Abstract
Demethylation of 5-methylcytosine in genomic DNA is believed to be one of the mechanisms underlying replicative life-span of mammalian cells. Both proliferation associated SNF2-like gene (PASG, also termed Lsh) and DNA methyltransferase 3B (Dnmt3b) knockout mice result in embryonic genomic hypomethylation and a replicative senescent phenotype. However, it is unclear whether gradual demethylation of DNA during somatic cell division is directly involved in senescence. In this study, we retrovirally transduced TIG-7 human fibroblasts with a shRNA against PASG and compared the rate of change in DNA methylation as well as the replicative life-span to control cells under low (3%) and ambient (20%) oxygen. Expression of PASG protein was decreased by approximately 80% compared to control cells following transduction of PASG shRNA gene. The rate of cell growth was the same in both control and PASG-suppressed cells. The rate of demethylation of DNA was significantly increased in PASG-suppressed cells as compared control cells. However, decreased PASG expression did not shorten the replicative life-span of TIG-7 cells. Culture under low oxygen extended the life-span of TIG-7 cells but did not alter the rate of DNA demethylation. While knockout of PASG during development results in genomic hypomethylation and premature senescence, our results show that while downregulation of PASG expression in a somatic cell also leads to DNA hypomethylation, there is no associated senescent phenotype. These results suggest differences in cellular consequences of hypomethylation mediated by PASG during development compared to that in somatic cells.
Keywords: epigenetics, DNA methylation, PASG, LSH, senescence
Introduction
Normal primary human cells have a limited replicative potential in culture and irreversibly stop dividing after relatively restricted number of divisions—a phenomenon termed cellular senescence.1 Senescent cells are morphologically altered and express specific senescence-associated genes.2 The number of cell divisions preceding senescence depends on cell type, genetic backgrounds of donor cells and culture conditions.3 This limitation of proliferative potential is thought to arise by an intrinsic mechanism that counts the number of cell divisions. Telomere shortening, which occurs as a consequence of incomplete DNA replication at the chromosome ends, is proposed to be one mechanism for mediating senescence.4,5 At present, it is thought that telomere shortening triggers uncapping of the t-loop of the ends of chromosomes which results in the recruitment and activation of DNA damage sensors, such as ataxia-telangiectasia mutated (ATM) and meiotic recombination 11 (MRE11), to the unprotected chromosome ends, leading to cell cycle arrest.6 Gradual demethylation of 5-methylcyosine in DNA has also been shown to be another possible mechanism for counting cell divisions.7–9 In human cells, 60–90% of the cytosine residues in CpG dinucleotides are methylated. Methylation of CpG islands is associated with condensation of chromatin and is also enriched with hypoacetylated histones, leading to transcriptional silencing.10 DNA methylation has been shown to be essential for normal development, X chromosome inactivation and genome imprinting.11 The level of DNA methylation decreases in normal mammalian cells during in vitro culture8 and in tissues during aging.9,12 Exposure of cells to inhibitors of DNA methyltransferase, e.g., 5-azacytidine (aza-C) and 5-azadeoxycytidine (aza-dC), leads to decreased genomic methylation, shortening of in vitro lifespan13,14 and premature senescence of normal human fibroblasts.15 Premature senescence mediated by aza-dC was not observed in p21-deficient fibroblasts, suggesting that the induction of senescence occurs by activation of cell cycle checkpoint pathways in response to DNA damage or to DNA demethylation, rather than transcriptional activation of particular genes by DNA demethylation.16 Therefore, other experimental strategies that do not utilize demethylating agents would potentially provide an alternative approach to investigating the relationship between DNA demethylation and senescence in the absence of potentially DNA damaging agents. Mouse knockout models have attempted to in part address this issue.
Homologous recombination mediated disruption of both proliferation associated SNF2-like gene (PASG, also termed LSH, HELLS or SMARCA6)17,18 and DNA methyltransferase 3B (Dnmt3b)19 in mice results in embryonic genomic hypomethylation and a replicative senescent phenotype. However, it is unclear whether gradual demethylation of DNA during somatic cell division is directly involved in senescence, because MEFs from PASG and Dnmt3b knockout mice have gone through embryogenesis with a hypomethylated genome.
PASG (Lsh) encodes an SNF-2-like protein that has been shown to contribute to genomic methylation.17,18 Sun et al. and Fan et al. demonstrated that PASG hypomorphic mice had genomic hypomethylation as well as premature aging phenotype that was associated with decreased proliferation and increased replicative senescence.18,20 In addition, PASG has been shown to play a role in CpG methylation of pericentromeric DNA in mouse cells.17,21 Loss of PASG (Lsh) function also results in abnormal centrosome numbers, abnormal spindle formation and micronuclei.20 While the loss of PASG (Lsh) has been implicated in abnormalities of de novo DNA methylation,22 its role in maintenance DNA methylation remains unclear.
In the current study, we used retroviral transduction of TIG-7 human fibroblasts with shRNA against PASG and compared DNA methylation during culture under low or ambient oxygen levels. The results indicate a role for PASG in maintenance methylation in somatic cells but not necessarily in the mediation of senescence.
Results
shRNA inhibiton of PASG expression in TIG-7 cells
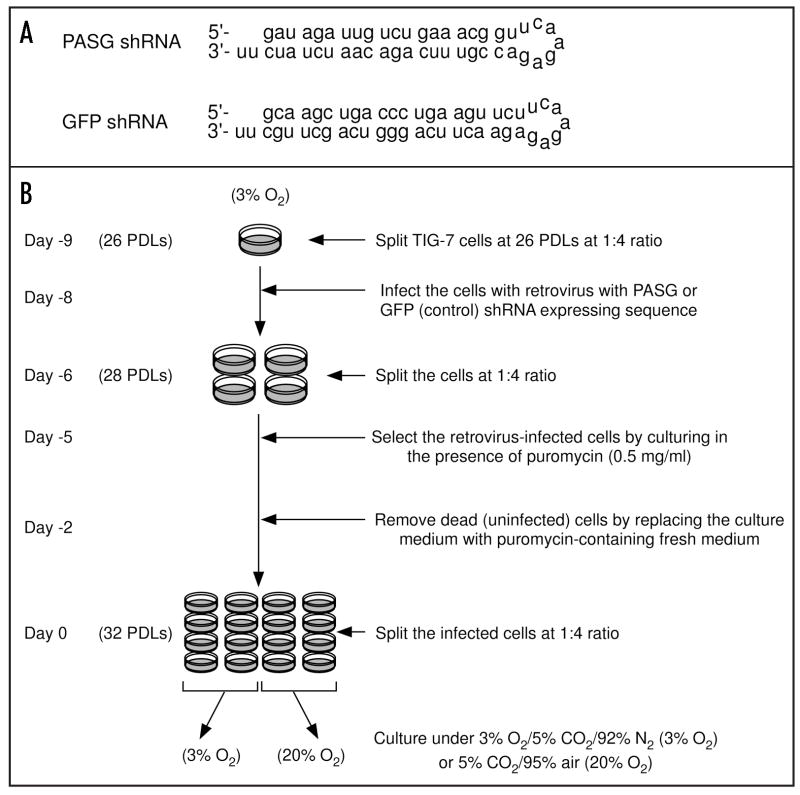
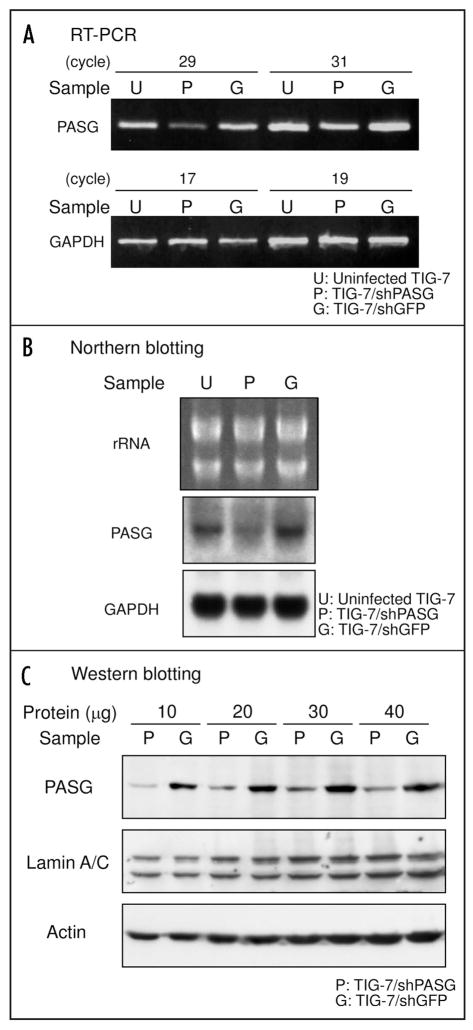
TIG-7 fibroblasts were transduced at 26 PDLs with either pSUPER.retro-shPASG (TIG-7/shPASG) or a control vector pSUPER.retro-shGFP (TIG-7/shGFP) followed by puromycin selection for five days as shown in Figure 1B. The predicted sequences of the short hairpin transcript of PASG shRNA and GFP shRNA are shown in Figure 1A. Expression of PASG in transduced cells was analyzed by RT-PCR, Northern and Western blot analyses (Fig. 2). In TIG-7/shPASG cells, PASG mRNA levels were reduced to less than 40% compared to levels in uninfected TIG-7 or TIG-7/shGFP cells (Fig. 2A and B). PASG protein levels in TIG-7/shPASG cells were also decreased to almost 20% as compared to that in TIG-7/shGFP cells (Fig. 2C), demonstrating that expression of the PASG shRNA can efficiently suppress the targeted gene in TIG-7 cells.
Figure 1.
Sequences of the predicted short hairpin transcripts specific to PASG and GFP (as a control) mRNA (A) and experimental scheme for retrovirus infection into TIG-7 cells (B).
Figure 2.
Reduced expression of PASG in PASG shRNA gene-transduced TIG-7 cells. Total RNA samples were prepared from uninfected, PASG shRNA gene or GFP shRNA gene-transduced cells and PASG mRNA levels were determined by RT-PCR (A) and Northern blot hybridization (B) analysis as described in Materials and Methods. In (A) the housekeeping gene GAPDH was used as an internal control. In (B) GAPDH signals and ethidium bromide-staining pattern of rRNA were used as a loading control. (C) nuclear protein samples were separated by SDS-PAGE and PASG protein levels were determined by Western blot analyses. Signals of lamin A/C and actin were used as loading controls.
shRNA inhibition of PASG expression does not affect growth rate or replicative life-span of TIG-7 cells
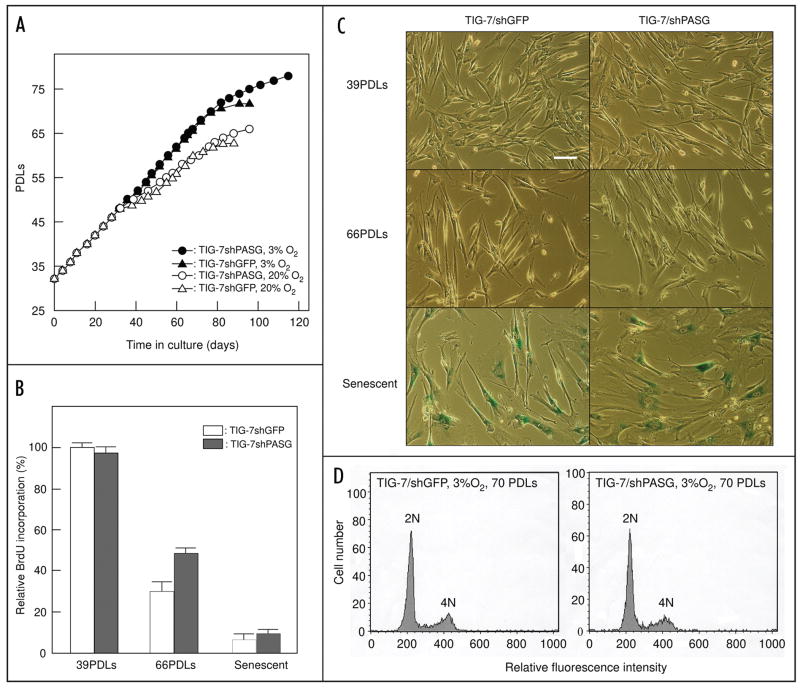
We repeatedly subcultured TIG-7/shPASG and TIG-7/shGFP cells to determine whether knockdown of PASG expression affects the growth rate and/or shortens replicative life-span. In addition, we compared growth under low (3%) or ambient (20%) oxygen conditions. Similar to previous reports, culture under low oxygen conditions extends the life-span of both TIG-7/shPASG and TIG-7/shGFP cells. However, decreased PASG expression did not affect either the rate of growth or the replicative life-span (Fig. 3A). The growth of TIG-7/shPASG and TIG-7/shGFP cells was similar in ambient or low oxygen conditions up to 48 PDLs. Under ambient oxygen conditions, cells cultured for more than 48 PDLs exhibited gradual retardation of population growth; cells stopped dividing when they reached 66 and 63 PDLs in TIG-7/shPASG and TIG-7/shGFP cells, respectively. In low oxygen conditions, the rate of population growth was unchanged up to 64 PDLs, then slowed gradually followed by senescence at 78 and 72 PDLs in TIG-7/shPASG and TIG-7/shGFP cells, respectively. Similarity of the replicative rate between TIG-7/shPASG and TIG-7/shGFP cells was additionally confirmed by cell proliferation analysis based on BrdU incorporation (Fig. 3B) and senescence-associated β-galactosidase assay (Fig. 3C). Further, there was no significant alteration in chromosome aneuploidy or content in TIG-7/shPASG compared to the TIG-7/shGFP control cells (Fig. 3D).
Figure 3.
Cellular life-span of TIG-7/shPASG and TIG-7/shGFP control cells. (A) Population Growth analysis. TIG-7/shPASG (circles) or TIG-7/shGFP (triangles) cells were cultured under either 3% (solid symbols) or 20% oxygen (open symbols) until reaching senescence. The experiments were started from 32 PDLs. (B) BrdU incorporation analysis. Cells cultured under 3% oxygen at the indicated PDLs were labeled with BrdU (10 μM) for 24 hours. The amounts of incorporated BrdU were determined as described in Materials and Methods. The level of BrdU incorporation was expressed relative to that of TIG-7/shGFP control cells at 39 PDLs. Values are the mean ± S. D. of triplicates. (C) Morphology and expression of senescence-associated β-galactosidase. Cells were cultured under 3% oxygen and β-galactosidase assay was performed at indicated PDLs. Bar, 100 μm. PDLs of senescent TIG-7/shGFP and TIG-7/shPASG cells in (B and C) were 72 and 78, respectively. (D) Aneuploidy was not induced in TIG-7/shPASG cells. Cells at 70 PDLs cultured under 3% oxygen were analyzed as described in Materials and Methods.
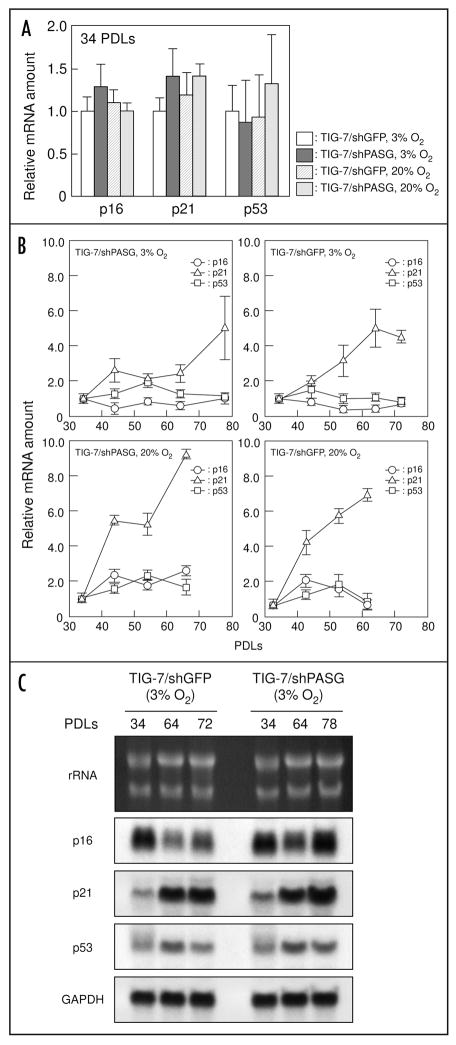
We further analyzed the RNA expression of three senescence-related genes, p16, p21 and p53 by real-time PCR. At 34 PDLs, they were expressed at comparable levels in TIG-7/shPASG and TIG-7/shGFP control cells cultured both 3% and 20% oxygen conditions (Fig. 4A). In addition, a gradual increase in p21 mRNA expression was observed during repetitive passages (Fig. 4B). This was reconfirmed by Northern blot hybridization analysis (Fig. 4C). It is noted that rate of the increase of p21 in the cells cultured under low oxygen conditions was lower than that under ambient oxygen conditions. These results suggest that decreased expression of PASG does not induce premature senescence in this somatic cell culture system.
Figure 4.
mRNA expression levels of p16, p21 and p53 gene in TIG-7/shPASG and TIG-7/shGFP control cells. (A and B), quantification of p16, p21 and p53 gene expression was performed by real-time PCR as described in Materials and Methods. (A), RNA samples from the cells at 34 PDLs were analyzed and the mRNA levels of p16, p21 and p53 were expressed relative to that of TIG-7/shGFP control cells cultured under 3% oxygen. (B), changes in mRNA levels of p16, p21 and p53 during the passage of TIG-7/shPASG and TIG-7/shGFP control cells. mRNA levels at indicated PDLs were expressed relative to that at 34 PDLs. Values are the mean ± S.D. of triplicates. (C), Northern blot hybridization. Indicated RNA samples were separated on agarose electrophoresis and probed with p16, p21 and p53 cDNA. GAPDH signals and ethidium bromide-staining pattern of rRNA were used as loading controls.
Inhibition of PASG expression enhances DNA demethylation in TIG-7 cells
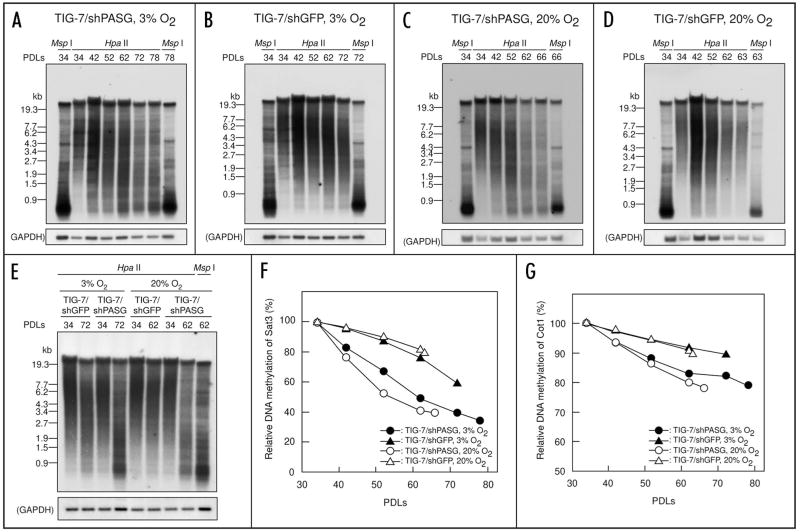
We used Southern blot analysis to determine relative methylation levels of Sat3 sequences, a classical satellite enriched in heavily methylated constitutive heterochromatin regions of human chromosome 1, 9 and 16, during the passages of TIG-7/shPASG and TIG-7/shGFP cells (Fig. 5). When digested with Hpa II, which cuts only unmethylated DNA, the size of DNA fragments containing the probe sequence decreased with increase in PDLs, indicative of gradual demethlyation as previously reported.23 We also assessed the methylation levels of additional, repetitive genomic sequences by re-hybridizing the membranes with a human Cot-1 DNA probe. Relative methylation levels of Sat3 and Cot-1 DNA were calculated as described in Materials and Methods and plotted against the PDLs (Fig. 5F and G). The rate of demethylation of both Sat3 and highly repetitive sequences as assessed by Hpa II digestion was faster in TIG-7/shPASG cells than that in TIG-7/shGFP cells at both ambient and low oxygen conditions. However, ambient versus low oxygen tension did not affect the rate of demethylation. When digested with Msp I, which is a methylation insensitive isoschizomer of Hpa II, no difference in the DNA samples from young and senescent cells was observed (Fig. 5). In both TIG-7/shPASG and TIG-7/shGFP control cells, the rate of DNA demethylation at Sat3 sequences was faster than that in the Cot-1 repetitive sequences, as previously described.23 Moreover, the rate of demethylation at both the Sat3 and Cot-1 sequences was approximately two times faster in TIG-7/shPASG cells than in TIG-7/shGFP cells, irrespective of oxygen growth conditions.
Figure 5.
Accelerated DNA demethylation at satellite 3 and highly repetitive (Cot 1) DNA sequence during passages in TIG-7/shPASG cells. (A–E), autoradiograms probed with satellite 3 sequence. Genomic DNA samples prepared from the transduced cells at the PDLs indicated were digested with Hpa II or Msp I, resolved in 1% agarose gel, and subjected to Southern blotting analysis using a 32P-labeled oligonucleotide for satellite 3. The membranes were re-hybridized with 32P-labeled GAPDH sequence as a loading control. (A) TIG-7/shPASG cells cultured under 3% oxygen. (B) TIG-7/shGFP cells cultured under 3% oxygen. (C) TIG-7/shPASG cells cultured under 20% oxygen. (D) TIG-7/shGFP cells cultured at 20% oxygen. (E) DNA samples from TIG-7/shPASG and TIG-7/shGFP control cells were analyzed on the same blot for direct comparison of DNA methylation. (F and G) relative DNA methylation levels in the satellite 3 (F) and the general repetitive (Cot-1) DNA (G) during the passage. The methylation levels were determined from autoradiograms and expressed relative to that of the cells at 34 PDLs (3 days after of initial culture) as described in Materials and Methods.
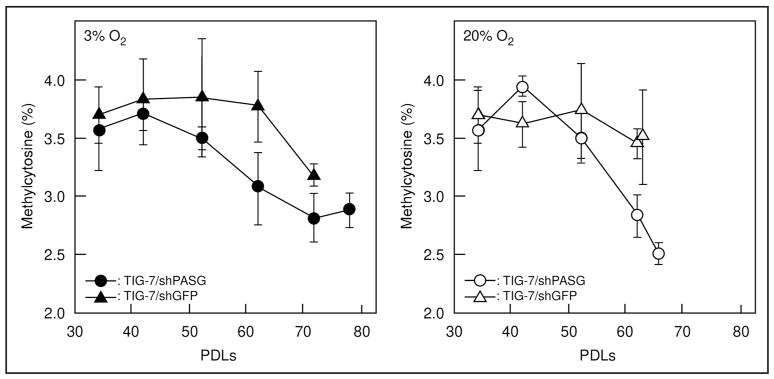
We further analyzed total 5-methylcytosine content in DNA samples by liquid chromatography followed by tandem mass spectrometry to determine the methylcytosine content of total DNA during culture (Fig. 6). Consistent with observations of Sat3 and Cot-1 DNA methylation, a more rapid decrease of methylcytosine content was observed in the TIG-7/siPASG cells compared to the control TIG-7/siGFP cells at both ambient and low oxygen conditions (Fig. 6). At ambient oxygen condition, where changes in methylation are most apparent, no difference in methylcytosine content was observed compared to early passage (42 PDLs) TIG-7/siPASG versus TIG-7/siGFP (3.9% versus 3.6%, respectively, p = 0.23). By passage 62, TIG-7/siPASG cells contained significantly less methylated DNA than control treated cells (2.8% versus 3.9%, respectively, p = 0.032). Methylcytosine content by 62 PDLs is nearly 30% lower in TIG-7/siPASG cells than in control treated cells, a result similar to that reported for PASG knock-out mice.18 These results support the conclusion that decreased PASG expression leads to accelerated DNA demethylation during culture of TIG-7 cells.
Figure 6.
Change in methylcytosine content of total genomic DNA during the passage. The rate of methylcytosine content was determined by LC-MS analysis as described in Materials and Methods. Left and right panels represent results when the cells were cultured under 3% and 20% oxygen, respectively. Values are means ± S. D. of four independent results.
Culture in low oxygen does not affect the rate of DNA demethylation during the passage of TIG-7 cells
The rate of DNA demethylation in cells cultured in low versus ambient oxygen conditions was also compared to determine whether oxygen stress affects maintenance of DNA methylation. No statistically significant changes in the rate of DNA demethylation during culture under low oxygen conditions were observed in either TIG-7/shPASG or TIG-7/shGFP cells (Figs. 5F and G and 6).
Neither knockdown of PASG nor culture in low oxygen affects telomere shortening in of TIG-7 cells
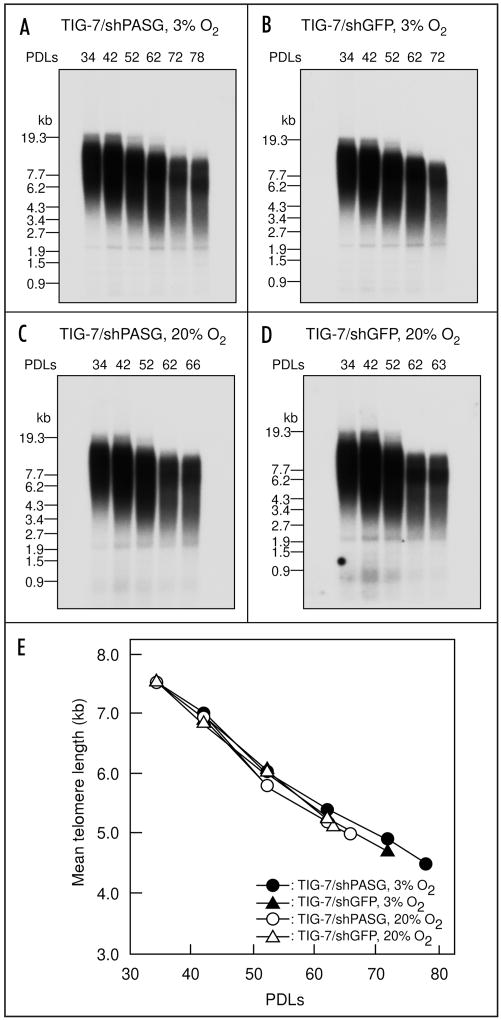
Telomere shortening during culture was analyzed with the same DNA samples used for methylation analysis. As shown in Figure 7, the rate of telomere shortening was similar between TIG-7/shPASG cells and TIG-7/shGFP cells, suggesting that PASG is not involved in maintenance of telomere length. In addition, we observed similar telomere shortening rates in these cells both under low and ambient oxygen conditions (Fig. 7).
Figure 7.
Neither PASG siRNA gene transduction nor oxygen concentration in culture affects the rate of telomere shortening during the passage. The same DNA samples used in Figure 4 were digested with Alu I, Cfo I, Hae III, Hinf I, Msp I and Rsa I, resolved in 0.5% agarose gel, transferred to nylon membrane, and probed with a 32P-labeled oligonucleotide for (TTAGGG)3. (A) TIG-7/shPASG cells cultured under 3% oxygen. (B) TIG-7/shGFP cells cultured under 3% oxygen. (C) TIG-7/shPASG cells cultured under 20% oxygen. (D) TIG-7/shGFP cells cultured under 20% oxygen. (E) mean telomere length analysis. Signals with (TTAGGG)3 were quantified and mean telomere length in each DNA sample was calculated as described in Materials and Methods.
Discussion
Involvement of DNA hypomethylation in premature senescence has been demonstrated in mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) from PASG knockout mice and from Dnmt3b knockout mice.18,19,24 Aneuploidy was also increased in MEFs in culture from these embryonic knockout models, demonstrating the potential involvement of genomic instability in premature senescence, possibly secondary to hypomethylation of the genome. However, it is unclear whether gradual demethylation of DNA during somatic cell division is directly involved in senescence, because DNA in MEFs from PASG and Dnmt3b knockout mice have gone through embryogenesis with a hypomethylated genome.
In our current study, we demonstrated that decreased PASG expression in TIG-7 cells results in accelerated loss of DNA methylation over time in culture. Expression of PASG protein in TIG-7/shPASG cells was decreased to less than 20% compared to control TIG-7/shGFP cells. The growth rate of TIG-7/shPASG cells was similar to that of control cells. Methylation levels in both heavily methylated Sat3 sequence and Cot-1 repetitive sequences decreased approximately two times faster in TIG-7/shPASG compared to control TIG-7/shGFP cells. In addition, the total 5-methylcytosine content of genomic DNA showed a greater decrease TIG-7/shPASG during culture compared to control TIG-7/shGFP cells. These results demonstrate the likely involvement of PASG in maintenance of DNA methylation. Based on analysis of the methylation status of an episomal DNA vector, Zhu et al. reported that, in contrast to maintenance of previously methylated DNA, the acquisition of DNA methylation (de novo methylation) requires PASG (LSH).22 They further demonstrated interaction of LSH with de novo DNA methyltransferases, DNMT3A and DNMT3B, but not with a maintenance DNA methyltransferase, DNMT1, in P19 mouse embryonic carcinoma cells. A possible explanation for this apparent discrepancy may be due to the different experimental systems used. In our study, we used mortal, somatic cells to determine methylation status of endogenous DNA, whereas Zhu et al. used an immortalized mouse cell line and examined methylation of an exogenous, viral DNA. In addition, data showing PASG (LSH) interaction with DNMT1 further support a role for PASG in maintenance methylation.24
Unlike the observations made in hypomorphic knockout mice,18 knockdown of PASG expression did not shorten the replicative lifespan of TIG-7 primary cells compared to that of control cells despite accelerated genomic demethylation in the former. When senescence occurred, DNA methylation levels of Sat3 sequences in TIG-7/shPASG cells were approximately half those observed in TIG-7/shGFP control cells, demonstrating that PASG-dependent DNA demethylation does not trigger induction of senescence in these human fibroblasts.
There is currently no explanation why decreased expression of PASG induces premature senescence in MEFs but not in TIG-7 fibroblasts. One possibility is that different genomic regions and, thus, molecular pathways, are sensitive to alteration as a result of abnormal methylation during early embryonic development compared to somatic cells. Differences in imprinted loci have, for instance, been observed in Lsh knockout mice compared to wild type controls, which may play a more important role during embryonic epigenetic patterning than in differentiated somatic cells.25 It is also possible that TIG-7/shPASG cells undergo senescence in culture before their DNA methylation levels decrease below a critical point sufficient to trigger a replicative senescence program. Also, since TIG-7/shPASG cells retain 10–20% of PASG protein compared to PASG−/− MEFs, another possibility is that residual PASG in TIG-7/shPASG cells may allow them to maintain their growth and escape premature senescence, despite similar levels of genomic DNA methylation, thus suggesting possible other functions of PASG.
Alternatively, mouse cells might be more sensitive to decreased PASG expression than human cells. Chromosomes of Mus musculus are telocentric with long, pericentromeric heterochromatic regions compared to human chromosomes which typically have a short and long arm separated by a centromere. In mice, PASG (LSH) protein localizes in part to pericentromeric heterochromatin, where it is thought to contribute to normal centromere function, such as spindle formation and chromosome segregation, during mitosis.21
A relationship between genomic hypomethylation and senescence has been demonstrated using demethylating agents leading to demethylation and activation of cell cycle checkpoints, such as p21.15 However, it could be argued that the use of such agents might also lead to DNA damage, followed by cell cycle arrest and DNA repair responses. In addition, conditional knockout of Dnmt1 leads to p53-mediated apoptosis.26 A sharp decline of DNA methylation was also observed soon after the treatment with demethylating agents or in the conditional knockout of Dnmt1.15,26 Our results show that gradual loss of DNA methylation during cell replication due to decreased PASG expression had no significant effect on inducing senescence in normal somatic cells, despite the significant decrease in DNA methylation. Therefore, we would suggest that acute demethylation by interruption of DNA methyltransferase activity likely results in different patterns of genomic hypomethylation, possibly related in part to DNA damage responses, and cellular consequences than more gradual loss of methylation.
As reported previously, we also observed that culture under low oxygen extended the life-span of human cells. However, we did not observe a difference in either the rate of demethylation or telomere shortening between low and ambient oxygen conditions. These results are in contrast with previous reports that oxidative damage events contribute to telomere shortening as well as chromosomal end-replication.27 The reasons underlying these differing observations are unclear, but further studies concerning the effect of oxidative stress in cells with decreased PASG expression and hypomethylated genomes may shed light on potential adaptive mechanisms.
The results presented here demonstrate a role for PASG in the maintenance of genomic methylation in somatic cells but suggest that alterations of this genomic methylation function may not be related to the induction of the replicative senescence phenotype. Mutations and/or altered expression in chromatin remodeling proteins have been causally linked or associated with a variety of human cancers.28–35 We have also identified an in-frame deletion variant of the highly conserved STRAGGL domain of PASG in human acute leukemias36 and have shown that this alteration in PASG is associated with a poorer outcome and complex karyotypes in acute myelogenous leukemia (manuscript in preparation). We would therefore suggest that mutations and functionally altered forms of PASG occurring in somatic cells, particularly those with a high proliferative rate, such as hematopoietic progenitors, may lead to genomic hypomethylation, chromosome instability and predisposition to malignant transformation or altered cancer cell behavior. Further studies designed to determine the precise mechanisms of action of wild-type and altered forms of PASG (LSH) in embryonic as wells as post-natal somatic cells may provide an important link to understanding the relationship between early hypomethylation events, senescence and the development of cancer.
Materials and Methods
Plasmid construction
pSUPER.retro-shPASG and a control construct, pSUPER.retro-shGFP, were generated by cloning annealed oligonucleotides targeting PASG (5′c cGA TAG ATT GTC TGA AAC GGt tca aga gaC CGT TTC AGA CAA TCT ATC ttt ttg gaaa-3′ and 5′-agc ttt tcc aaa aaG ATA GAT TGT CTG AAA CGG tct ctt gaa CCG TTT CAG ACA ATC TAT Cggg-3′) and GFP (5′-gat ccc cGC AAG CTG ACC CTG AAG TTC ttc aag aga GAA CTT CAG GGT CAG CTT GCt ttt tgg aaa-3′ and 5′-agc ttt tcc aaa aaG CAA GCT GAC CCT GAA GTT Ctc tct tga aGA ACT TCA GGG TCA GCT TGC ggg-3′) into the Bgl II and Hind III of pSUPER.retro (OligoEngine, Seattle, WA, USA),37 downstream of the H1 promoter. The 19-nucleotide PASG target sequences and 20-nucleotide GFP target sequences are indicated in capitals in the oligonucleotide sequences. The predicted sequences of the short hairpin transcript of PASG shRNA and GFP shRNA are shown in Figure 1A.
Cell culture and retrovirus infection
The human embryonic lung fibroblast cell line, TIG-7 was obtained from the Japanese Collection of Research Bioresources Cell Bank (Osaka, Japan). Phoenix-Ampho packaging cells for retrovirus production (www.stanford.edu/group/nolan/retroviral_systems/retsys.html) were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (Manassas, VA, USA). All cell lines were cultured in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s Medium (Nissui Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) supplemented with 10% fetal calf serum (Roche Diagnostics GmbH, Mannheim, Germany) and 60 μg/ml anamycin (Sigma Chemical Inc., St. Louis, MO, USA). Phoenix-Ampho cells were maintained at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere under 5% CO2/95% air. Untransduced and shRNA-transduced TIG-7 cells were maintained at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere under either 5% CO2/95% air (20% or ambient oxygen condition) or 3% O2/5% CO2/95% N2 (3% or low oxygen condition). A multi-gas incubator (Model MCO-18M, Sanyo Electric Co., Ltd. Osaka, Japan) was used when cultured at 3% oxygen condition.
Amphotropic retroviral supernatants were produced by transfection of each pSUPER.retro shRNA-expressing vector into Phoenix-Ampho packaging cells using Lipofectamine™ 2,000 reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA). Twenty-four hours after transfection, the culture medium was changed to fresh medium and cells were incubated for a further 24 hours prior to collection and filtering viral supernatant through a 0.45-μM filter.
Transduction of shRNA gene with the viral supernatants was performed according to the experimental scheme in Figure 1B. Day 0 denotes placement of cells in the final experimental culture conditions (20% or 3% O2) after antibiotic selection of transduced cells. Confluent TIG-7 cells at 26 population doubling levels (PDLs) were subcultured at a ratio of 1:4 (day −9). On the next day (day −8), cells were infected with the viral supernatants in the presence of polybrene (4 μg/ml) for 5 hours then allowed to recover for 48 hours in fresh medium. The infected cells were split into four plates on day −6. Selection in puromycin at 0.5 μg/ml was begun on day −5, twenty-four hours after re-splitting. At day 0, transduced had cells reached confluence, were split again at a ratio of 1:4 and were cultured in either 3% or 20% oxygen condition until reaching senescence. When the growth rate of the cells became slower during later times in culture, cells were passaged at a ratio of 1:2.
Measurement of bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) incorporation and senescence-associated β-galactosidase assay
Quantitation of cell proliferation based on the measurement of BrdU incorporation during DNA synthesis was performed using Cell Proliferation ELISA, BrdU (colorimetric) (Roche Diagnostics GmbH, Mannheim, Germany) according to the manufacture’s instructions. Briefly, 5 × 103 cells were cultured in a 96-well tissue culture plate and incubated for 24 hours. BrdU was then added to the cells at the final concentration of 10 μM and cultured for additional 24 hours. The amount of incorporated BrdU in newly synthesized cellular DNA was quantitated using anti-BrdU monoclonal antibody conjugated with peroxidase and tetramethyl-benzidine. Senescence-associated β-galactosidase assay was performed as described previously.23
FACS analysis of DNA content
Cells harvested by trypsinization and washed with phosphate buffered saline (PBS) were resusupened in staining solution containing 10 mM sodium phosphate (pH 7.4), 150 mM NaCl, 0.2% (v/v) Triton X-100, 0.2 mg/ml DNase-free RNase A and 50 μg/ml propidium iodide. Then, DNA content of the cells was determined by FACSCalibur™ Flow Cytometry System (Becton Dickinson, San Jose, CA, USA) using the Cell-Quest program.
RT-PCR analysis and northern blot analysis
Total RNA was prepared from retrovirus-shRNA transduced cells at 34 PDLs using using TRIZOL® Reagent (Invitrogen) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. After treatment with DNase I (Invitrogen), first-strand cDNA synthesis was carried out using SuperScript First-Strand Synthesis System for RT-PCR (Invitrogen) with 2 μg total RNA and 0.5 μg oligo(dT). PCR was performed with 1 μl first-strand cDNA, 200 nM of primers, PCR buffer (10 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.3, 50 mM KCl, 1.5 mM MgCl2) and 1 unit of recombinant Taq DNA polymerase (TaKaRa Bio Inc., Shiga, Japan) in a total volume of 25 μl in a TP-400 thermal cycler (TaKaRa Bio Inc.,) as follows: initial denaturation at 95°C for 5 minutes followed by 17–31 cycles (indicated in Fig. 2) of 95°C for 30 seconds, 55°C for 30 seconds, and 72°C for 1 minute. The primers used were: PASG, 5′-TGC AGA TTC ATC CTG TGG TAA TCA-3′ and 5′-TGG TGC AGC ATA TGC AAT ACA TTC-3′; and for glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH), 5′-GAC CTC AAC TAC ATG GTC TAC ATG-3′ and 5′-TGT CGC TGT TGA AGT CAG AGG AGAC-3′. PCR products were visualized after electrophoresis in 1.5% agarose gel and ethidium bromide staining.
Northern blot hybridization was performed as described previously.23 Briefly, total RNA samples (20 μg per lane) prepared from cells were electrophoretically separated in a 1% formaldehyde-agarose gel. Following ethidium bromide staining, RNA was transferred to nylon membranes (Biodyne B, Pall Corporation, East Hills, NY, USA). The membranes were hybridized to PASG, p16, p21, p53 and GAPDH cDNA probes labeled with γ-32P-dCTP (SBP-205, Institute of Isotopes Co., Ltd., Budapest, Hungary) using BcaBEST™ random primed DNA-labeling kit (TaKaRa Bio Inc.,) at 42°C in a mixture consisting of 5xSSPE (0.9 M NaCl, 50 mM sodium phosphate, and 5 mM EDTA, pH 7.7), 50% formamide, 5xDen-haldt’s solution, 0.5% SDS, and 100 μg/ml herring testis DNA for 16 hours. The membranes were washed four times at 68°C in 2xSSPE and 0.5% SDS for 20 minutes and twice at 68°C in 0.2xSSPE plus 0.5% SDS for 20 minutes followed autoradiography.
Quantitative RT-PCR
The quantification of p16, p21 and p53 gene expression was performed by real-time PCR on an ABI Prism® 7,000 Sequence Detection System (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). Quantitative-PCR reactions were carried out in a total volume of 20 μL on 25 ng of cDNA using FastStart Universal Probe Master (ROX) (Roshe Diagnostics GmbH) and Universal ProbeLibrary assays designed with the ProbeFinder software (Roche Diagnostics). The primer sequences and Universal Probe numbers used are available upon request. ABI Prism® 7,000 Sequence Detection System was programmed to an initial step of 2 minutes at 50°C and 10 minutes at 95°C, followed by 40 cycles of 15 sec at 95°C and 1 minute at 60°C. GAPDH was used as the endogenous control gene. Analysis of relative gene expression was performed by the 2−ΔΔCt method.38
Western blot analysis
Cells at 45 PDLs were collected and re-suspended in nuclei preparation buffer (10 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.4, 5 mM MgCl2, 2 mM B-mercaptoethanol and 1 mM phenylmethylsulphonylfluoride). Cells were homogenized by passing through a 21 gage needle after the addition of 0.05 volume of 10% NP-40 and centrifuged at 700 g for 10 minutes. Pelleted nuclei were washed twice with nuclei preparation buffer, then re-suspended with TM-2 buffer (10 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.4, 2 mM MgCl2, 1 mM phenylmethylsulphonylfluoride). Proteins were quantified using the BCA protein assay kit (Pierce, Rockford, IL, USA).
Nuclear protein samples were separated on sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) polyacrylamide gels (10% acrylamide) and transferred to polyvinylidene difluoride membranes (Millipore, Bedford, Mass, USA). Detection of PASG, Lamin A/C and β-actin proteins was performed using mouse anti-Lsh at 1:1000 (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc., Santa Cruz, CA, USA), goat anti-Lamin A/C at 1:5000 (N-18) (Santa Cruz Biotechnology) and mouse anti-β-actin at 1:20,000 (MP Biomedicals, Inc., Aurora, OH, USA) monoclonal antibodies, respectively. The antigen-antibody complexes were detected by horseradish peroxidase-conjugated anti-mouse IgG (GE Healthcare UK Limited, Buckinghamshire, UK) or anti-goat IgG (Santa Cruz Biotechnology) and visualized using the ECL system (GE Healthcare UK Limited) following the manufacturer’s instructions. Relative protein quantification was performed using Multi Gauge Ver2.2 image analyzing software (Fuji Photo Film Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan).
Southern blot analysis
Genomic DNA samples were prepared using Blood & Cell Culture DNA Mini Kit (Qiagen K.K., Tokyo, Japan) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. The samples were digested with restriction endonucleases, resolved by agarose electrophoresis and transferred onto a nylon membrane as previously described.23 To determine methylation levels of satellite sequences and genomic DNA, CpG methylation-sensitive Hpa II and CpG methylation-insensitive isoschizomer Msp I were used.39 The membranes were hybridized at 37°C in a mixture containing 0.43 M sodium phosphate (pH 7.2), 7% SDS and 20 mM EDTA for 20 hours. The membrane was washed four times at 37°C with 2xSSC (300 mM NaCl and 30 mM trisodium citrate) containing 0.1% SDS and twice at 37°C with 0.1xSSC containing 0.1% SDS for 20 minutes and then exposed to an X-ray film at −80°C. Radioactive signal was quantified using an imaging analyzer BAS2500 (Fuji Photo Film) to analyze DNA methylation status and mean telomere length.
An oligonucleotide probe for satellite 3 (Sat3) sequences was prepared as described previously.23 To determine terminal restriction fragments containing telomere sequences, oligonucleotide was used as a probe. Oligonucleotide probes were end-(TTAGGG)3 labeled with γ-32P ATP (SBP-401, Institute of Isotopes Co., Ltd.) using T4 polynucleotide kinase (TaKaRa Bio Inc.,) at 37°C. Human 23 Cot-1 DNA (Invitrogen) and intron 2 sequence of the GAPDH were labeled with γ-32P dCTP using BcaBEST™ random primed DNA-labeling kit.
Calculation of DNA methylation status from southern blot analysis
DNA methylation status in the Sat3 sequences and Cot-1 DNA was determined by counting radioactivity following Southern blot analysis as described previously.23,39 For the Sat3 sequences, the activity of the total lane (A) and the region between the top and 2.9 kb (B) were counted for each lane and the ratio (B/A) was taken to represent a relative methylation level. For Cot-1 DNA, the activity of the total lane (A) and the region between 2.9 and 1.5 kb (B) were counted for each lane and the ratio (r = B/A) was calculated for Hpa II (rH) and Msp I (rM) digestions. The ratio R = rH/rM was calculated for each DNA sample and the DNA methylation level estimated as (1 − R), which theoretically ranged from 0 (fully demethylated) to 1 (fully methylated). In each case, the level was expressed relative to that of the cells at 34 PDLs.
Determination of methylcytosine content by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis
Determination of 5-methyl-cytidine content was carried out as previously described.40 Briefly, 10–20 ng of genomic DNA was re-suspended in 50 μl of high-performance liquid chromatography grade water and digested to near completion with nuclease P1 (Sigma Chemical Inc.), and treated with alkaline phosphatase. Separation and quantitation of 5-methylcytosine and cytosine was performed on an API 3000 LC/MS instrument (Applied Biosystems) fitted with a 250 × 2.00 mm, 5-μm C18 column. Fifteen μl of samples or standards (consisting of serial dilutions of 5-methylcytosine and cytosine in a buffer identical to samples) were injected in quadruplicate along with 250 μl/minute of a mobile phase profile consisting of 98% solution A (5 mM NH4OAc, 0.1% formic acid, pH ~3) and 2% solution B (90% acetonitrile) for 4 minutes, followed by a linear ramping to 60% solution A and 40% solution B in 1 minutes, then ramping to 98% solution A and 2% solution B in 1 minute, and finally maintaining this composition isocratically for the final 5 minutes. Cytosine was monitored in MRM mode with the ion pair 227/112, while 5-methylcytosine was monitored in MRM mode with the ion pair 242/126. The quantity of each analyte was calculated with reference to the standard dilution series, and the ratio of 5-methylcytosine to total cytosine (5-methylcytosine plus cytosine) was calculated.41
Determination of mean telomere length
Mean telomere length of the cells in each PDLs was determined by analyzing signals obtained by Southern blotting with probe using (TTAGGG)3 the program Telo-run (www.swmed.edu/home_pages/cellbio/shay-wright/research).
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Science and Culture of Japan (T.S.) as well as grants from the Children’s Cancer Foundation (R.J.A.), the Lyles Parachini Fund (R.J.A.), the Michael Corb Fund (R.J.A.), the Michael Garil Leukemia Survivors Program (R.J.A.), Alex’s Lemonade Stand Foundation (J.E.F.), ASCO Foundation (J.E.F.), NIH grant CA120535 (R.J.A.) and a Department of Defense Grant (R.J.A.). Dr. Arceci is a recipient of the King Fahd Endowed Chair in Pediatric Oncology at Johns Hopkins.
Abbreviations
- PASG
proliferation associated SNF2-like gene
- LSH
Lymphocyte Specific Helicase
- DNMT
DNA methyltransferase
- aza-C
5-azacytidine
- aza-dC
5-azadeoxycytidine
- PDLs
population doubling levels
- Sat3
satellite 3
- GAPDH
glycelaldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase
- MEFs
mouse embryonic fibroblasts
References
- 1.Hayflick L. The limited in vitro lifetime of human diploid cell strains. Exp Cell Res. 1965;37:614–36. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(65)90211-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Campisi J. The biology of replicative senescence. Eur J Cancer. 1997;33:703–9. doi: 10.1016/S0959-8049(96)00058-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Stanulis-Praeger BM. Cellular senescence revisited: a review. Mech Ageing Dev. 1987;38:1–48. doi: 10.1016/0047-6374(87)90109-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Harley CB. Telomere loss: mitotic clock or genetic time bomb? Mutat Res. 1991;256:271–82. doi: 10.1016/0921-8734(91)90018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Harley CB, Vaziri H, Counter CM, Allsopp RC. The telomere hypothesis of cellular aging. Exp Gerontol. 1992;27:375–82. doi: 10.1016/0531-5565(92)90068-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Herbig U, Jobling WA, Chen BP, Chen DJ, Sedivy JM. Telomere shortening triggers senescence of human cells through a pathway involving ATM, p53 and p21CIP1, but not p16INK4a. Mol Cell. 2004;14:501–13. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(04)00256-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Hoal-van Helden EG, van Helden PD. Age-related methylation changes in DNA may reflect the proliferative potential of organs. Mutat Res. 1989;219:263–6. doi: 10.1016/0921-8734(89)90027-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Wilson VL, Jones PA. DNA methylation decreases in aging but not in immortal cells. Science. 1983;220:1055–7. doi: 10.1126/science.6844925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Wilson VL, Smith RA, Ma S, Cutler RG. Genomic 5-methyldeoxycytidine decreases with age. J Biol Chem. 1987;262:9948–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Razin A. CpG methylation, chromatin structure and gene silencing-a three-way connection. EMBO J. 1998;17:4905–8. doi: 10.1093/emboj/17.17.4905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Constancia M, Pickard B, Kelsey G, Reik W. Imprinting mechanisms. Genome Res. 1998;8:881–900. doi: 10.1101/gr.8.9.881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Singhal RP, Mays-Hoopes LL, Eichhorn GL. DNA methylation in aging of mice. Mech Ageing Dev. 1987;41:199–210. doi: 10.1016/0047-6374(87)90040-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Fairweather DS, Fox M, Margison GP. The in vitro lifespan of MRC-5 cells is shortened by 5-azacytidine-induced demethylation. Exp Cell Res. 1987;168:153–9. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(87)90424-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Holliday R. Strong effects of 5-azacytidine on the in vitro lifespan of human diploid fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res. 1986;166:543–52. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(86)90499-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Young JI, Smith JR. DNA methyltransferase inhibition in normal human fibroblasts induces a p21-dependent cell cycle withdrawal. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:19610–6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M009470200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Zhu WG, Hileman T, Ke Y, Wang P, Lu S, Duan W, Dai Z, Tong T, Villalona-Calero MA, Plass C, Otterson GA. 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine activates the p53/p21Waf1/Cip1 pathway to inhibit cell proliferation. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:15161–6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M311703200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Dennis K, Fan T, Geiman T, Yan Q, Muegge K. Lsh, a member of the SNF2 family, is required for genome-wide methylation. Genes Dev. 2001;15:2940–4. doi: 10.1101/gad.929101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Sun LQ, Lee DW, Zhang Q, Xiao W, Raabe EH, Meeker A, Miao D, Huso DL, Arceci RJ. Growth retardation and premature aging phenotypes in mice with disruption of the SNF2-like gene, PASG. Genes Dev. 2004;18:1035–46. doi: 10.1101/gad.1176104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Dodge JE, Okano M, Dick F, Tsujimoto N, Chen T, Wang S, Ueda Y, Dyson N, Li E. Inactivation of Dnmt3b in mouse embryonic fibroblasts results in DNA hypomethylation, chromosomal instability, and spontaneous immortalization. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:17986–91. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M413246200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Fan T, Yan Q, Huang J, Austin S, Cho E, Ferris D, Muegge K. Lsh-deficient murine embryonal fibroblasts show reduced proliferation with signs of abnormal mitosis. Cancer Res. 2003;63:4677–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Yan Q, Cho E, Lockett S, Muegge K. Association of Lsh, a regulator of DNA methylation, with pericentromeric heterochromatin is dependent on intact heterochromatin. Mol Cell Biol. 2003;23:8416–28. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.23.8416-8428.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Zhu H, Geiman TM, Xi S, Jiang Q, Schmidtmann A, Chen T, Li E, Muegge K. Lsh is involved in de novo methylation of DNA. EMBO J. 2006;25:335–45. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Suzuki T, Fujii M, Ayusawa D. Demethylation of classical satellite 2 and 3 DNA with chromosomal instability in senescent human fibroblasts. Exp Gerontol. 2002;37:1005–14. doi: 10.1016/s0531-5565(02)00061-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Myant K, Stancheva I. LSH cooperates with DNA methyltransferases to repress transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 2008;28:215–26. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01073-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Fan T, Hagan JP, Kozlov SV, Stewart CL, Muegge K. Lsh controls silencing of the imprinted Cdkn1c gene. Development. 2005;132:635–44. doi: 10.1242/dev.01612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Jackson-Grusby L, Beard C, Possemato R, Tudor M, Fambrough D, Csankovszki G, Dausman J, Lee P, Wilson C, Lander E, Jaenisch R. Loss of genomic methylation causes p53-dependent apoptosis and epigenetic deregulation. Nat Genet. 2001;27:31–9. doi: 10.1038/83730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Forsyth NR, Evans AP, Shay JW, Wright WE. Developmental differences in the immortalization of lung fibroblasts by telomerase. Aging Cell. 2003;2:235–43. doi: 10.1046/j.1474-9728.2003.00057.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Gunduz E, Gunduz M, Ouchida M, Nagatsuka H, Beder L, Tsujigiwa H, Fukushima K, Nishizaki K, Shimizu K, Nagai N. Genetic and epigenetic alterations of BRG1 promote oral cancer development. Int J Oncol. 2005;26:201–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Medina PP, Cespedes MS. Involvement of the chromatin-remodeling factor BRG1/SMARCA4 in human cancer. Epigenetics. 2008;3:64–8. doi: 10.4161/epi.3.2.6153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Medina PP, Romero OA, Kohno T, Montuenga LM, Pio R, Yokota J, Sanchez-Cespedes M. Frequent BRG1/SMARCA4-inactivating mutations in human lung cancer cell lines. Hum Mutat. 2008;29:617–22. doi: 10.1002/humu.20730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Modena P, Lualdi E, Facchinetti F, Galli L, Teixeira MR, Pilotti S, Sozzi G. SMARCB1/INI1 tumor suppressor gene is frequently inactivated in epithelioid sarcomas. Cancer Res. 2005;65:4012–9. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-3050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Reisman DN, Sciarrotta J, Wang W, Funkhouser WK, Weissman BE. Loss of BRG1/BRM in human lung cancer cell lines and primary lung cancers: correlation with poor prognosis. Cancer Res. 2003;63:560–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Sansam CG, Roberts CW. Epigenetics and cancer: altered chromatin remodeling via Snf5 loss leads to aberrant cell cycle regulation. Cell Cycle. 2006;5:621–4. doi: 10.4161/cc.5.6.2579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Vries RG, Bezrookove V, Zuijderduijn LM, Kia SK, Houweling A, Oruetxebarria I, Raap AK, Verrijzer CP. Cancer-associated mutations in chromatin remodeler hSNF5 promote chromosomal instability by compromising the mitotic checkpoint. Genes Dev. 2005;19:665–70. doi: 10.1101/gad.335805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Yamamichi N, Inada K, Ichinose M, Yamamichi-Nishina M, Mizutani T, Watanabe H, Shiogama K, Fujishiro M, Okazaki T, Yahagi N, Haraguchi T, Fujita S, Tsutsumi Y, Omata M, Iba H. Frequent loss of Brm expression in gastric cancer correlates with histologic features and differentiation state. Cancer Res. 2007;67:10727–35. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-2601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Lee DW, Zhang K, Ning ZQ, Raabe EH, Tintner S, Wieland R, Wilkins BJ, Kim JM, Blough RI, Arceci RJ. Proliferation-associated SNF2-like gene (PASG): a SNF2 family member altered in leukemia. Cancer Res. 2000;60:3612–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Brummelkamp TR, Bernards R, Agami R. Stable suppression of tumorigenicity by virus-mediated RNA interference. Cancer Cell. 2002;2:243–7. doi: 10.1016/s1535-6108(02)00122-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCt Method. Methods. 2001;25:402–8. doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Vilain A, Bernardino J, Gerbault-Seureau M, Vogt N, Niveleau A, Lefrancois D, Malfoy B, Dutrillaux B. DNA methylation and chromosome instability in lymphoblastoid cell lines. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 2000;90:93–101. doi: 10.1159/000015641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Yegnasubramanian SHM, Zhang Y, Gurel B, Cornish TC, Wu Z, Irizarry RL, Morgan JD, Hicks J, DeWeese TL, Isaacs WB, Bova GS, De Marzo AM, Nelson WG. DNA hypomethylation arises later in prostate cancer progression than CpG island hypermethylation and contributes to metastatic tumor heterogeneity. Cancer Res. 2008 doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-6088. In press. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Agoston AT, Argani P, Yegnasubramanian S, De Marzo AM, Ansari-Lari MA, Hicks JL, Davidson NE, Nelson WG. Increased protein stability causes DNA methyltransferase 1 dysregulation in breast cancer. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:18302–10. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M501675200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]