Abstract
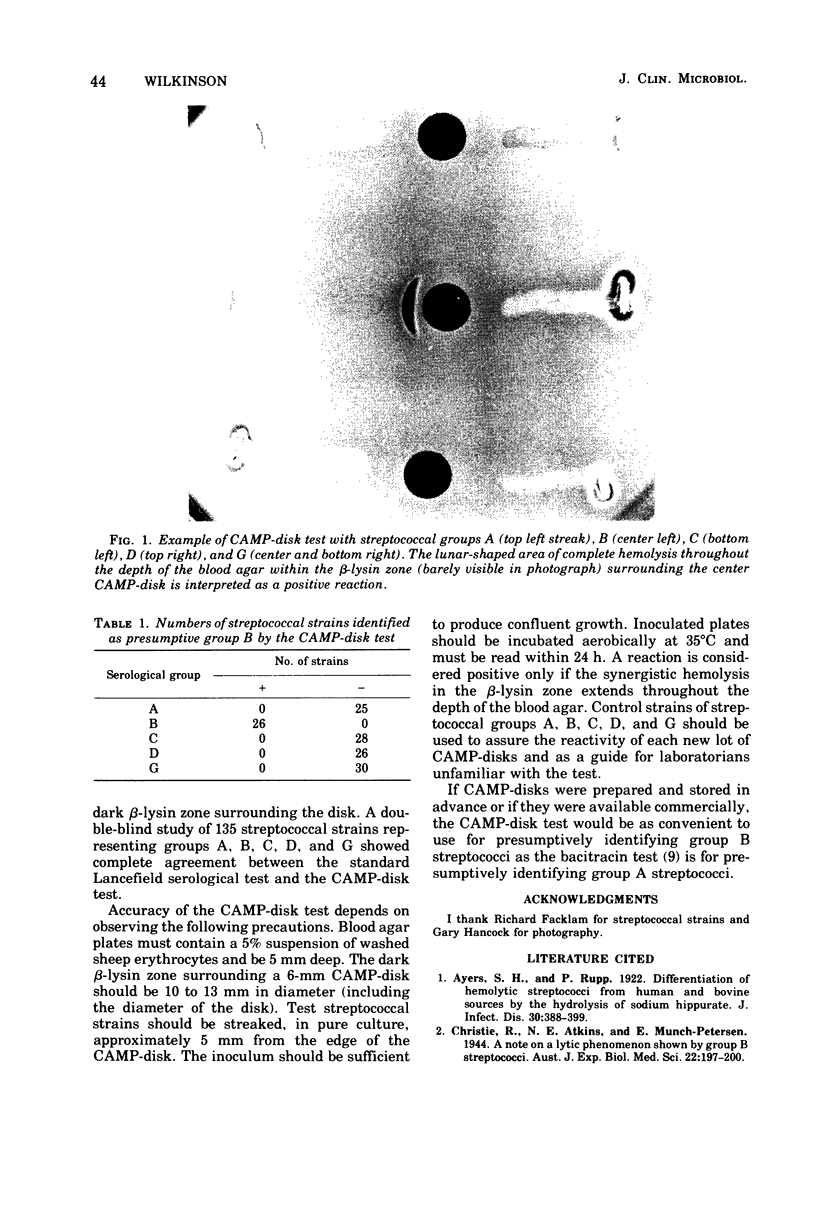
The modification of the CAMP test for goup B streptococci involved substituting a paper disk impregnated with partially purified beta-hemolysin for the staphylococcal culture that was the source of beta-hemolysin in the original test. The disk is placed onto a sheep blood agar plate beside the streak of Streptococcus being tested. The plate is then incubated aerobically at 35 degrees C. A positive reaction consists of a lunar-shaped clear zone that appears within 24 h in the dark beta-hemolysin zone surrounding the disk. A double-blind study of 135 randomly coded streptococcal isolates showed complete agreement between the CAMP-disk test and the standard Lancefield precipitin test. All group B streptococci tested had positive reactions, and all strains tested from streptococcal groups A, C, D, and G were negative. The CAMP-disk test is a simple and convenient way to identify presumptively group B streptococci.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Darling C. L. Standardization and evaluation of the CAMP reaction for the prompt, presumptive identification of Streptococcus agalactiae (Lancefield group B) in clinical material. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Feb;1(2):171–174. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.2.171-174.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Facklam R. R., Padula J. F., Thacker L. G., Wortham E. C., Sconyers B. J. Presumptive identification of group A, B, and D streptococci. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Jan;27(1):107–113. doi: 10.1128/am.27.1.107-113.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAQUE R. U., BALDWIN J. N. PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF STAPHYLOCOCCAL BETA-HEMOLYSIN. I. PRODUCTION OF BETA-HEMOLYSIN. J Bacteriol. 1964 Nov;88:1304–1309. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.5.1304-1309.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haque R. U., Baldwin J. N. Purification and properties of staphylococcal beta hemolysin. II. Purification of beta hemolysin. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):751–759. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.751-759.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAXTED W. R. The use of bacitracin for identifying group A haemolytic streptococci. J Clin Pathol. 1953 Aug;6(3):224–226. doi: 10.1136/jcp.6.3.224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCracken G. H., Jr The rate of bacteriologic response to antimicrobial therapy in neonatal meningitis. Am J Dis Child. 1972 Jun;123(6):547–553. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1972.02110120071004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romero R., Wilkinson H. W. Identification of group B streptococci by immunofluorescence staining. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Aug;28(2):199–204. doi: 10.1128/am.28.2.199-204.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson H. W., Facklam R. R., Wortham E. C. Distribution by serological type of group B streptococci isolated from a variety of clinical material over a five-year period (with special reference to neonatal sepsis and meningitis). Infect Immun. 1973 Aug;8(2):228–235. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.2.228-235.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]