Abstract
Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF), the most common severe congenital heart malformation, occurs sporadically, without other anomaly, and from unknown cause in 70% of cases. A genome-wide survey of 114 TOF patients and their unaffected parents identified 11 de novo copy number variants (CNVs) that were absent or extremely rare (<0.1%) in 2,265 controls. A second, independent TOF cohort (n = 398) was then examined for additional CNVs at these loci. In 1% (5/512, p = 0.0002, OR = 22.3) of non-syndromic sporadic TOF cases we identified CNVs at chromosome 1q21.1. Recurrent CNVs were also identified at 3p25.1, 7p21.3 and 22q11.2. CNVs in a single TOF case occurred at six loci, two that encode known (NOTCH1, JAG1) disease genes. Our data predicts that at least 10% (4.5–15.5, 95% CI) of sporadic, non-syndromic TOF reflects de novo CNVs and implicates mutations within these loci as etiologic in other cases of TOF.
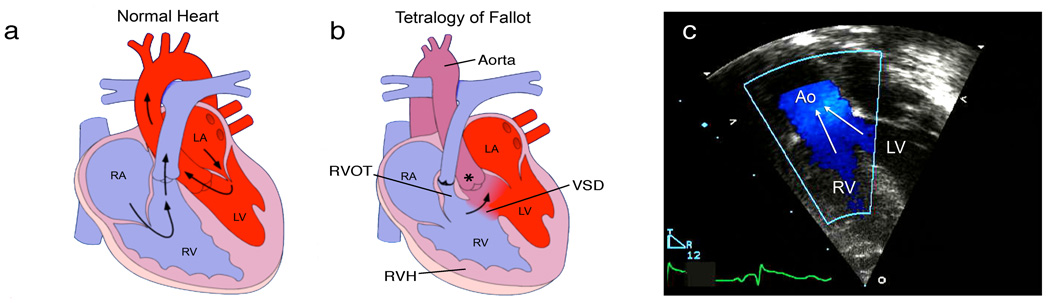
The combination of a malpositioned aorta that overrides both ventricles, ventricular septal defect, pulmonary stenosis (which obstructs blood flow into the lungs) and right ventricular hypertrophy (Figure 1) defines TOF. The most prevalent form of cyanotic heart disease, TOF occurs in one of 3,000 live births and accounts for 10% of all major congenital heart disease1. With recent advances in corrective surgery early lethality from TOF is rare but long-term sequelae, including arrhythmia, ventricular dysfunction and often life-long disability, persist.
Figure 1.
Anatomy and pathophysiology of tetralogy of Fallot (TOF). Normal heart structure (a) promotes unidirectional flow of deoxygenated blood (blue) into the lungs and oxygenated blood (red) into the aorta. In TOF (b) pulmonary stenosis and narrowing of the right ventricular outflow tract (RVOT) impedes the flow of deoxygenated blood into the lungs, and both the ventricular septal defect (VSD) and overriding aorta (*) promote the flow of deoxygenated blood into the systemic circulation, to produce cyanosis (sometimes referred to as “blue baby” syndrome). Right ventricular hypertrophy (RVH) is also present. (c) A Doppler echocardiogram shows mixing of deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle (RV) and oxygenated blood from the left ventricle (LV) as blood is pumped out the overriding aorta (Ao) in a patient with TOF. RA, right atrium; LA, left atrium. Images from Multimedia Library of Congenital Heart Disease, Children’s Hospital, Boston, MA, editor Robert Geggel, MD, www.childrenshospital.org/mml/cvp, with permission.
TOF can arise in the context of prenatal infections, exposure to teratogens, maternal illness, and from dominant mutations that usually alter gene dosage. Haploinsufficiency of cardiac transcription factors genes (NKX2.5, TBX1, TBX5, GATA4) or the transmembrane receptors, NOTCH1 and NOTCH2 and their ligand JAG1 can cause TOF but, more commonly, mutations in these genes produce other heart malformations2–7. Cytogenetic abnormalities, including deletions of chromosome 22q11.2 (DiGeorge syndrome) or trisomy 21 (Down syndrome), account for 15% and 7% respectively of TOF cases, however these patients usually have multiple non-cardiac abnormalities8,9. Large de novo CNVs, identified by array CGH, occur with major congenital anomalies10,11; these typically include congenital heart disease (CHD) in half of all cases12. Far less is known about genes that cause sporadic and isolated CHD, particularly genes involved in complex malformations.
We hypothesized that de novo mutations that alter the dosage of genes involved in cardiac development might account for isolated TOF. We surveyed the genome of 121 TOF trios, each comprised of one proband and two unaffected parents, using the Affymetrix 6.0 array (Supplementary Figure 1). CNVs identified in TOF cases, but absent from parental samples (putative de novo CNVs), by the algorithm Birdseye13 were studied further. CNVs that corresponded to known copy number polymorphisms (CNPs)14 or that were smaller than 20 kb were discarded. To distinguish between potentially pathogenic variants and unidentified benign CNPs we examined all putative de novo TOF CNVs in 2,265 controls genotyped on the Affymetrix 6.0 array (15 and unpublished) and those TOF CNVs that shared ≥ 50% overlap with CNVs found in ≥ 0.1% of control samples were designated as CNPs and were not studied further. Seven individuals with an excess of rare de novo CNVs were removed from the analysis. Of the 32 remaining putative de novo CNVs, 11 were independently validated using multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA) (Supplementary Table 1) and 21 (66%) were false positives; 12 CNVs were inherited and 9 CNVs could not be confirmed by MLPA (data not shown). In summary, genome-wide analyses and validation identified 11 rare de novo CNVs at 10 unique loci from 114 TOF trios.
We considered whether the frequency of de novo CNVs differed between TOF cases and healthy subjects, by analyzing 98 control trios, including 55 HapMap trios, genotyped using the Affymetrix 6.0 array (Supplementary Figure 1). Using the same computational algorithm, 20 putative de novo CNVs were identified: 12 in HapMap trios and 8 in other control trios. Seven of the CNVs found in HapMap trios have been previously attributed to cell line artifacts (chromosome 14: 105,829,131–106,116,317 in NA10854, NA10838, NA06991, NA18857 and NA19154; chr 22:20,777,493–21,581,602 in NA12707 and NA19154)16 and two CNVs in HapMap trios and seven CNVs found in the other control trios fulfilled our criteria as CNPs. Four CNVs were validated by MLPA as being de novo in the control trios (Supplementary Table 2).
The frequency of rare de novo CNVs was greater in TOF trios than in control trios but the difference was not statistically significant (11/114 vs. 4/98, p = 0.18). Although de novo CNVs and pathogenesis appears to be related in schizophrenia17,18 and autism19, our trio study may be underpowered to detect a similar relationship in TOF. Alternatively, TOF mutations may be incompletely penetrant; a consideration that prompted assessment of whether inherited CNVs occurred at loci discovered by de novo CNVs analyses. In three TOF trios we identified CNVs at the 1q21.1, 3p25.1 and 7p21.3 loci that were inherited from unaffected parents (Table 1), a finding that supports the role of additional genetic or environmental interactions in TOF.
Table 1.
TOF CNVs identified in 512 TOF patients include new, known and candidate loci.
| Location# | Proband | Start | Length | Inheritance | CN | Controls | P value | OR | Genes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1q21.1 | 749 | 144,643,825 | 1,196,685 | de novo | gain | 0 | 0.0002 | 22.3 | PRKAB2, FM05, CHDJL,BCL9, ACP6, GJA5 |
| 201.67011 | 144,963,019 | 1,334,788 | de novo | gain | |||||
| 200.4301 | 143,543,612 | 3,262,280 | inherited | gain | |||||
| 200.2501 | 144,965,244 | 1,346,170 | n/a† | gain | |||||
| 37011 | 143,667,750 | 3,878,714 | n/a† | loss | |||||
| 3p25.1 | 756 | 9,795,587 | 12,380,330 | de novo | gain | 0 | 0.03 | 8.9 | RAF J, TMEM40 |
| 4192 | 12,605,755 | 175,375 | inherited | gain | |||||
| 7p21.3 | 2102 | 8,900,139 | 190,905 | de novo | gain | 0 | 0.03 | 8.9 | none |
| 36482 | 8,887,744 | 58,603 | inherited | loss | |||||
| 22q11.2 | 2573 | 17,185,856 | 2,865,869 | de novo | loss | 1* | 0.09 | 8.9 | TBX1 |
| 2360 | 17,190,089 | 2,293,683 | de novo | loss | |||||
| 9q34.3 | 1275 | 138,337,602 | 190,917 | de novo | loss | 0 | 0.2 | >100 | NOTCH1 |
| 20p12.2 | 201.650 | 8,682,747 | 3,935,604 | de novo | loss | 0 | 0.2 | >100 | JAG1 |
| 2p23.3 | 3208 | 25,951,553 | 266,886 | de novo | gain | 0 | 0.2 | >100 | ASXL2, KIF3C, RAB10 |
| 2p15 | 216 | 60,152,611 | 1,810,354 | de novo | gain | 0 | 0.2 | >100 | 9 genes |
| 4q22.1 | 2231 | 89,403,169 | 45,684 | de novo | gain | 0 | 0.2 | >100 | PPM1K |
| 10q11.21 | 201.040 | 43,904,505 | 53,379 | de novo | loss | 0 | 0.2 | >100 | none |
Abbreviations and definitions: Location, cytogenetic location; Proband, patients from cohort of 512 TOF subjects (see methods); Start, beginning of CNV based on Build 36.1 of the reference genome; Length, size of CNV in base pairs; Inheritance, whether or not the CNV was found in a parent based on array and/or MLPA results; CN, copy number of variant found in TOF patients; Controls, frequency of the CNV in the control population (2,265 individuals), *control CNVwas a loss; P value, likelihood that this number of variants was observed in 512 probands given the frequency in the controls determined using two-tailed Fisher’s exact probability test; OR, odds ratio (OR calculation includes parents with the CNV as controls); Genes, reference genes within the TOF locus expressed in the right ventricular outflow tract. Known TOF disease genes are in bold type.
Parental DNA not available.
Identified from MLPA screen of 398 TOF probands.
Inherited CNV identified from 6.0 array data of 114 TOF trios.
To further evaluate the pathogenicity of CNVs, we used MLPA to assess nine loci in a second cohort of sporadic, non-syndromic TOF cases (n = 398). Because the cases in this validation cohort had prior chromosome 22q11.2 analyses, this locus was excluded from further study. At least two unique synthetic oligonucleotide MLPA probes (Supplementary Table 3) were designed to hybridize within each of the nine loci. MLPA studies demonstrated four additional TOF patients with 1q21.1 CNVs (three duplications, one deletion, Supplementary Table 1). The boundaries of these CNVs were delineated by Affymetrix 6.0 array analyses. In combination with our initial genome-wide studies a total of 17 CNVs were found at 10 loci in 512 TOF cases (Table 1). CNVs at each of these loci were absent or very rare in 2,265 controls. CNVs at four loci (1q21.1, 3p25.1, 7p21.3 and 22q11.2) were found in at least two TOF cases. Since small CNVs would be predicted to escape detection by the array platform and detection algorithm used here, our data defines a minimum estimate, approximately 10% (11/114), for the frequency of de novo CNVs in sporadic, isolated TOF. This is lower than the 25–30% frequency of de novo events seen in individuals with syndromic heart malformations that occur with additional birth defects10,11 but importantly, identified causes for isolated TOF.
At chromosome 1q21.1 CNVs were found in five TOF cases (Figures 2a and 2b) that are structurally complex (Supplementary Figure 2). The shared duplicated segment in four TOF cases spans a small interval on chromosome 1q21.1 where seven validated genes are encoded: PRKAB2, PDIA3P, FMO5, CHD1L, BCL9, ACP6 and GJA5. Transcriptional analyses of human right ventricular outflow tract (RVOT), which is malformed in TOF, demonstrated six of these genes are expressed. Among these six genes, PRKAB2, CHD1L, BCL9 and GJA5 had enriched expression in RVOT (Table 2), a finding that increases their candidacy as disease genes. In 96 independent sporadic TOF cases we sequenced exons and flanking splice sites in GJA5 and CHD1L, which encode connexin 40 and chromodomain helicase DNA binding protein-1 respectively. No non-synonymous changes at conserved residues or small insertions/deletions were identified (data not shown).
Figure 2.
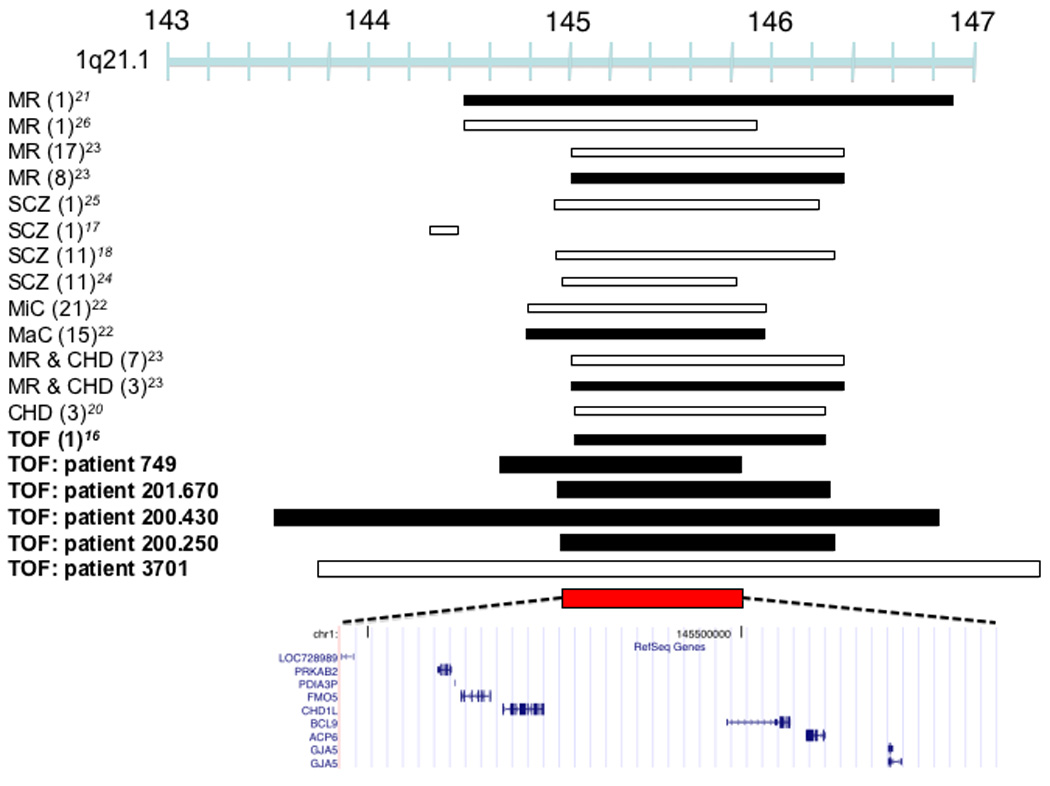

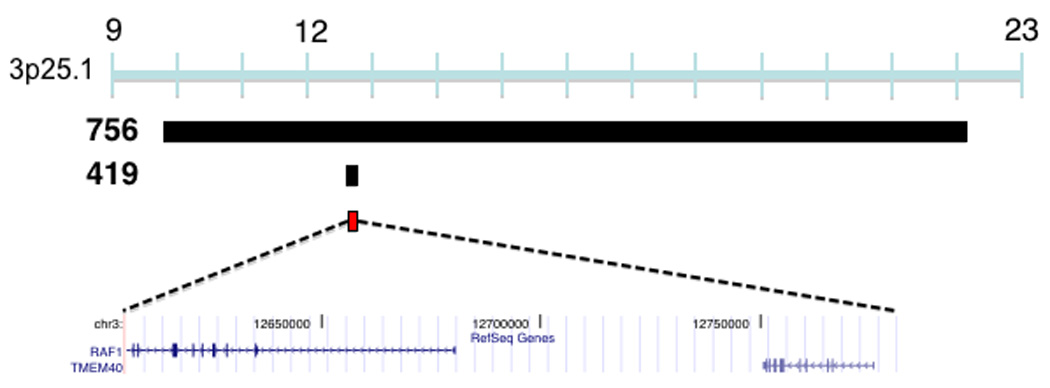
CNVs associated with TOF. (a) Duplications in four TOF patients (749, 201.670, 200.430, 200.250) and a deletion (patient 3701) overlap a 875,266 bp region at 1q21 (chr1:144,965,244-145,840,510) which encompasses six known genes that are expressed in the human right ventricular outflow tract. Previously described duplications at this locus are associated with mental retardation (MR)21, TOF16, macrocephaly (MaC)22 and other congenital phenotypes23. Studies have identified multiple patients (number of patients in parentheses, only the minimal overlapping region between patients is shown) that carry deletions at this locus with congenital heart disease other than TOF (CHD), MR, schizophrenia (SCZ), microcephaly (MiC) or that carry deletions with CHD and MR. (b) Plot showing normalized probe intensity measurements across 1q21 in the four TOF patients carrying a deletion (turquoise), the one TOF patient with a duplication (green) and 273 CN-neutral controls (gray lines and summarized as mean (black) ± 2*median absolute deviation (dark blue lines). The vertical dotted lines indicate the boundaries of the 875,266 bp overlapping region. The absence of circles on the colored lines indicates an absence of probes due to segmental duplications and there is a known CNP downstream of our region of interest. (c) A 12,380,330 bp duplication on chromosome 3 was found in a single TOF patient (756) and an inherited duplication was found within this interval in patient 419 which narrows the interval to a region (chr3:12,605,755-12,781,130) affecting RAF1. White bars indicate deletion, black bars indicate duplication, and red bars indicate the region of overlap between TOF CNVs. Chromosome position is indicated in Mb by the blue bar. All coordinates are based on build 36.1 of the human reference genome.
Table 2.
Expression of TOF CNV genes in the human right ventricular outflow tract.
| CNV# | Gene | Tag count |
|---|---|---|
| 1q21.1 | PRKAB2 | 8±3 |
| PDIA3P | 0 | |
| FM05 | 1± 1 | |
| CHD1L | 12 ±6 | |
| BCL9 | 11 ±4 | |
| ACP6 | 3±2 | |
| GJA5 | 8±4 | |
| 3p25.1 | RAF1 | 99 ±20 |
| TMEM40 | 1± 1 | |
| 7p21.3 | no genes | 0 |
| 22q11.2 | TBX1 | 2± 1 |
| 9q34.3 | NOTCH1 | 22 ±6 |
| 20p12.2 | JAG1 | 43 ±8 |
| 2p23.3 | ASXL2 | 23 ±5 |
| KIF3C | 4± 1 | |
| RAB10 | 70 ±24 | |
| 2p15 | BCL11A | 15 ± 4 |
| PAPOLG | 12 ±4 | |
| PEL | 2± 1 | |
| PUS10 | 0 | |
| PEX13 | 13 ±4 | |
| KIAA1841 | 10±4 | |
| AHSA2 | 30 ± 10 | |
| USP34 | 33 ± 15 | |
| SNORA70B | 0 | |
| XPOl | 40 ± 11 | |
| FAM161A | 0 | |
| CCT4 | 59 ± 15 | |
| 4q22.1 | PPM1K | 17±6 |
| 10q11.21 | no genes | 0 |
Abbreviations and definitions: CNV, cytogenetic location of TOF copy number variant identified in Table 1; Gene, name of reference gene within TOF CNV according to Build 36.1 of the human reference genome; Tag count, number of sense tags mapped to reference gene from four separate human right ventricular outflow tract mRNA expression libraries, expressed as mean ± standard deviation. For loci containing a known disease gene (bold) the expression profile for only that gene is shown.
Chromosome 1q21.1 has been previously implicated in CHD20 but more recently CNVs at this locus were identified in subjects with neuro-cognitive, psychiatric, and developmental phenotypes 17,18,21–26. Notably, there is no perfect correlation between 1q21 dosage and phenotype in all studies to date (including ours). Two studies described mild (7 cases) or severe (5 cases, not including TOF) cardiovascular malformations, but 9 of these cases had additional phenotypes: developmental or intellectual disabilities, dysmorphic features or other congenital anomalies22,23. In contrast, all TOF cases with 1q21.1 CNVs identified in our study had normal cognition, social behavior, and neurologic function (Table 3). The remarkable combination of structural heart malformations and functional (non-structural) brain deficits resembles the DiGeorge phenotype, due to chromosome 22q11.2 deletions that disrupt TBX18,9. While the variable length of 1q21.1 CNVs may imply that these mutations alter contiguous genes with distinct roles in cognition and heart development, we speculate that this locus contains a single causal gene which, like TBX1, functions in progenitor cells (perhaps neural crest cells), critical for both cardiovascular and brain development. Regardless of whether these or another explanation accounts for both clinical phenotypes, we note that less than 0.2% of patients with neuro-psychiatric disorders and 0.02% of controls had chromosome 1q21.1 duplications23. In contrast, 1q21.1 duplications were significantly (p = 0.007) more common in TOF, occurring in 1% of patients studied here.
Table 3.
Phenotype data for TOF patients with 1q21.1 and 3p25.1 CNVs
| Proband# | CNV | CN | Age | Gender | Extra-cardiac Features | Development | Neuro-Psychiatric Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 749 | 1q21.1 | gain | 21 (< 1) | F | None | Normal | None |
| 201.670 | 1q21.1 | gain | 9(<1) | F | None | Normal | None |
| 200.430 | 1q21.1 | gain | 4(<1) | M | None | Normal | None |
| 200.250 | 1q21.1 | gain | 19 (<1) | F | None | Normal | None |
| 3701 | 1q21.1 | loss | 19 (< 1) | M | None | Normal | None |
| 756 | 3p25.1 | gain | 13 (< 1) | M | High-arched palate, malocclusion, subtle auricular dysplasia | Normal | Hyperactivity |
| 419 | 3p25.1 | gain | 15 (<1) | F | None | Normal | None |
Abbreviations and definitions: Proband, individual patient identification number; CNV, cytogenetic location of copy number variant; CN, copy number; Age, current age and (age at diagnosis) in years; Gender, female (F) or male (M).
Two TOF cases shared overlapping duplications at the 3p25.1 locus. Whereas one duplication spanned 12 Mb, the other duplication affected only two genes, RAF1 and TMEM40 (Figure 2c). RAF1 is expressed at approximately 100-fold higher levels than TMEM40 in the RVOT (Table 2). Gain-of-function point mutations of RAF1 cause Noonan syndrome, a multisystem disorder with cardiac manifestations, that rarely causes TOF but moreover produces one of its components: hypertrophy, atrial or ventricular septal defects, or pulmonary stenosis27,28. Identification of CNVs at 3p25.1 in TOF cases prompted re-evaluation for signs of Noonan syndrome (Table 3). Subtle craniofacial abnormalities were identified in one case (patient 756), suggesting some phenotypic overlap between RAF1 gain-of-function mutations and increases in RAF1 copy number produced by the 12 Mb duplication. The smaller 3p25.1 CNV truncates and duplicates RAF1 and further study is necessary to determine which alteration causes the TOF phenotype.
Reciprocal CNVs were found at 7p21.3 in two TOF cases but since no known genes, mRNAs, microRNAs or ESTs are encoded at this locus (Supplementary Figure 3) ongoing RVOT transcript analyses and re-sequencing may help identify the target of these CNVs.
Chromosome 22q11.2 deletions were identified in two TOF patients who lacked any extra-cardiac phenotype that accompanies the DiGeorge syndrome29. A large 22q11.2 deletion was also found in one control subject. These data confirm substantial incomplete penetrance of 22q11.2 deletions30. Whether genetic mechanisms that compensate for the deleterious consequence of 22q11.2 deletions also influence other CNVs is unknown.
Of six de novo CNVs found in only one TOF subject two altered previously described congenital heart disease genes, NOTCH1 and JAG1. NOTCH1 null mutations primarily cause familial bicuspid aortic valve and less commonly other malformations7. Mice engineered to lack components of the NOTCH1 signaling pathway have TOF-like phenotypes31. Our findings provide direct evidence for NOTCH1 mutations in TOF. JAG1 mutations are known to cause TOF in the context of Alagille syndrome and in isolation4,32. The patient with the 4 Mb de novo deletion of JAG1 identified here has no clinical features of Alagille syndrome. The finding of CNVs that altered NOTCH1 and JAG1 underscores the need for assessing gene dosage in mutation analyses of congenital heart disease genes
Four other loci were altered by CNVs in individual TOF patients. CNVs at these candidate TOF loci occurred at a similar low frequency to NOTCH1 and JAG1 mutations, emphasizing the genetic heterogeneity of TOF. Three genes are encoded at the 2p23.3 locus: RAB10, KIF3C and ASXL2. Although none were previously implicated in cardiac development, each is expressed in the RVOT (Table 2). The expression of RAB10, which encodes a GTPase, is highest. Because KRAS, another GTPase, is activated by Noonan syndrome mutations33, RAB10 is a promising candidate gene in TOF.
Pathogenicity of a 1.8 Mb de novo duplication at 2p15 found in one TOF case is likely given its size and the absence of CNVs at this locus in all controls. Of 12 genes encoded in the duplicated interval nine are expressed in the human RVOT (Table 2) and none are previously implicated in cardiogenesis. The 4q22.1 deletion encompasses PPM1K and transcripts encoding this phosphatase were present in RVOT tissues. The deletion at 10q11.21 contains no known genes, coding or non-coding RNAs.
In summary, our studies defined seven new loci that substantially increase risk (odds ratio ≥ 8.9) for sporadic, non-syndromic TOF. While some loci are large (>100 kb) and three loci exhibited incomplete penetrance, expression data of human RVOT implicates an important subset of genes, prioritizing further investigation. Moreover these data indicate de novo CNVs at 10 loci accounted for 10% of TOF, which explains sporadic presentation and defines genetic heterogeneity in this serious heart malformation.
Methods
Study subjects
TOF cases and parents from Brigham & Women’s Hospital, Children’s Hospital Boston and the Instituto do Coração da Universidade de São Paulo, Brazil provided informed consent for participation in these studies, which were performed in accordance with institutional guidelines. TOF was diagnosed based on non-invasive imaging (2D-echocardiography and/or MRI) and/or invasive studies (cardiac catheterization and/or surgery). TOF patients with clinical features of developmental syndromes, multiple major developmental anomalies, or major cytogenetic abnormalities were excluded. When 22q11.2 analyses (routinely obtained on all Boston subjects and obtained when clinically indicated on Brazilian subjects) revealed microdeletion, subjects were excluded. TOF parents had neither significant congenital or cardiac disease. Control subjects were assembled from the BRASS15 cohort (n = 538), Multiple Sclerosis patients (n = 934) and healthy controls (n = 271) collected from Brigham & Women’s Hospital and unrelated TOF parents (n = 228). Control trios were assembled from HapMap CEU and YRI subjects (n = 165) and South American controls (n = 129). Control subjects and trios had neither significant congenital or cardiac disease.
Genotyping and identification of CNVs
Genotyping was performed using the Affymetrix Human Genome-Wide SNP Array 6.0 at the Broad Institute (TOF trios and controls) and Affymetrix (HapMap trios). Genotypes from X and Y chromosomes were excluded from analyses. 121 TOF trios and 98 control trios were initially analyzed using Birdseed v.1.5 with 97.8 ± 1.3% and 99.7 ± 0.6% average call rates achieved, respectively (Supplementary Figure 1). There was no evidence of non-paternity (determined by the number of Mendelian errors present in each trio as calculated by PLINK34) in the trios used. Genotype information on the CEU and YRI HapMap trios was obtained directly from Affymetrix. The Birdseye13 CNV-detection algorithm was used to identify de novo CNVs in trios using a confidence (LOD) score of 1010 for the proband to be copy number (CN) variable (CN = 0,1,3 or 4) and a LOD score of 106 for the parents to be CN variable. This was done in order to maximize the probability that the child truly possessed a de novo CNV. CNVs in proband samples that were absent from both parental samples were considered putative de novo CNVs. Those putative de novo CNVs that corresponded to known copy number polymorphisms (CNPs)14 or that were smaller than 20 kb were discarded. De novo CNVs with ≥ 50% overlap with CNVs found in ≥ 0.1% of 2,265 control samples were designated CNPs. When an excessive number of de novo CNVs (> 3 SDs above the mean number of CNVs per individual) was identified, subjects were excluded from analyses. Artifactual CNVs due to cell line artifacts (see main text) were identified in HapMap samples and were discarded16. CNV locations are based on the March 2006 human reference sequence (National Center for Biotechnology Information [NCBI] Build 36.1). For non-trio controls, CNV calls were based on Birdseye using a LOD score of 1010 to be CN variable (CN = 0, 1, 3 or 4).
Multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA)
At least two independent MLPA probes (Supplementary Table 3) corresponding to sequences encompassed by CNVs were designed to confirm each de novo CNV in samples from TOF cases and parents and to identify novel CNVs at these loci (excluding chromosome 22q11.2 deletions) in a screen of a second cohort of 398 TOF subjects. Synthetic oligonucleotide probes with a final product size of 90–160 bp (including universal sequences) were designed from genomic sequences (March 2006 human reference sequence, NCBI Build 36.1). Probe design sought to maximize unique hybridization using the BLAT program (http://genome.ucsc.edu), a Tm > 65°C and GC content 40–60% according to IDT Oligoanalyzer 3.0 (http://www.idtdna.com/analyzer/Applications/OligoAnalyzer/), absence of known SNPs (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/SNP/) within the hybridizing region and to have no more than three cytosine or guanine bases flanking the ligation site35. Probes were designed to differ by at least four bp in length to prevent overlapping mobility during electrophoresis. To allow ligation, downstream probes were 5´-phosphorylated and all probes used in these studies (sequences available upon request) were PAGE-purified following synthesis (IDT, Coralville, IA). DNA was purified from peripheral blood lymphocytes using routine phenol-chloroform extraction or from epithelial cells in saliva according to the manufacturer’s instructions (http://www.dnagenotek.com/). DNA quality was assessed by agarose gel electrophoresis following denaturation and only high quality DNA samples and MRC-Holland reagents (Amsterdam, The Netherlands) were used for MLPA. MLPA reactions were performed as described 36, with a maximum of 20 probes (final concentration = 2 fM) and 100 ng genomic DNA. After heating (95°C) for one minute, hybridization reactions continued for 16 hours (60°C). Hybridized probes were ligated using 1 U ligase-65 for 15 minutes (54°C) followed by ligase deactivation (98°C for five minutes). Ligation product (5 µL) was added to PCR buffer, heated (60°C) and then PCR reagents (2.5 nmol dNTPs, SALSA polymerase, 10 pmol universal primers: 5´-FAM-GGGTTCCCTAAGGGTTGA-3´, 5´-TCTAGATTGGATCTTGCTGGCAC-3´) were added to achieve a final 25 µL reaction. PCR was carried out for 33 cycles (95°C for 30 seconds, 60°C for 30 seconds and 72°C for one minute). Products were resolved by capillary electrophoresis on an Applied Biosystems 3730xl and peaks were manually reviewed in GeneMapper 3.7 (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA). MLPA studies were performed in triplicate in at least two separate experiments.
Calculation of MLPA dosage quotient (DQ)
Copy number was deduced from DQ. A peak ratio was calculated by dividing probe peak area by the sum of all peak areas in each reaction. Each experimental peak ratio was divided by the average of control peak ratios to normalize for variation in probe signal strength. Control peak ratios were derived from probes hybridizing to unique, non-deleted chromosomal locations on unrelated genes. The normalized peak ratio was divided by the average of each probe’s peak ratio among control samples (individuals without TOF or other CHD) to eliminate variation between samples37.
Human right ventricular outflow tract mRNA expression libraries
Expression libraries were created from RNA isolated from right ventricular outflow tract tissue collected from four TOF patients at the time of primary surgical repair (mean patient age 2.6 ± 2 months). Tissue was snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen and maintained at –80˚C prior to processing. RNA extraction and library construction and amplification was carried out as previously described38. Amplified library was sequenced on an Illumina Genome Analyzer (Illumina, San Diego, CA). Each library generated more than 2,000,000 reads with a Chastity score (Illumina, San Diego, CA) > 2. Sense tags were assigned to cognate gene identities and unique tags assigned to the same UniGene cluster or gene symbol were combined38.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the participation of families and we thank Carrie Sougnez and Melissa Parkin for technical assistance and Dr. Robert Geggel for supplying TOF images. This work was supported by grants from HHMI (CES), NIH (to CES, JGS, REB, and to the Broad Institute [National Center for Research Resources]), Pediatric Scientist Development Program (SCG) and Sarnoff Cardiovascular Research Foundation (JCL). MS controls were genotyped in collaboration with Affymetrix, Inc.
References
- 1.Ferencz C, et al. Congenital heart disease: prevalence at livebirth. The Baltimore-Washington Infant Study. Am J Epidemiol. 1985;121:31–36. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Schott JJ, et al. Congenital heart disease caused by mutations in the transcription factor NKX2-5. Science. 1998;281:108–111. doi: 10.1126/science.281.5373.108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Basson CT, et al. Mutations in human TBX5 [corrected] cause limb and cardiac malformation in Holt-Oram syndrome. Nat Genet. 1997;15:30–35. doi: 10.1038/ng0197-30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Eldadah ZA, et al. Familial Tetralogy of Fallot caused by mutation in the jagged1 gene. Hum Mol Genet. 2001;10:163–169. doi: 10.1093/hmg/10.2.163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Tomita-Mitchell A, Maslen CL, Morris CD, Garg V, Goldmuntz E. GATA4 sequence variants in patients with congenital heart disease. J Med Genet. 2007;44:779–783. doi: 10.1136/jmg.2007.052183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.McDaniell RWD, Sanchez-Lara PA, Pai A, Krantz ID, Piccoli DA, Spinner NB. NOTCH2 mutations cause Alagille syndrome, a heterogeneous disorder of the notch signaling pathway. Am J Hum Genet. 2006;79:169–173. doi: 10.1086/505332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Garg V, et al. Mutations in NOTCH1 cause aortic valve disease. Nature. 2005;437:270–274. doi: 10.1038/nature03940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Goldmuntz E, et al. Frequency of 22q11 deletions in patients with conotruncal defects. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1998;32:492–498. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(98)00259-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Yagi H, et al. Role of TBX1 in human del22q11.2 syndrome. Lancet. 2003;362:1366–1373. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(03)14632-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Thienpont B, et al. Submicroscopic chromosomal imbalances detected by array-CGH are a frequent cause of congenital heart defects in selected patients. Eur Heart J. 2007;28:2778–2784. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehl560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Richards AA, et al. Cryptic chromosomal abnormalities identified in children with congenital heart disease. Pediatr Res. 2008 doi: 10.1203/PDR.0b013e31818095d0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Loffredo CA. Epidemiology of cardiovascular malformations: prevalence and risk factors. Am J Med Genet. 2000;97:319–325. doi: 10.1002/1096-8628(200024)97:4<319::aid-ajmg1283>3.0.co;2-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Korn JM, et al. Integrated genotype calling and association analysis of SNPs, common copy number polymorphisms and rare CNVs. Nat Genet. 2008 doi: 10.1038/ng.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.McCarroll SA, et al. Integrated detection and population-genetic analysis of SNPs and copy number variation. Nat Genet. 2008;40:1166–1174. doi: 10.1038/ng.238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Sato M, et al. The validity of a rheumatoid arthritis medical records-based index of severity compared with the DAS28. Arthritis Res Ther. 2006;8:R57. doi: 10.1186/ar1921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Redon R, et al. Global variation in copy number in the human genome. Nature. 2006;444:444–454. doi: 10.1038/nature05329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Xu B, et al. Strong association of de novo copy number mutations with sporadic schizophrenia. Nat Genet. 2008;40:880–885. doi: 10.1038/ng.162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Stefansson H, et al. Large recurrent microdeletions associated with schizophrenia. Nature. 2008 doi: 10.1038/nature07229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Sebat J, et al. Strong association of de novo copy number mutations with autism. Science. 2007;316:445–449. doi: 10.1126/science.1138659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Christiansen J, et al. Chromosome 1q21.1 contiguous gene deletion is associated with congenital heart disease. Circ Res. 2004;94:1429–1435. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000130528.72330.5c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.de Vries BB, et al. Diagnostic genome profiling in mental retardation. Am J Hum Genet. 2005;77:606–616. doi: 10.1086/491719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Brunetti-Pierri N, et al. Recurrent reciprocal 1q21.1 deletions and duplications associated with microcephaly or macrocephaly and developmental and behavioral abnormalities. Nat Genet. 2008;40:1466–1471. doi: 10.1038/ng.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Mefford HC, et al. Recurrent Rearrangements of Chromosome 1q21.1 and Variable Pediatric Phenotypes. N Engl J Med. 2008 doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0805384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Stone JL, et al. Rare chromosomal deletions and duplications increase risk of schizophrenia. Nature. 2008 doi: 10.1038/nature07239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Walsh T, et al. Rare structural variants disrupt multiple genes in neurodevelopmental pathways in schizophrenia. Science. 2008;320:539–543. doi: 10.1126/science.1155174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Sharp AJ, et al. Discovery of previously unidentified genomic disorders from the duplication architecture of the human genome. Nat Genet. 2006;38:1038–1042. doi: 10.1038/ng1862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Razzaque MA, et al. Germline gain-of-function mutations in RAF1 cause Noonan syndrome. Nat Genet. 2007;39:1013–1017. doi: 10.1038/ng2078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Pandit B, et al. Gain-of-function RAF1 mutations cause Noonan and LEOPARD syndromes with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Nat Genet. 2007;39:1007–1012. doi: 10.1038/ng2073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Bassett AS, et al. Clinical features of 78 adults with 22q11 Deletion Syndrome. Am J Med Genet A. 2005;138:307–313. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.30984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.McDonald-McGinn DM, et al. Phenotype of the 22q11.2 deletion in individuals identified through an affected relative: cast a wide FISHing net! Genet Med. 2001;3:23–29. doi: 10.1097/00125817-200101000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Niessen K, Karsan A. Notch signaling in cardiac development. Circ Res. 2008;102:1169–1181. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.108.174318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Krantz ID, et al. Spectrum and frequency of jagged1 (JAG1) mutations in Alagille syndrome patients and their families. Am J Hum Genet. 1998;62:1361–1369. doi: 10.1086/301875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Schubbert S, et al. Germline KRAS mutations cause Noonan syndrome. Nat Genet. 2006;38:331–336. doi: 10.1038/ng1748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Purcell S, et al. PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet. 2007;81:559–575. doi: 10.1086/519795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Stern RF, et al. Multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification using a completely synthetic probe set. Biotechniques. 2004;37:399–405. doi: 10.2144/04373ST04. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Schouten JP, et al. Relative quantification of 40 nucleic acid sequences by multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002;30:e57. doi: 10.1093/nar/gnf056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Yau SC, Bobrow M, Mathew CG, Abbs SJ. Accurate diagnosis of carriers of deletions and duplications in Duchenne/Becker muscular dystrophy by fluorescent dosage analysis. J Med Genet. 1996;33:550–558. doi: 10.1136/jmg.33.7.550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Kim JB, et al. Polony multiplex analysis of gene expression (PMAGE) in mouse hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Science. 2007;316:1481–1484. doi: 10.1126/science.1137325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.