcm.2.6.556-558.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan W. J. Marine vibrios associated with superficial septic lesions. J Clin Pathol. 1976 Nov;29(11):1014–1015. doi: 10.1136/jcp.29.11.1014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorsteinsson S. B., Minuth J. N., Musher D. M. Clinical manifestations of halophilic non-cholera Vibrio infections. Lancet. 1974 Nov 30;2(7892):1283–1284. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)90141-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zide N., Davis J., Ehrenkranz N. J. Fulminating vibrio parahemolyticus septicemia. A syndrome of erythemia multiforme, hemolytic anemia, and hypotension. Arch Intern Med. 1974 Mar;133(3):479–481. doi: 10.1001/archinte.133.3.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


