Abstract
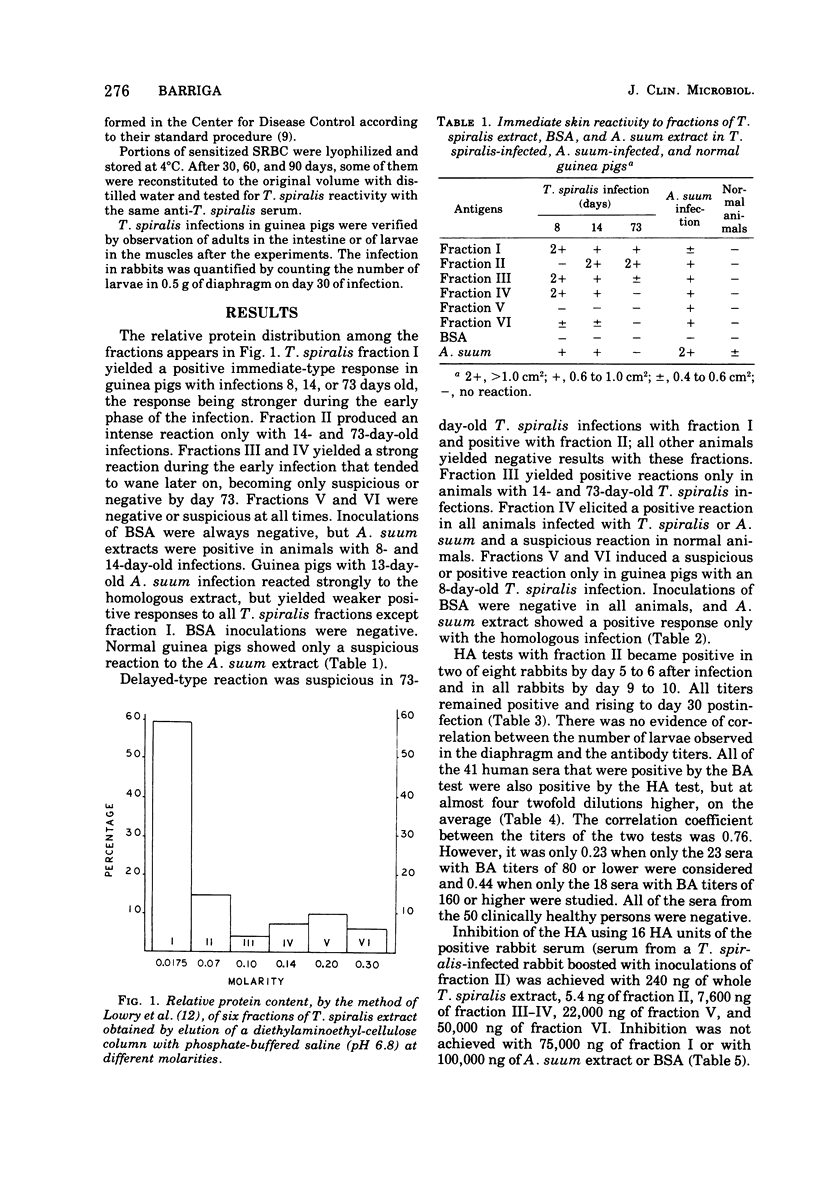
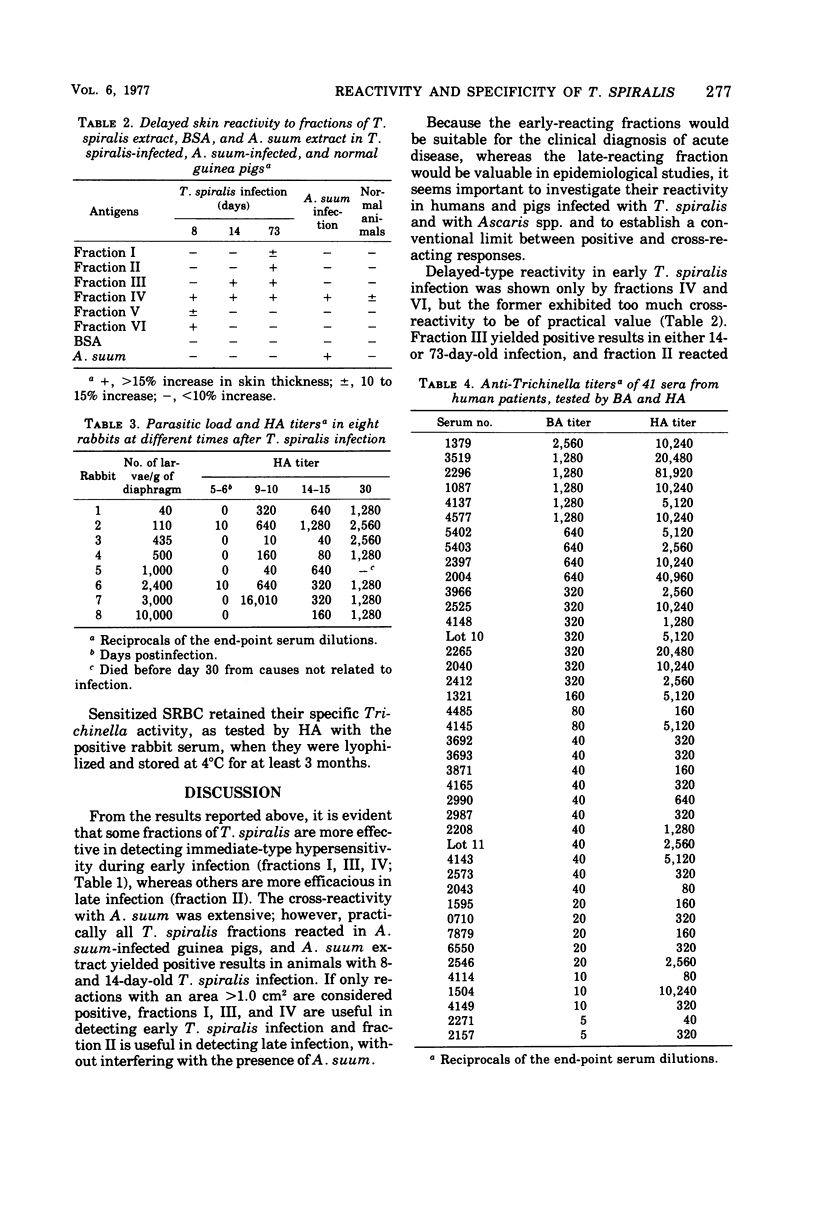
Six diethylaminoethyl-cellulose fractions of a larval Trichinella spiralis extract, an Ascaris suum extract, and a nonrelated protein were used for cutaneous tests in guinea pigs with 8-, 14-, and 73-day-old T. spiralis infections, in guinea pigs with 13-day-old A. suum infections, and in normal guinea pigs. A selected T. spiralis fraction was used in hemagglutination (HA) tests with sera of 8 T. spiralis-infected rabbits, 41 sera of trichinellosis patients positive by bentonite agglutination tests, and 50 sera of clinically healthy persons. Immediate-type cutaneous reactions revealed extensive cross-reactivity between both parasites, although the establishment of conventional limits for considering a reaction positive allowed the specific diagnosis of acute or chronic trichinellosis with different fractions. Delayed-type reactions were specific with all fractions except one, and different fractions reacted during either the acute or the chronic phase of trichinellosis. HA detected anti-Trichinella antibodies in all the rabbits 9 to 10 days postinfection, in all trichinellosis patients, and in none of the healthy people. Correlation between HA and bentonite agglutination titers and other considerations suggest that HA with the selected fraction detects early antibodies. HA inhibition tests with A. suum extract suggest lack of HA cross-reactivity between the A. suum- and T. spiralis-selected fractions. The use of different fractions in diverse tests for clinical or epidemiological studies is suggested.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avrameas S., Taudou B., Chuilon S. Glutaraldehyde, cyanuric chloride and tetrazotized O-dianisidine as coupling reagents in the passive hemagglutination test. Immunochemistry. 1969 Jan;6(1):67–76. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(69)90179-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOZAR M., KOZAR Z., KARMANSKA K. THE COMPARATIVE EVALUATION OF SOME AGGLUTINATION TESTS IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF TRICHINELLOSIS. Wiad Parazytol. 1964;10:717–737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagan I. G. Evaluation of routine serologic testing for parasitic diseases. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1965 Nov;55(11):1820–1829. doi: 10.2105/ajph.55.11.1820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruitenberg E. J., Steerenberg P. A., Brosi B. J., Buys J. Serodiagnosis of Trichinella spiralis infections in pigs by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays. Bull World Health Organ. 1974;51(1):108–109. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. S., Gore R. W., Sadun E. H. Trichinella spiralis: antigen-antibody interaction assayed by radioactive iodinated antigen. Exp Parasitol. 1972 Apr;31(2):299–306. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(72)90121-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann W. J., Steele J. H., Kagan I. G. Trichiniasis in the U.S. population, 1966-70. Prevalence and epidemiologic factors. Health Serv Rep. 1973 Aug-Sep;88(7):606–623. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



