Abstract
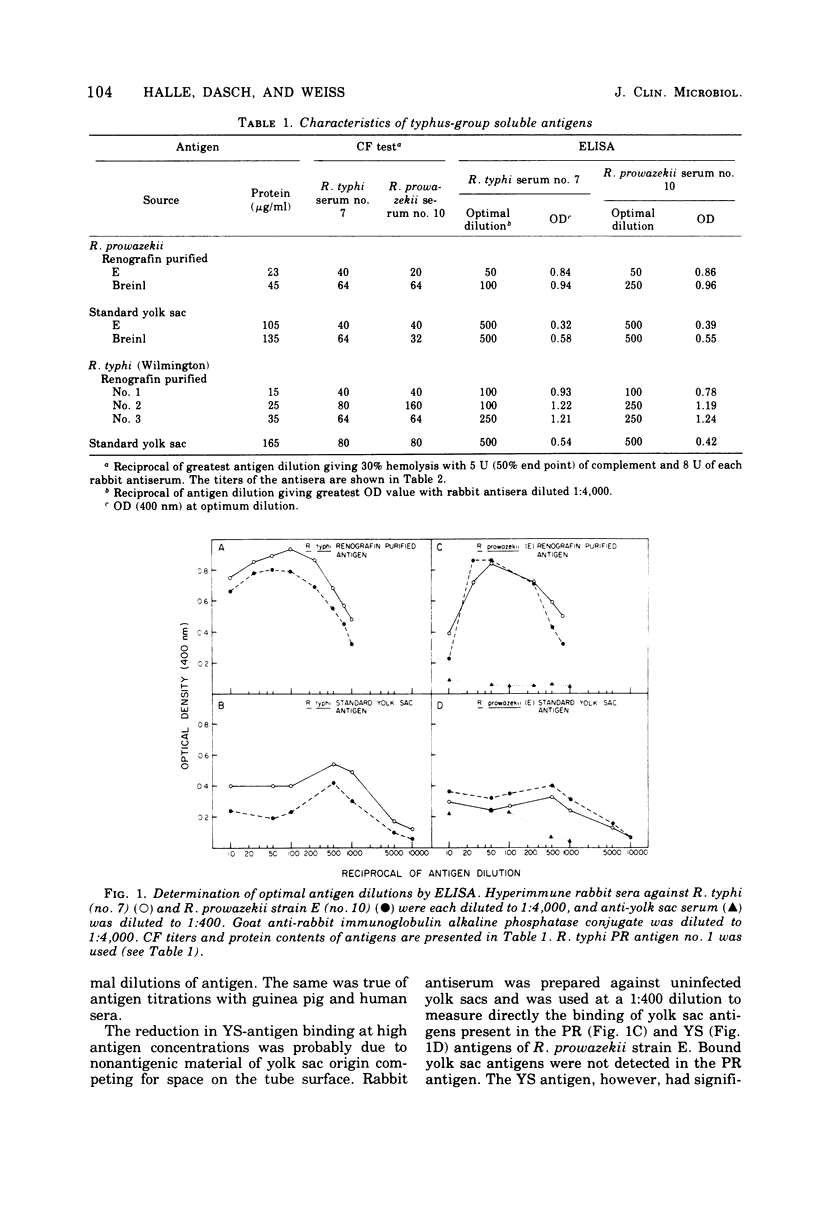
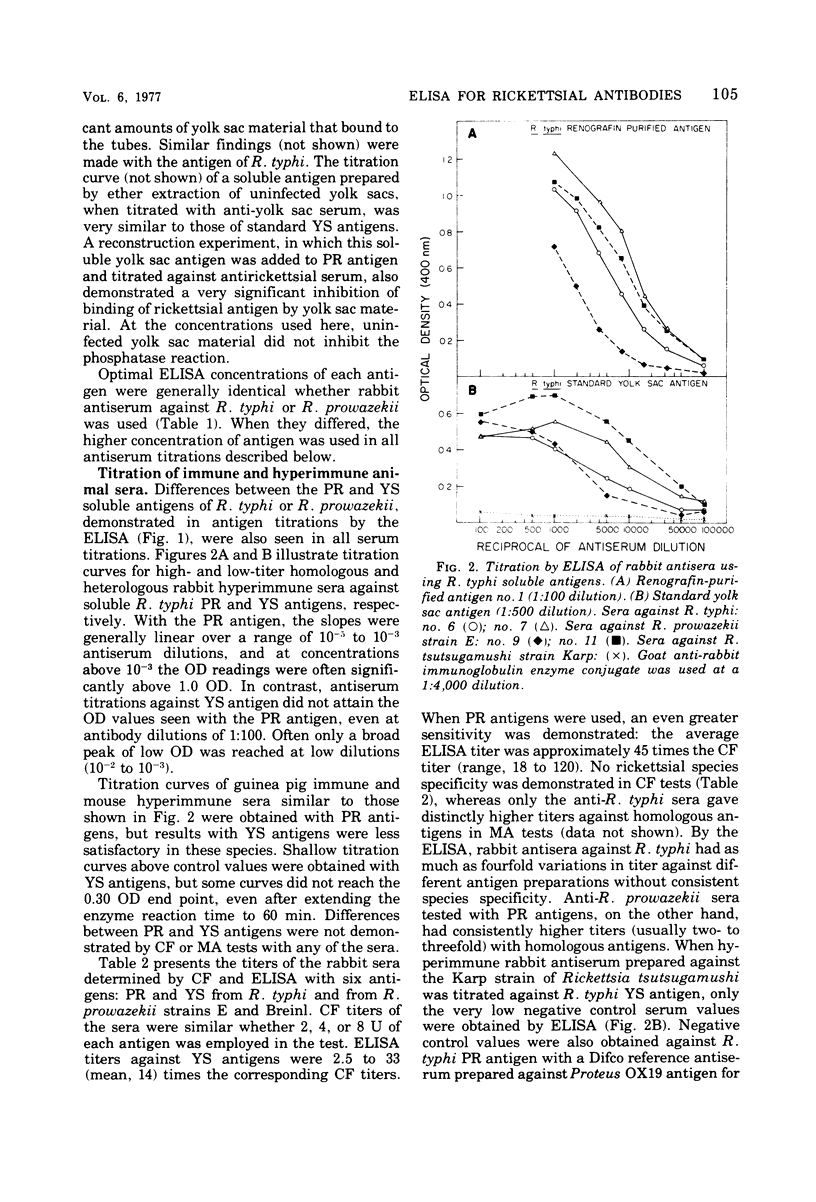
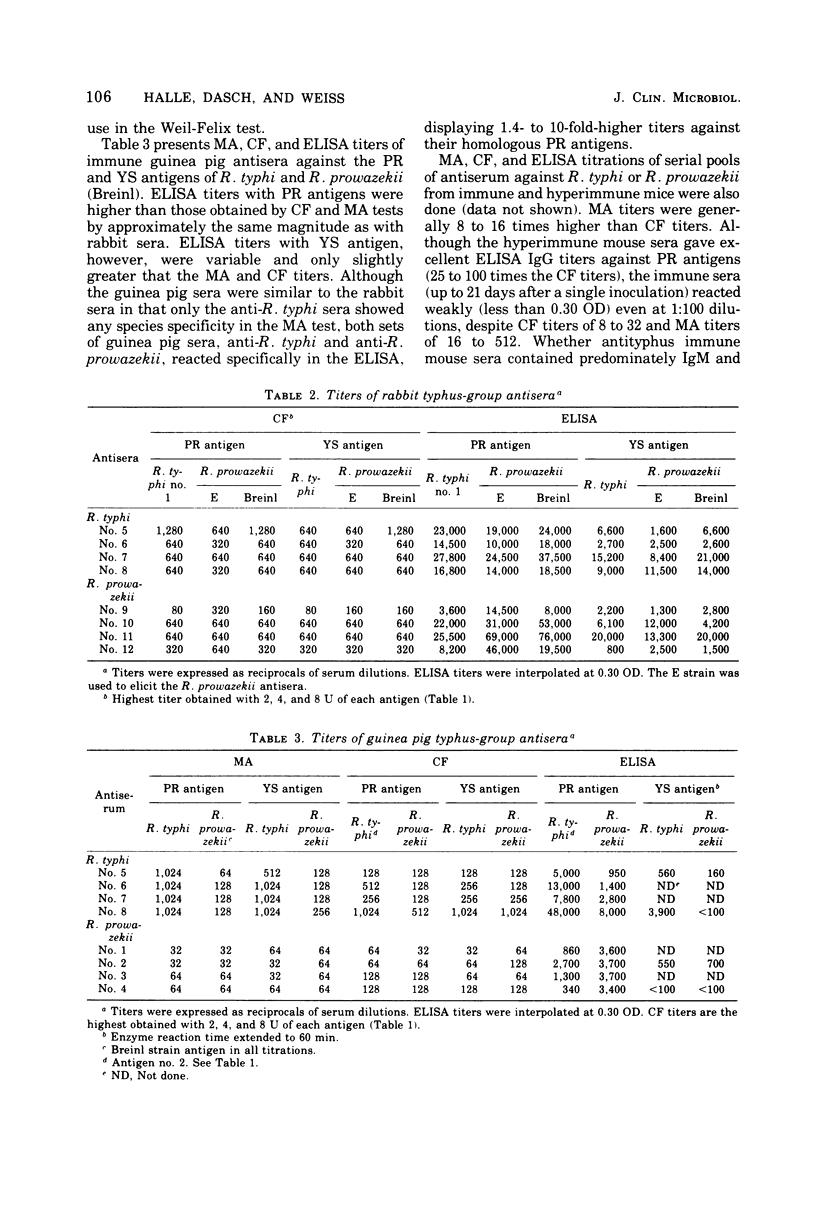
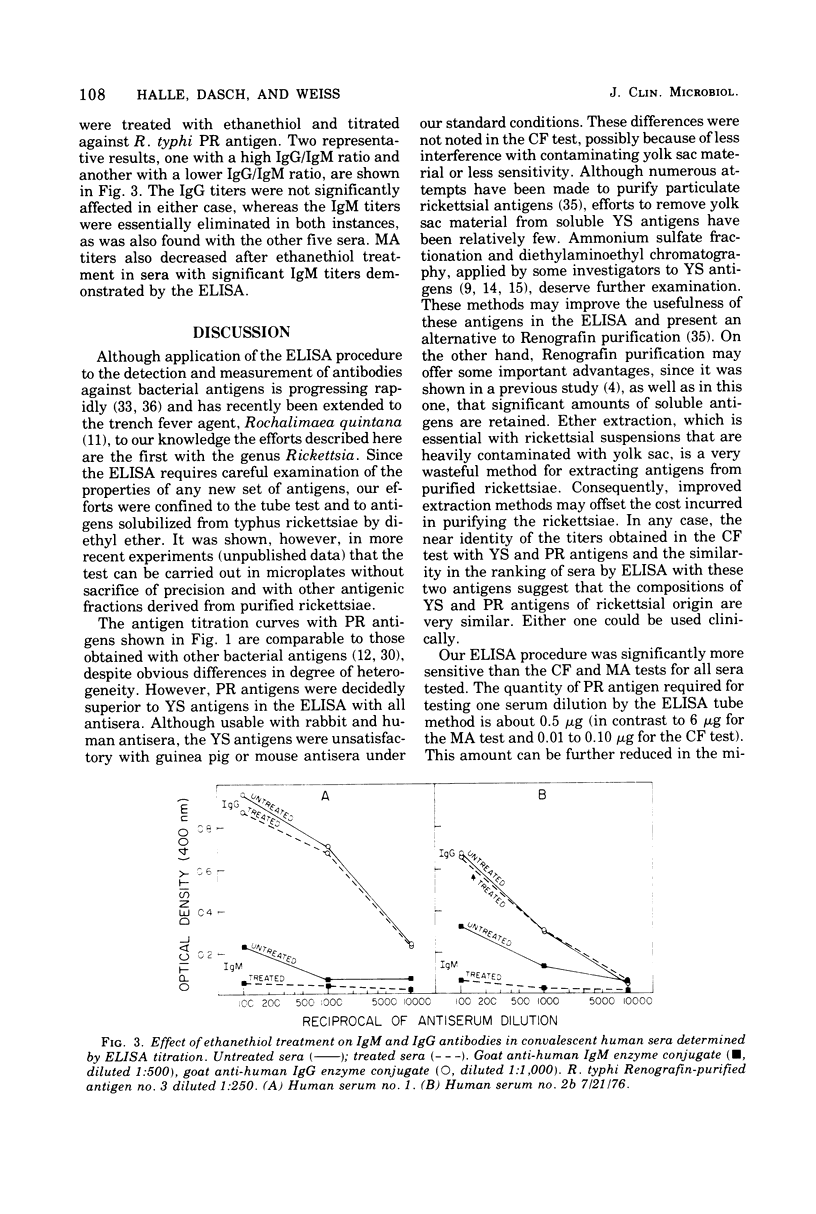
An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) has been developed for the titration of rickettsial antibodies in human and animal sera. Two preparations of soluble typhus-group antigens were obtained from Rickettsia typhi and Rickettsia prowazekii by ether extraction: a standard antigen from infected yolk sacs (YS antigen) and one free of yolk sac contaminants from Renografin-purified rickettsiae (PR antigen). Rabbit, mouse, and guinea pig sera were obtained by immunization with viable purified R. typhi or R. prowazekii. Human sera were obtained from individuals who had recovered from laboratory infections with either typhus rickettsia months or years previously. Goat-derived anti-immunoglobulins were conjugated to alkaline phosphatase with glutaraldehyde. Although the PR and YS antigens gave equivalent antibody titers in the complement fixation test, the PR antigen was clearly superior in the ELISA. With this antigen, the titration curves of all antisera were linear over a wider range of serum concentrations and the titers were higher than with the YS antigen. With YS and PR antigens, ELISA titers were higher than those obtained by complement fixation by one and two orders of magnitude, respectively. In human sera, immunoglobulin G and immunoglobulin M antibodies were demonstrated by their respective anti-immunoglobulins and by differential susceptibility to ethanethiol. ELISA titers showed some type specificity, whereas none was observed in complement fixation tests. The ELISA is highly sensitive, reproducible, and easily adaptable to the various requirements of clinical and research laboratories.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anacker R. L., Gerloff R. K., Thomas L. A., Mann R. E., Bickel W. D. Immunological properties of Rickettsia rickettsii purified by zonal centrifugation. Infect Immun. 1975 Jun;11(6):1203–1209. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.6.1203-1209.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bozeman F. M., Elisberg B. L., Humphries J. W., Runcik K., Palmer D. B., Jr Serologic evidence of Rickettsia canada infection of man. J Infect Dis. 1970 Apr;121(4):367–371. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.4.367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANG S. M. A serologically-active erythrocyte-sensitizing substance from typhus rickettsiae. I. Isolation and titration. J Immunol. 1953 Mar;70(3):212–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasch G. A., Weiss E. Characterization of the Madrid E strain of Rickettsia prowazekii purified by renografin density gradient centrifugation. Infect Immun. 1977 Jan;15(1):280–286. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.1.280-286.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Quantitative assay of immunoglobulin G. Immunochemistry. 1971 Sep;8(9):871–874. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90454-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiset P., Ormsbee R. A., Silberman R., Peacock M., Spielman S. H. A microagglutination technique for detection and measurement of rickettsial antibodies. Acta Virol. 1969 Jan;13(1):60–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golinevitch H. M., Voronova Z. A. The superficial protective antigen of R. prowazeki. J Hyg Epidemiol Microbiol Immunol. 1968;12(4):413–419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golinevitch H., Voronova Z., Friazinova I., Doutova G., Dolgov H., Goudima O., Nikolskaya V., Botcharova T. L'antigène soluble purifié de R. prowazeki (le vaccine chimique antityphique) Rev Immunol Ther Antimicrob. 1969 Jul-Sep;33(4):229–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann J. E., Hollingdale M. R., Collins M. F., Vinson J. W. Enzyme immunoassay and radioimmunoprecipitation tests for the detection of antibodies to Rochalimaea (Rickettsia) quintana. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1977 Feb;154(2):285–288. doi: 10.3181/00379727-154-39655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Svennerholm A. M. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays for cholera serology. Infect Immun. 1973 May;7(5):759–763. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.5.759-763.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukin E. P., Vasil'ev N. N., Vorob'ev A. A., Malina V. P. Immunologicheskie svoistva rastvorimogo antilena rikketsii provacheka. I. Antigennaia struktura rikketsii Provacheka po dannym khromatograficheskogo analiza na DEAE-tselliuloze. Zh Mikrobiol Epidemiol Immunobiol. 1965 Apr;42(4):41–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukin E. P., Vasil'ev N. N., Vorob'ev A. A., Shevelev V. M. Izuchenie immunologicheskikh svoistv rastvorimogo antigena rikketsii provacheka. II. Vydelenie pri pomoshchi DEAE-tselliulozy rastvorimogo antigena Provacheka i ego immunologicheskoe izuchenie. Zh Mikrobiol Epidemiol Immunobiol. 1965 May;42(5):114–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURRAY E. S., GAON J. A., O'CONNOR J. M., MULAHASANOVIC M. SEROLOGIC STUDIES OF PRIMARY EPIDEMIC TYPHUS AND RECRUDESCENT TYPHUS (BRILL-ZINSSER DISEASE). I. DIFFERENCES IN COMPLEMENT-FIXING ANTIBODIES: HIGH ANTIGEN REQUIREMENT AND HEAT LABILITY. J Immunol. 1965 May;94:723–733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURRAY E. S., O'CONNOR J. M., GAON J. A. DIFFERENTIATION OF 19S AND 7S COMPLEMENT FIXING ANTIBODIES IN PRIMARY VERSUS RECRUDESCENT TYPHUS BY EITHER ETHANETHIOL OR HEAT. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 May;119:291–297. doi: 10.3181/00379727-119-30161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURRAY E. S., O'CONNOR J. M., GAON J. A. SEROLOGIC STUDIES OF PRIMARY EPIDEMIC TYPHUS AND RECRUDESCENT TYPHUS (BRILL-ZINSSER DISEASE). II. DIFFERENCES IN IMMUNOELECTROPHORETIC PATTERNS, RESPONSE TO 2-MERCAPTOETHANOL AND RELATIONSHIPS TO 19 S AND 7 S ANTIBODIES. J Immunol. 1965 May;94:734–740. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason R. A., Wenzel R. P., Seligmann E. B., Jr, Ginn R. K. A reference, inactivated, epidemic typhus vaccine: clinical trials in man. J Biol Stand. 1976;4(3):217–224. doi: 10.1016/s0092-1157(76)80006-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ormsbee R., Peacock M., Philip R., Casper E., Plorde J., Gabre-Kidan T., Wright L. Serologic diagnosis of epidemic typhus fever. Am J Epidemiol. 1977 Mar;105(3):261–271. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philip R. N., Casper E. A., MacCormack J. N., Sexton D., Thomas L. A., Anacker R. L., Burgdorfer W., Vick S. A comparison of serologic methods for diagnosis of Rocky Mountain spotted fever. Am J Epidemiol. 1977 Jan;105(1):56–67. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philip R. N., Casper E. A., Ormsbee R. A., Peacock M. G., Burgdorfer W. Microimmunofluorescence test for the serological study of rocky mountain spotted fever and typhus. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Jan;3(1):51–61. doi: 10.1128/jcm.3.1.51-61.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiss-Gutfreund R. J., Cappucinelli P., Cavallo G. The soluble antigens of Rickettsia prowazeki, R. typhi and R. canada. Investigation of their interrelationship by various serological methods. Z Immunitatsforsch Exp Klin Immunol. 1975 Feb;148(4):315–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruitenberg E. J., Buys J. Application of the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for the serodiagnosis of human African trypanosomiasis (sleeping sickness). Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1977 Jan;26(1):31–36. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1977.26.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEVER J. L. Application of a microtechnique to viral serological investigations. J Immunol. 1962 Mar;88:320–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schinski V. D., Clutter W. C., Murrell K. D. Enzyme- and 125I-labeled anti-immunoglobulin assays in the immunodiagnosis of schistosomiasis. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1976 Nov;25(6):824–831. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1976.25.824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepard C. C., Redus M. A., Tzianabos T., Warfield D. T. Recent experience with the complement fixation test in the laboratory diagnosis of rickettsial diseases in the United States. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Sep;4(3):277–283. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.3.277-283.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirai A., Dietel J. W., Osterman J. V. Indirect hemagglutination test for human antibody to typhus and spotted fever group rickettsiae. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Nov;2(5):430–437. doi: 10.1128/jcm.2.5.430-437.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. W., Kaijser B. The local immune response to Escherichia coli O and K antigen in experimental pyelonephritis. J Clin Invest. 1976 Aug;58(2):276–281. doi: 10.1172/JCI108469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voller A., Bidwell D. E., Bartlett A. Enzyme immunoassays in diagnostic medicine. Theory and practice. Bull World Health Organ. 1976;53(1):55–65. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. P., Grayston J. T. Human serology in Chlamydia trachomatis infection with microimmunofluorescence. J Infect Dis. 1974 Oct;130(4):388–397. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.4.388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E., Coolbaugh J. C., Williams J. C. Separation of viable Rickettsia typhi from yolk sac and L cell host components by renografin density gradient centrifugation. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Sep;30(3):456–463. doi: 10.1128/am.30.3.456-463.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisdom G. B. Enzyme-immunoassay. Clin Chem. 1976 Aug;22(8):1243–1255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


