Abstract
The nitrate dissimilation pathway is important for anaerobic growth in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. In addition, this pathway contributes to P. aeruginosa virulence by using the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans as a model host, as well as biofilm formation and motility. We used a set of nitrate dissimilation pathway mutants to evaluate the virulence of P. aeruginosa PA14 in a model of P. aeruginosa-phagocyte interaction by using the human monocytic cell line THP-1. Both membrane nitrate reductase and nitrite reductase enzyme complexes were important for cytotoxicity during the interaction of P. aeruginosa PA14 with THP-1 cells. Furthermore, deletion mutations in genes encoding membrane nitrate reductase (ΔnarGH) and nitrite reductase (ΔnirS) produced defects in the expression of type III secretion system (T3SS) components, extracellular protease, and elastase. Interestingly, exotoxin A expression was unaffected in these mutants. Addition of exogenous nitric oxide (NO)-generating compounds to ΔnirS mutant cultures restored the production of T3SS phospholipase ExoU, whereas nitrite addition had no effect. These data suggest that NO generated via nitrite reductase NirS contributes to the regulation of expression of selected virulence factors in P. aeruginosa PA14.
The ubiquitous gram-negative bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa is an opportunistic pathogen responsible for both acute and chronic infections. P. aeruginosa is commonly an etiologic agent in ear infections (8), infections of burn wounds (27), corneal keratitis (21, 30), and pulmonary infections in patients with cystic fibrosis (16) and ventilator-associated pneumonia (5). P. aeruginosa is frequently resistant to conventional antibiotic therapy and the antimicrobial effector mechanisms of phagocytes (9), particularly in the biofilm mode of growth (15).
The establishment of P. aeruginosa infection is accompanied by the synthesis of a diverse array of virulence factors composed of various exoproteins, such as elastase and exotoxin A, as well as the mucoid exopolysaccharide alginate (20). The type III secretion system (T3SS), a mechanism whereby cytotoxic effector proteins are directly secreted into the host cell cytoplasm following contact of the bacterium with a target cell (11), has also been identified as a virulence determinant of P. aeruginosa that contributes significantly to the pathogenesis of acute infection (45, 46). The P. aeruginosa T3SS plays a major role in triggering cell death in phagocytes and epithelial cells (17) and is composed of at least 20 proteins, including (i) a secretory apparatus, (ii) machinery devoted to the direct translocation of effectors into the host cell cytoplasm, and (iii) four effector proteins, ExoS, ExoT, ExoU, and ExoY, that contribute to host cell toxicity (19, 46). Regulation of virulence factor expression in P. aeruginosa is hierarchical and highly complex, involving quorum sensing (37, 44) and responses to environmental signals, including stresses applied via host defense mechanisms (46).
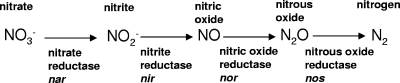
P. aeruginosa is capable of growing anaerobically by using nitrate as a terminal electron acceptor through the denitrification pathway. The pathway and the operons (47) encoding the enzymatic steps are shown in Fig. 1. The pathway intermediate nitric oxide (NO) is highly reactive with iron-containing prosthetic groups of proteins such as heme and Fe-S clusters (18). NO detoxification by NO reductase during anaerobic growth is therefore important for maintenance of cell function. In addition, NO is a potent antimicrobial effector produced by phagocytes (4), and P. aeruginosa flavohemoglobin has an important role in NO detoxification under aerobic conditions (1). Hence, P. aeruginosa must control NO toxicity produced both internally and by the host in order to survive under different environmental conditions.
FIG. 1.
Schematic of the denitrification pathway in P. aeruginosa. The representative operons are in italics.
NO is also widely appreciated as an important signaling molecule in many biological systems (7). We recently demonstrated roles for membrane nitrate reductase and nitrite reductase, the first two enzymes in the denitrification pathway, in swarming motility, biofilm formation, and virulence in the surrogate nematode host Caenorhabditis elegans (43).
These processes were assayed under aerobic conditions, indicating that the roles played by nitrate reductase and nitrite reductase were distinct from their contribution to the bioenergetics of P. aeruginosa anaerobic growth (43). The finding that similar phenotypes were displayed by a nitrate reductase (ΔnarGH) mutant and a nitrite reductase (ΔnirS) mutant suggested that nitrite or NO served as a signaling molecule in these processes, since downstream NO reductase and nitrous oxide reductase mutants behaved comparably to wild-type P. aeruginosa.
In this study, we used a set of denitrification pathway mutants to evaluate the virulence of P. aeruginosa PA14 in a model of phagocyte interaction by using the human monocytic cell line THP-1 (41). We show that both membrane nitrate reductase and nitrite reductase enzyme complexes are important for virulence during the interaction of P. aeruginosa PA14 with THP-1 cells. Furthermore, the ΔnarGH and ΔnirS deletion mutants were defective in the expression of T3SS components, extracellular protease, and elastase. Interestingly, exotoxin A expression was unaffected in these mutants. Addition of exogenous NO-generating compounds to ΔnirS mutant cultures restored production of T3SS phospholipase ExoU production, whereas nitrite addition had no effect. These data provide genetic and biochemical evidence indicating that NO generated via nitrite reductase contributes to the regulation of expression of selected virulence factors in P. aeruginosa PA14.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Strains.
P. aeruginosa strain PA14 (31) served as the parental strain for all studies. Mutant strains derived from PA14 are described in Table 1. For experiments analyzing exotoxin A production, P. aeruginosa PA103 was used as a positive control and toxA mutant PA103-29 (28) was used as a negative control.
TABLE 1.
Strains used in this study
| Strain | Description | Reference(s) |
|---|---|---|
| PA14 | Parental wild type | 31 |
| PA14 ΔnarGH | Membrane nitrate reductase polar deletion mutant | 43 |
| PA14 ΔnirS | Nitrite reductase polar deletion mutant | 43 |
| Complemented PA14 ΔnarGH | ΔnarGH::mini-Tn7-narX′K1K2GHJI; insertion of wild-type copy of narX′K1K2GHJI downstream of glmS site in membrane nitrate reductase mutant | 43 |
| Complemented PA14 ΔnirS | ΔnirS complemented with cosmid pMO011424 containing entire nir operon; Tetr Kanr | 32, 43 |
| PA14 MAR2xT7::norB | NO reductase mutant; Gmr | 24 |
| PA14 MAR2xT7::nosZ | Nitrous oxide reductase mutant; Gmr | 24 |
| PA14 MAR2xT7::pcrV | T3SS mutant deficient in proper translocation of effector molecules; Gmr | 24 |
| PA14 ΔexoU | T3SS effector mutant deficient in phospholipase activity | 26 |
| PA14 ΔexoT | T3SS effector mutant deficient in ADP ribosylation and small G-protein activating protein activity | 26 |
| PA103 | Overproduces ToxA protein | 28 |
| PA103-29 | ToxA-deficient mutant of PA103 | 28 |
P. aeruginosa-THP-1 cell coculture system.
P. aeruginosa-phagocyte interactions were performed with the human monocytic cell line THP-1 (41). THP-1 cells (American Type Culture Collection, Manassas, VA) were routinely cultured in RPMI 1640 tissue culture medium supplemented with 1% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum, 10 mM HEPES, 1 mM sodium pyruvate, 2.5 g/liter glucose, 0.05 mM β-mercaptoethanol, penicillin-streptomycin, and GlutaMAX (Invitrogen Corp.). P. aeruginosa strains were grown overnight in LB medium and washed twice with phosphate-buffered saline. In a total volume of 100 μl of RPMI 1640 tissue culture medium supplemented with 1% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum, 4 × 105 unstimulated THP-1 cells were mixed with 4 × 104 bacteria (multiplicity of infection [MOI] of 0.1) in 1-ml round-bottom culture tubes at 37°C. In some experiments, the MOI was increased to 1.0 or 10, as indicated in the figures. Organisms and THP-1 cells were brought together by spinning the tubes at 500 × g for 7 min, after which they were cocultured at 37°C for various intervals of time. Immediately after the mixing of bacteria with THP-1 cells and at 2, 4, and 6 h of incubation, 650 μl sterile distilled H2O was added to the tube, the tube contents were vortexed vigorously to lyse host cells, and aliquots were plated on LB agar to quantitate CFU. CFU were determined after 24 h of incubation at 37°C. Data are expressed as CFU per milliliter. In the absence of host cells, all bacterial strains grew to approximately 1 × 107 to 3 × 107 CFU/ml after 6 h of incubation (data not shown).
Cytotoxicity assay.
The cytotoxicity of P. aeruginosa for THP-1 cells was determined by measuring lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release following coculture. At an MOI of either 0.1 or 1.0, as indicated in the figures, strains were combined with THP-1 cells in the wells of an opaque 96-well microtiter dish with 4 × 105 THP-1 cells per well and a final volume of 100 μl per well. Organisms and THP-1 cells were brought together by spinning the plates at 500 × g for 7 min, after which they were cocultured for 6 h at 37°C. After coculture, LDH release was measured by adding the CytoTox-One Homogeneous Membrane Integrity Assay reagent (Promega) in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions. As a negative control, THP-1 cells were incubated in the absence of P. aeruginosa (described as “untreated” [see Fig. 3]). In addition, wells containing only P. aeruginosa were included in each assay. LDH release in experimental samples was calculated as a percentage of the LDH released by uninfected THP-1 cells that had been lysed with the Triton X-100 provided in the kit.
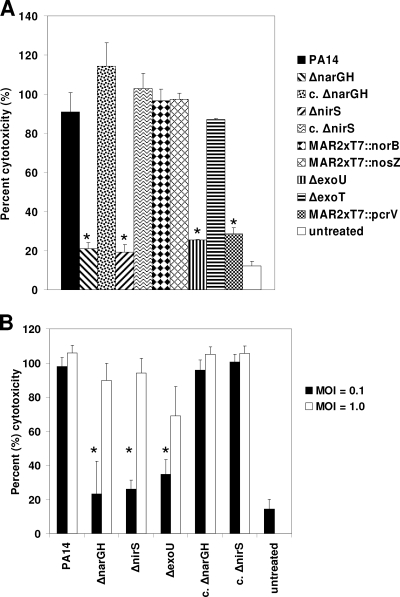
FIG. 3.
Cytotoxicity of P. aeruginosa for THP-1 cells. (A) Cytotoxicity for THP-1 cells was determined by measuring LDH release following interaction with P. aeruginosa. Wild-type PA14 and denitrification pathway mutants were cocultured with THP-1 cells at an MOI of 0.1 for 6 h. T3SS (ΔexoU, ΔexoT, and MAR2xT7::pcrV) mutants were also examined. Compared to wild-type PA14, the membrane nitrate reductase (ΔnarGH) and nitrite reductase (ΔnirS) mutants induced significantly less cytotoxicity against THP-1 cells, similar to the ΔexoU and MAR2xT7::pcrV T3SS mutants. In contrast, the genetically complemented ΔnarGH and ΔnirS mutant strains (c. ΔnarGH and c. ΔnirS, respectively), as well as the ΔexoT, MAR2xT7::norB, and MAR2xT7::nosZ T3SS mutants, induced cytotoxicity comparably to that of wild-type PA14. (B) Comparison of cytotoxicity against THP-1 cells at MOIs of 0.1 and 1.0. At the higher MOI of 1.0, all of the strains induced comparable levels of cytotoxicity. There was no significant release of LDH from strain PA14 in the absence of THP-1 cells (data not shown).
Induction of the T3SS in axenic culture and immunodetection of secreted proteins.
In accordance with the protocol of Lee et al. (23), all strains were grown overnight in LB broth, subcultured at a dilution of 1:1,000 in LB broth supplemented with 5 mM EGTA to chelate calcium and promote secretion of T3SS exoproducts, and grown at 37°C for 6 h with aeration. Cell densities were determined by measuring optical density at 660 nm (OD660), and culture supernatants were collected. The final OD660 was approximately 0.7 to 0.8. Proteins from the supernatant were precipitated with 10% trichloroacetic acid and 0.02% sodium deoxycholate. Pellets were washed with acetone to remove detergent and lipids. Protein precipitates were solubilized in sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis sample buffer in a volume normalized to the cell density based on the OD660 of each culture and fractionated on a 12% SDS-polyacrylamide gel. Proteins were either stained with Coomassie blue or transferred to nitrocellulose for detection by Western blotting with monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) against either phospholipase ExoU or translocator protein PcrV or with rabbit polyclonal antiserum against bifunctional type III cytotoxin ExoT (generously provided by Dara W. Frank, Milwaukee, WI). In some experiments, the EGTA-treated LB medium was supplemented with the exogenous NO donor S-nitrosoglutathione (GSNO) (1, 3), sodium nitroprusside dehydrate (SNP) (1), or 2,2′-(hydroxynitrosohydrazono)bis-ethanimine (DETA-NO) (6) or with sodium nitrite. GSNO, SNP, DETA-NO, or sodium nitrite was added to cultures in EGTA-treated LB broth 1 h prior to the harvesting of proteins from the culture supernatant (10). All chemicals were from Sigma-Aldrich.
Measurement of NO concentrations.
NO concentrations were measured with an Apollo 4000 Free Radical Analyzer with ISO NOP sensors (World Precision Instruments, Sarasota, FL). A standard curve for the conversion of picoamperes of electrical current to NO concentrations was generated by the addition of a range of concentrations of potassium nitrite (World Precision Instruments) to 0.1 M KI in 0.1 M H2SO4 (acidified KI), in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions. All standard curves and enzyme reactions were performed in temperature-controlled reaction vessels (World Precision Instruments) at a constant temperature of 37°C (6). Wild-type and ΔnirS mutant strain PA14 bacteria were grown in LB broth supplemented with 5 mM EGTA to an OD660 of 0.7 to 0.8. Cells were diluted to an OD660 of 0.04 in a total volume of 2 ml LB broth containing 3 mM SNP. Picoamperes of electrical current were measured at 1-s intervals for 5 min, allowing the cells to reach a steady state, and the picoamperes of electrical current were converted to nanomolar NO by using the standard curve described above. The NO concentration generated in the absence of P. aeruginosa was also determined.
Detection of P. aeruginosa exotoxin A secretion.
Trypticase soy broth (TSB) treated with Chelex was prepared as described previously (28) and used for exotoxin A production. Overnight cultures grown in TSB treated with Chelex were diluted 1:100 in fresh medium and allowed to grow for 24 h at 37°C with aeration. Cells were harvested by centrifugation, and the supernatant was collected for analysis of exotoxin A secretion by Western blotting. Proteins were separated on a 12% Tris-glycine SDS-polyacrylamide gel, transferred to membrane filters, and probed with polyclonal rabbit anti-exotoxin A antiserum (a generous gift from Abdul N. Hamood, Lubbock, TX) at a 1:4,000 dilution. Purified exotoxin A (1 μg) was used as a positive control in the Western blot assays.
Quantitation of total protease and LasB elastase secretion.
Total protease secretion was determined by the method of Rinderknecht et al. (34). A 50-μl volume of supernatant from an overnight culture of P. aeruginosa grown in peptone-TSB was added to 2 ml of 10 mM HEPES buffer (pH 7.5) containing 20 mg of hide powder blue (Sigma-Aldrich) as a substrate. Release of bound dye was indicative of protease activity. The suspension was mixed at 37°C for 1 h, insoluble substrate was removed by centrifugation, and the A595 of the supernatant was determined. Absorbance readings were normalized to the protein concentration of the culture supernatant determined by the bicinchoninic acid method (Pierce).
A similar experiment was performed to evaluate LasB elastase secretion (40). A 100-μl volume of supernatant from an overnight culture grown in peptone-TSB was added to 2 ml of 0.1 M Tris-maleate with 0.1 mM CaCl2 (pH 7.0) containing 10 mg elastin-Congo red (Sigma-Aldrich). The suspension was mixed at 37°C for 18 h, insoluble substrate was removed by centrifugation, and the A495 of the supernatant was determined. Absorbance readings were normalized to the protein concentration of the culture supernatant determined by the bicinchoninic acid method (Pierce).
Reverse transcription (RT)-PCR.
For detection of transcripts encoding P. aeruginosa exoproducts from axenic cultures, organisms were grown in calcium-chelated LB medium as described above. After 6 h, RNA was extracted from 2 ml of culture with RNAprotect Bacteria Reagent and RNeasy Mini Spin columns in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions (Qiagen). For detection of transcripts during interaction with phagocytes, P. aeruginosa-THP-1 cell cocultures were incubated at an MOI of either 0.1 or 1.0 at 37°C; after 2 h of incubation, RNA was extracted in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions. RNA was treated with RNase-free DNase I (Invitrogen). PCR with oligonucleotide primers GroEL F1 and GroEL R1 (Table 2) was used to confirm the absence of contaminating DNA in the purified RNA. In addition, reverse transcriptase was omitted from negative control RT-PCRs to confirm the absence of contaminating DNA in the RNA samples. The oligonucleotides used in the RT-PCRs and the predicted sizes of the respective amplicons are shown Table 2.
TABLE 2.
Oligonucleotides used in this study
| Name | Sequence (5′→3′) | Predicted amplicon size (bp) |
|---|---|---|
| narH RT S | 5′GAGATCGACGACTACTACGAACC 3′ | 677 |
| narH RT AS | 5′CACCTGCTCCACGCTCAACC 3′ | |
| GroEL F1 | 5′CGCTCGCAAGAAAATGCTGGTC 3′ | 550 |
| GroEL R1 | 5′CGACGGACAGTTCGTTTTCCAG 3′ | |
| nirS RT S | 5′AGGTCGTTGAGCTGTTTCTTCG 3′ | 437 |
| nirS RT AS | 5′GCCAAGGACGACATGAAAGC 3′ | |
| ExoU RT S | 5′GGGAATACTTTCGGGAAGTT 3′ | 428 |
| Exo U RT AS | 5′CGATCTCGCTGCTAATGTGTT 3′ | |
| PcrV RT S | 5′ATGGAAGTCAGAAACCTTAATGCC 3′ | 629 |
| PcrV RT AS | 5′AAATCCTTGATCGACAGCTTGC 3′ | |
| ExoT RT S | 5′CATATTCAATCATCTCAGCAGAACC 3′ | 398 |
| ExoT RT AS | 5′AGTCTCTCCTCTGTCAAAGTCG 3′ | |
| RhlA RT S | 5′GAAAGTCTGTTGGTATCGGTTTGC 3′ | 494 |
| RhlA RT AS | 5′TATTGCCGACGGTCTCGTTG 3′ | |
| LasB RT S | 5′TTTCTACGCTTGACCTGTTGTTCG 3′ | 635 |
| LasB RT AS | 5′TACTTGCCGATCTTCTGGTTGC 3′ | |
| ToxA RT S | 5′TCAGTCATCGCCTGCATTTC 3′ | 460 |
| ToxA RT AS | 5′CTCGCGTTGATAGGGTGACC 3′ |
Statistical analysis.
CFU, cytotoxicity, elastin-Congo red (elastase), and hide powder blue (protease) assays were performed in triplicate in three independent experiments. Data presented are the mean ± the standard deviation (SD) of all nine samples. For cytotoxicity assays, mean blank values were subtracted from mean results, and the results were normalized to percent lysis relative to maximum-lysis samples. For these calculations, the final SD was calculated by standard error propagation methods. For all assays, statistical comparisons were performed with the Student t test, and P values of ≤0.05 were considered significant.
RESULTS
Membrane nitrate reductase (ΔnarGH) and nitrite reductase (ΔnirS) mutants are sensitive to killing by the human monocyte cell line THP-1.
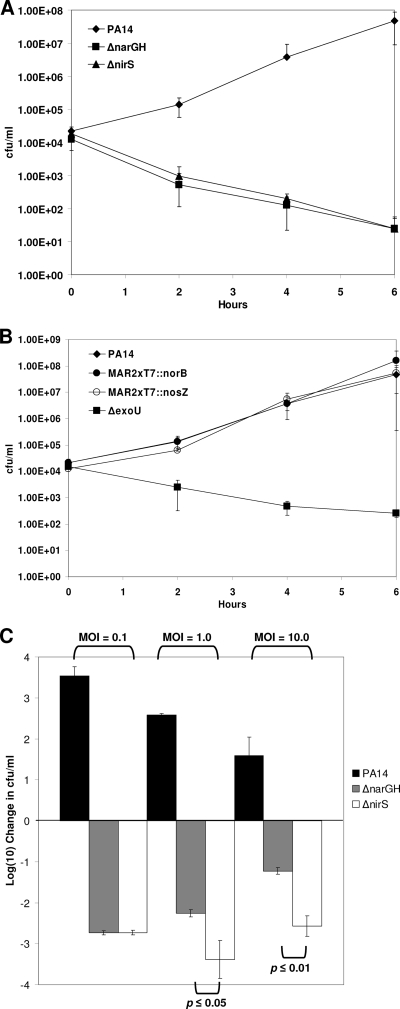
We showed previously that both the P. aeruginosa membrane nitrate reductase (ΔnarGH) mutant and the nitrite reductase (ΔnirS) mutant were avirulent in the nematode C. elegans slow-kill and fast-kill assays compared to parental strain PA14 (43). In a model of the P. aeruginosa-phagocyte interaction, we evaluated the survival of the wild-type PA14, ΔnarGH and ΔnirS mutant, and several other mutant strains (Fig. 2) after cocultivation with the human monocytic cell line THP-1 (41). We initiated our studies at a low MOI of 0.1 to provide a strong challenge to the bacterium by the phagocyte line. In coculture with THP-1 cells, wild-type PA14 organism numbers increased by several orders of magnitude during the incubation period. In contrast, the ΔnarGH and ΔnirS mutants were almost completely eliminated by the THP-1 human monocyte line after 6 h of incubation (Fig. 2A), whereas the genetically complemented ΔnarGH and ΔnirS mutants grew similarly to wild-type PA14 (data not shown). A T3SS phospholipase (ΔexoU) mutant was killed comparably to the ΔnarGH and ΔnirS mutants (Fig. 2B). However, the MAR2xT7::norB and MAR2xT7::nosZ transposon mutants, defective in the nitrate dissimilation pathway downstream of nitrite reductase, grew similarly to wild-type PA14 during cocultivation with THP-1 cells (Fig. 2B). In the absence of host cells, all bacterial strains grew to approximately 1 × 107 to 3 × 107 CFU/ml after 6 h of incubation (data not shown). At increased MOIs of 1.0 and 10, both the ΔnarGH and ΔnirS mutants were killed to a significantly greater degree than wild-type PA14 in the THP-1 cell-P. aeruginosa coculture (P ≤ 0.01) (Fig. 2C). Furthermore, the ΔnirS mutant was killed more effectively than the ΔnarGH mutant by THP-1 cells at MOIs of 1.0 (P ≤ 0.05) and 10.0 (P ≤ 0.01).
FIG. 2.
P. aeruginosa interaction with human monocytic cell line THP-1. (A) Wild-type PA14 and membrane nitrate reductase (ΔnarGH) and nitrite reductase (ΔnirS) mutant strains were cocultured with THP-1 cells at an MOI of 0.1 for up to 6 h. The ΔnarGH and ΔnirS mutants displayed reduced viability over time compared to that of wild-type PA14, as measured by CFU per milliliter. (B) Wild-type PA14 and NO reductase (MAR2xT7::norB), nitrous oxide reductase (MAR2xT7::nosZ), and T3SS (ΔexoU) mutants were cocultured with THP-1 cells as for panel A. Only ΔexoU displayed reduced viability over time. (C) Comparison of wild-type PA14 and ΔnarGH and ΔnirS mutant strain interactions with THP-1 cells at different MOIs. At all of the MOIs used, the two mutants displayed a reduction in viability compared to that of wild-type PA14. At MOIs of 1.0 and 10, the viability of the ΔnirS mutant was significantly less than that of the ΔnarGH mutant.
The cytotoxicity of the ΔnarGH and ΔnirS mutants for THP-1 cells is diminished at low MOIs.
To determine whether the decreased survival of the ΔnarGH and ΔnirS mutants correlated with reduced cytotoxicity against THP-1 cells, we compared the abilities of the mutants and their respective complemented strains with that of wild-type PA14 to induce release of LDH from THP-1 cells. Both the ΔnarGH and ΔnirS mutants displayed significantly less cytotoxicity against THP-1 cells than did wild-type PA14 and the complemented strains (P ≤ 0.01) at an MOI of 0.1 (Fig. 3). As expected, the ΔexoU and MAR2xT7::pcrV T3SS mutants also displayed significantly reduced cytotoxicity compared to that of wild-type PA14 (P ≤ 0.01). In contrast, the ΔexoT, MAR2xT7::norB, and MAR2xT7::nosZ mutants displayed levels of cytotoxicity similar to that of wild-type PA14 (Fig. 3A).
To determine whether increasing the MOI would affect cytotoxicity, we compared LDH release from THP-1 cells treated with P. aeruginosa at MOIs of 0.1 and 1.0 in a separate experiment (Fig. 3B). Even though the ΔnarGH and ΔnirS mutants were killed to a significant degree by THP-1 cells at an MOI of 1.0 compared to wild-type PA14 (Fig. 2C), the increased MOI resulted in a level of LDH release comparable to that of wild-type PA14 for both mutants, as well as for the ΔexoU mutant. These data suggested induction of other cytotoxic effectors at the higher MOI and led us to examine the mutants for expression of P. aeruginosa virulence factors with cytotoxic potential.
The ΔnarGH and ΔnirS mutants display decreased secretion of T3SS exoproducts ExoU, ExoT, and PcrV.
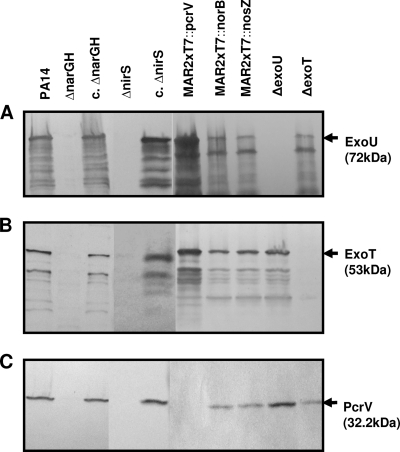
To explore the possibility that reduced T3SS exoproduct secretion contributed to the increased sensitivity of the ΔnarGH and ΔnirS mutants to phagocyte killing and their decreased cytotoxicity, we compared the production of selected T3SS exoproducts by the mutants and their respective genetically complemented strains to that by wild-type PA14. Supernatants of strains grown in calcium-depleted LB medium were analyzed by Western blotting with antibodies against ExoU, ExoT, or PcrV. The ΔnarGH and ΔnirS mutant strains displayed no detectable ExoU, ExoT, or PcrV secretion (Fig. 4A to C), whereas the complemented mutants and wild-type PA14 showed comparable degrees of secretion of each T3SS exoproduct. The MAR2xT7::norB and MAR2xT7::nosZ mutants also secreted levels of T3SS exoproducts comparable to those of wild-type PA14. Western blotting of whole-cell lysates from the ΔnarGH and ΔnirS mutants failed to detect the T3SS exoproducts, indicating that the products were not retained in the cells due to a secretion defect (data not shown).
FIG. 4.
Detection of T3SS exoproduct secretion by Western blotting. All strains were grown for 6 h in LB broth supplemented with 0.5 M EGTA to chelate calcium and induce expression of T3SS exoproducts (23). Culture supernatant proteins were precipitated and analyzed by Western blotting with a mouse MAb against either ExoU (A) or PcrV (C) or with rabbit polyclonal antiserum to ExoT (B). Representative Western blot assays are shown. T3SS exoproducts were not detected in the supernatant from either the ΔnarGH or the ΔnirS mutant. Supernatants from the ΔexoU (A), ΔexoT (B), and MAR2xT7::pcrV (C) mutant control strains were also negative for secretion of the corresponding exoproducts. c. ΔnarGH and c. ΔnirS, genetically complemented ΔnarGH and ΔnirS mutant strains, respectively.
These data indicate that a factor contributing to the decreased survival of the ΔnarGH and ΔnirS mutants following coculture with the THP-1 human monocyte line is their inability to generate and secrete T3SS exoproducts. Normal secretion of T3SS exoproducts by the MAR2xT7::norB and MAR2xT7::nosZ mutants suggests that the lack of a NO signal in the ΔnarGH and ΔnirS mutants contributes to this phenomenon and implicates endogenous NO production by nitrite reductase as an important regulator of the T3SS in P. aeruginosa PA14.
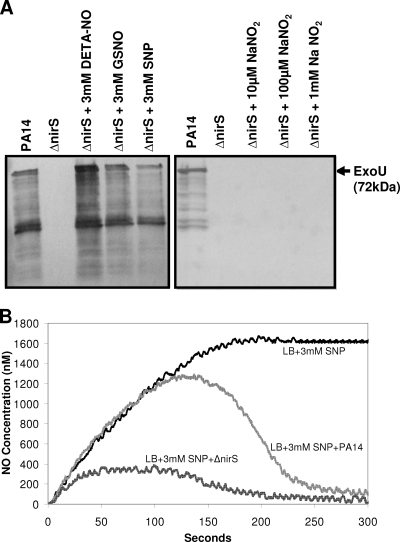
To test this possibility, the ΔnirS mutant was grown in EGTA-treated LB medium for 5 h and then supplemented with either GSNO, SNP, or DETA-NO at a final concentration of 3 mM (1). The culture was allowed to grow for an additional hour before the precipitation of proteins from the supernatant. The T3SS exoproduct ExoU was detected in culture supernatants following exposure to all three NO donors (Fig. 5A). In contrast, addition of increasing concentrations of sodium nitrite to ΔnirS mutant cultures did not stimulate ExoU expression (Fig. 5A). Thus, exogenous addition of a NO donor can rescue the T3SS expression deficiency of the ΔnirS mutant.
FIG. 5.
Restoration of ExoU expression in the ΔnirS mutant by supplementation with NO donors. (A) All strains were grown for 6 h in LB broth supplemented with 0.5 M EGTA to chelate calcium and induce the expression of T3SS exoproducts (23). Cultures were supplemented with either a NaNO2 or a NO donor (DETA-NO, GSNO, or SNP) 1 h prior to supernatant harvesting, as indicated. Culture supernatant proteins were precipitated and analyzed by Western blotting with a mouse MAb against ExoU. T3SS exoproducts were not detected in supernatants from the ΔnirS mutant supplemented with NaNO2. In contrast, exoproducts were detected in the supernatant of the ΔnirS mutant supplemented with all of the NO donors. (B) NO consumption by PA14 and the ΔnirS mutant in the presence of 3 mM SNP. The steady-state level of NO release by SNP occurred within 150 s, with a plateau at 1.6 μM (black line). The wild-type PA14 NO level peaked at 1.3 μM and reached a steady state at 200 nM (dark gray line). The ΔnirS mutant NO level peaked at 300 nM and reached a steady state at 100 nM.
We compared NO consumption between PA14 and the ΔnirS mutant in the presence of 3 mM SNP with a NO detector. A steady-state NO level is achieved in LB medium supplemented with SNP when the generation of NO by SNP is in equilibrium with the production of NO2−, as NO reacts with O2. The steady-state level of NO production from SNP alone plateaued within 150 s at 1.6 μM (Fig. 5B). The NO production of PA14 peaked at 1.3 μM and reached a steady-state level of 200 nM NO. In contrast, that of the ΔnirS mutant peaked at 300 nM and reached a steady-state NO level of 100 nM (Fig. 5B). These data suggest that the increased NO level in wild-type PA14 compared to that in the ΔnirS mutant is due to conversion of NO2− to NO by the functional NirS protein in PA14. In contrast, the ΔnirS mutant has only one source of available NO, that generated by SNP. In the absence of a NO donor, endogenous NO must be produced from NO2− by NirS. We determined the nitrite concentration in LB medium alone to be 5.5 μM (data not shown), indicating that wild-type strain PA14, but not the ΔnirS mutant, can produce endogenous NO under these culture conditions.
P. aeruginosa ΔnarGH and ΔnirS mutants display decreased total protease and elastase secretion but normal exotoxin A secretion.
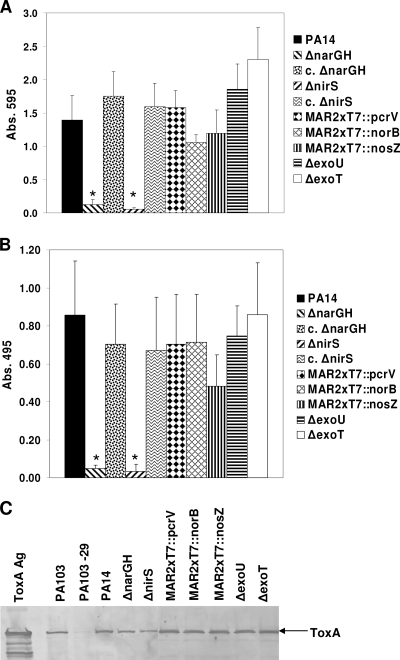
To determine whether the secretion of other P. aeruginosa exoproducts known to contribute to virulence was altered in the ΔnarGH and ΔnirS mutant strains, we evaluated the total protease, elastase (LasB), and exotoxin A secretion by these mutants. Both the ΔnarGH and ΔnirS mutants displayed a significant decrease (P ≤ 0.01) in total protease (Fig. 6A) and LasB elastase secretion (Fig. 6B) compared to that of wild-type PA14 and the complemented mutant strains. Wild-type PA14; the complemented ΔnarGH and ΔnirS mutants; the MAR2xT7::norB, MAR2xT7::nosZ, and T3SS mutants; and the ΔexoU, ΔexoT, and MAR2xT7::pcrV mutants all secreted comparable levels of both enzymes. In contrast, wild-type PA14, as well as all of the mutant strains derived from PA14, secreted comparable levels of exotoxin A (Fig. 6C). Purified exotoxin A and culture supernatant from P. aeruginosa PA103 were used as positive controls in the Western blot assay; culture supernatant from exotoxin A-deficient mutant P. aeruginosa PA103-29 (28) was used as a negative control (Fig. 6C).
FIG. 6.
Total protease, elastase, and exotoxin A secretion by denitrification pathway mutants. Culture supernatants from wild-type PA14 and denitrification pathway and T3SS mutants were compared for total protease (A) and elastase (B) activities. Only the ΔnarGH and ΔnirS mutants displayed significantly lower levels of protease and elastase secretion than wild-type PA14. Protease secretion was restored to normal in the genetically complemented ΔnarGH and ΔnirS mutant strains (c. ΔnarGH and c. ΔnirS, respectively). Supernatants from each strain were tested in triplicate in three separate experiments, and the data represent the mean ± SD. In contrast, wild-type PA14 and all of the mutant strains derived from PA14 secreted ToxA into their culture supernatants, as detected by Western blotting (C). P. aeruginosa PA103 and PA103-29 were used as positive and negative controls, respectively, for the production of exotoxin A; ToxA Ag is the purified P. aeruginosa exotoxin A (1 μg) used as a positive control for Western blotting. Abs. 495, absorbance at 495 nm.
Virulence factor expression is regulated at the level of transcription in the ΔnarGH and ΔnirS mutants.
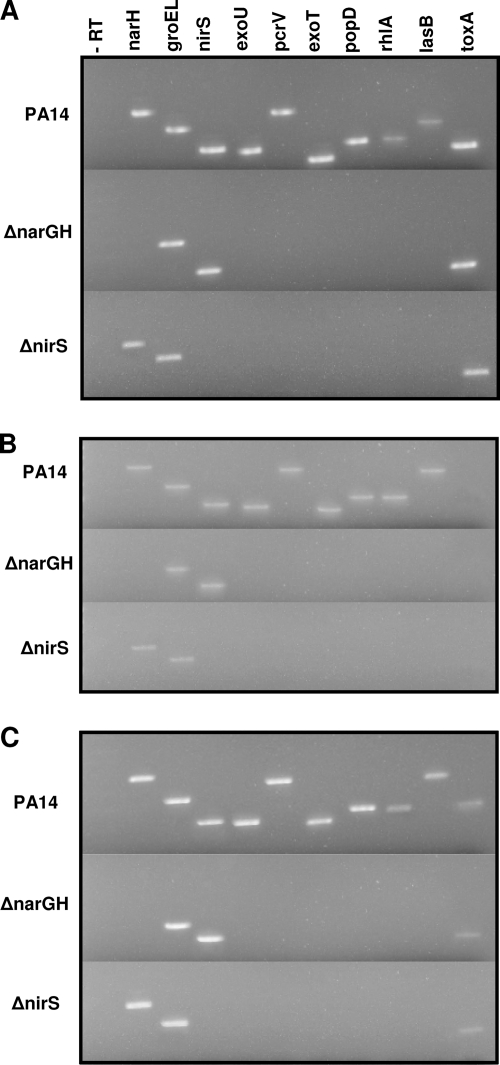
To determine whether lack of exoproduct secretion in the ΔnarGH and ΔnirS mutants was regulated at the level of transcription, we compared their steady-state mRNA levels to that of wild-type PA14 by RT-PCR both under T3SS-inducing culture conditions and during the P. aeruginosa-THP-1 cell interaction. groEL, narH, and nirS primers were used as positive controls in the RT-PCR; omission of reverse transcriptase served as a control for DNA contamination.
Under T3SS-inducing, axenic culture conditions (Fig. 7A), transcripts encoding the T3SS exoproducts ExoU, ExoT, PcrV, and PopD were not detected by RT-PCR in either the ΔnarGH or the ΔnirS mutant. The lasB elastase transcript was also not detected in the ΔnarGH and ΔnirS mutants. Earlier studies (43) demonstrated that the ΔnarGH mutant was defective in rhamnolipid production; accordingly, rhlA transcript expression was not detected in either the ΔnarGH or the ΔnirS mutant. As predicted from the Western blot assay data (Fig. 6C), toxA transcripts were detected in all three strains (Fig. 7A). Analysis of transcripts from the P. aeruginosa-THP-1 cell coculture at an MOI of either 0.1 (Fig. 7B) or 1.0 (Fig. 7C) also demonstrated lack of expression of T3SS exoproducts, rhlA, and lasB by the ΔnarGH and ΔnirS mutants. The toxA transcript was not detected at an MOI of 0.1 in wild-type PA14 or the ΔnarGH or ΔnirS mutant (Fig. 6B) but was present in all three strains at an MOI of 1.0 (Fig. 6C). To control for RNA integrity, groEL transcript was detected in all of the RT-PCR assays performed.
FIG. 7.
Detection of P. aeruginosa exoproduct gene expression by RT-PCR. Table 2 describes the oligonucleotides used for RT-PCR and the predicted size of each amplicon. (A) RT-PCR of mRNA extracted from axenic culture under T3SS-inducing conditions after 6 h of growth. (B) RT-PCR of mRNAs extracted from P. aeruginosa strains cocultured with the human monocytic cell line THP-1 at an MOI of 0.1. (C) RT-PCR of mRNAs extracted from P. aeruginosa strains cocultured with the human monocytic cell line THP-1 at an MOI of 1.0. In accordance with their secreted protein profiles, transcripts for proteases and T3SS exoproducts were not detected by RT-PCR in the ΔnarGH and ΔnirS mutants under any of the conditions tested. toxA transcripts were detected in wild-type PA14 and the ΔnarGH and ΔnirS mutants under T3SS-inducing culture conditions (A) and during the P. aeruginosa interaction with THP-1 cells at an MOI of 1.0 (C) but not at an MOI of 0.1 (B). The toxA expression profiles of the ΔnarGH and ΔnirS mutants correlate with the cytotoxicity data shown in Fig. 3B. −RT, control without reverse transcriptase.
Taken together, the results suggest that the increased susceptibility of the ΔnarGH and ΔnirS mutants to killing by THP-1 cells and the decreased cytotoxic capacity of these mutants are due to the lack of expression of T3SS exoproducts, and possibly lack of proteolytic enzyme expression, at an MOI of 0.1. However, the cytotoxicity against THP-1 cells at the higher MOI of 1.0 by the ΔnarGH, ΔnirS, and ΔexoU mutants (Fig. 3B) was likely attributable to induction of normal levels of exotoxin A expression (25, 29). The data are consistent with the hypothesis that endogenous NO generated by nitrite reductase contributed to regulation of expression at the level of transcription of T3SS exoproducts, rhamnolipid, protease, and elastase, but not exotoxin A, in P. aeruginosa PA14.
DISCUSSION
Dissimilation of nitrogen oxides, particularly nitrate and nitrite, drives energy metabolism under anaerobic conditions in a variety of bacteria, including P. aeruginosa (35). In addition to its role in anaerobic growth of P. aeruginosa, our previous work has shown that the nitrate dissimilation pathway modulates factors important in pathogenesis under conditions where oxygen is apparently not limiting, including motility, initiation of biofilm formation, and virulence in a surrogate model host, the nematode C. elegans (43). In the present study, we extended these observations to the P. aeruginosa-phagocyte interaction by using the pathogenic strain PA14 (31). Mutants deficient in membrane nitrate reductase and nitrite reductase, the first two steps of the nitrate dissimilation pathway (Fig. 1), were readily killed by the human monocytic cell line THP-1 (41), while mutants deficient in NO reductase and nitrous oxide reductase, the last two steps in the pathway, grew unchecked by THP-1 cells, similarly to wild-type PA14 (Fig. 2A and B).
We demonstrated that NirS expression in P. aeruginosa PA14 is required to induce the T3SS that translocates effector proteins ExoT and ExoU into host cells. A nirS mutant unable to express the T3SS could be rescued by the exogenous addition of a NO donor, suggesting that the product of nitrite reductase activity may act as a signaling molecule, allowing P. aeruginosa PA14 to induce the T3SS. Thus, the defects in virulence can be attributed to an inability to induce the T3SS in the nir mutant.
Transcriptional regulation of the P. aeruginosa T3SS is complex (46), but all T3SS genes are under the direct transcriptional control of ExsA, an AraC family transcriptional activator. ExsA activation is antagonized by two antiactivators, ExsD and PtrA. T3SS transcription is coupled to T3SS activity, controlled through modulation of cyclic AMP biosynthesis, repressed by a variety of stresses, involved with multiple two-component regulatory systems, and inversely related to biofilm formation (46). We propose that an additional environmental signal involved in T3SS regulation is NO.
Only a limited number of transcriptional regulators have been demonstrated to interact with NO (see reference 35 for a review of transcription factors regulating the denitrification pathway). P. aeruginosa has four members of the Crp/FNR family of transcriptional activators (22); Vfr is an ortholog of Crp, ANR is an ortholog of FNR and responds to anaerobiosis, and DNR responds to NO (12, 33). ANR regulates nar and dnr expression, while DNR regulates nirS, nirQ, norBC, and nos expression (2, 35). These four denitrification genes are the only ones predicted to be regulated by DNR (35). Direct binding of gaseous NO to a ferrous heme cofactor regulates the activity of DNR in P. aeruginosa (12). Brucella melitensis NnrA is a member of this family, and it is thought that NO may serve as the signal sensed by NnrA (14).
Under aerobic conditions, the P. aeruginosa flavohemoglobin (fhp) detoxifies NO and is regulated by the NO-responsive regulator FhpR (1). FhpR is an ortholog of Escherichia coli NorR, a σ54-dependent member of the NtrC family of transcriptional activators. Binding of NO to a nonheme iron center in the GAF domain results in mononitrosyl-iron complex formation and converts NorR to its active form (42). NorR regulons are small, and it has been predicted that P. aeruginosa NorR (FhpR) regulates only itself and the fhp-nnrS operon (35).
A third type of NO-responsive regulator is NsrR, a member of the Rrf2 family of transcriptional repressors. Although P. aeruginosa contains several members of the Rrf2 family (Pfam02082), it does not have a protein closely related to NsrR (35). Thus, it is unlikely that an Rrf2 family repressor is the NO-responsive regulator that affects T3SS expression. Other possibilities for NO regulation of virulence factor expression in P. aeruginosa PA14 would include a two-component sensor-response regulator that senses NO similarly to the sensing of nitrate by the sensor-response regulator NarX-NarL (39). Our previous work (43) showed that a C. elegans ΔnarXL mutant was fully virulent, likely precluding a role for this two-component system in virulence factor expression. However, the numerous “hypothetical” two-component sensor-response regulators in the PA14 genome are potential candidates.
Recent work by Schreiber et al. (36) indicates that, under aerobic conditions, a nirS-lacZ fusion in P. aeruginosa PAO1 expressed low but measurable levels of β-galactosidase activity, even without the addition of exogenous nitrate. Furthermore, denitrifying bacteria, such as P. stutzeri, avoid NO toxicity by using the enzymes in the nitrate dissimilation pathway to maintain a low, nanomolar, steady-state concentration of free NO in the cell (13). We propose that P. aeruginosa maintains a similar physiological level of NO via basal nitrate and nitrite reductase activities to regulate the expression of selected virulence factors. We believe that the 5 μM concentration of nitrite in LB broth is sufficient to provide substrate to NirS, which has very low activity in aerobically grown cells, resulting in a low steady-state level of NO.
The comparisons of the transcriptional profiles of the ΔnarGH and ΔnirS mutants with that of wild-type PA14 currently in progress, combined with nitrosylation profile comparisons (38) of these strains, should provide insight into the mechanisms of NO regulation of virulence factor expression in P. aeruginosa PA14. Understanding these mechanisms may suggest new therapeutic options for inhibiting virulence factor expression in P. aeruginosa.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation (IGLEWS03FG0) and the National Institutes of Health (R37AI33713). N.E.V. was supported in part by a grant (5 T32 AI007285) from the National Institutes of Health.
We thank Dara W. Frank (Milwaukee, WI) for antibodies to ExoU, ExoS, and PcrV; Abdul N. Hamood (Lubbock, TX) for purified ToxA antigen and ToxA antibody; Eliena Drenkhard for the T3SS exoproduct deletion mutants; and Michelle Dziejman for critical reading of the manuscript.
Editor: A. J. Bäumler
Footnotes
Published ahead of print on 3 August 2009.
REFERENCES
- 1.Arai, H., M. Hayashi, A. Kuroi, M. Ishii, and Y. Igarashi. 2005. Transcriptional regulation of the flavohemoglobin gene for aerobic nitric oxide detoxification by the second nitric oxide-responsive regulator of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol. 187:3960-3968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Arai, H., Y. Igarashi, and T. Kodama. 1995. Expression of the nir and nor genes for denitrification of Pseudomonas aeruginosa requires a novel CRP/FNR-related transcriptional regulator, DNR, in addition to ANR. FEBS Lett. 371:73-76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Barraud, N., D. J. Hassett, S. H. Hwang, S. A. Rice, S. Kjelleberg, and J. S. Webb. 2006. Involvement of nitric oxide in biofilm dispersal of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol. 188:7344-7353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bogdan, C. 2001. Nitric oxide and the immune response. Nat. Immunol. 2:907-916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Brewer, S. C., R. G. Wunderink, C. B. Jones, and K. V. Leeper, Jr. 1996. Ventilator-associated pneumonia due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Chest 109:1019-1029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Cardinale, J. A., and V. L. Clark. 2005. Determinants of nitric oxide steady-state levels during anaerobic respiration by Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Mol. Microbiol. 58:177-188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Cooper, C. E. 1999. Nitric oxide and iron proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1411:290-309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Dohar, J. E., P. A. Hebda, R. Veeh, M. Awad, J. W. Costerton, J. Hayes, and G. D. Ehrlich. 2005. Mucosal biofilm formation on middle-ear mucosa in a nonhuman primate model of chronic suppurative otitis media. Laryngoscope 115:1469-1472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Donlan, R. M., and J. W. Costerton. 2002. Biofilms: survival mechanisms of clinically relevant microorganisms. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 15:167-193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Firoved, A. M., S. R. Wood, W. Ornatowski, V. Deretic, and G. S. Timmins. 2004. Microarray analysis and functional characterization of the nitrosative stress response in nonmucoid and mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol. 186:4046-4050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Frank, D. W. 1997. The exoenzyme S regulon of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol. Microbiol. 26:621-629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Giardina, G., S. Rinaldo, K. A. Johnson, A. Di Matteo, M. Brunori, and F. Cutruzzola. 2008. NO sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: structure of the transcriptional regulator DNR. J. Mol. Biol. 378:1002-1015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Goretski, J., O. C. Zafiriou, and T. C. Hollocher. 1990. Steady-state nitric oxide concentrations during denitrification. J. Biol. Chem. 265:11535-11538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Haine, V., M. Dozot, J. Dornand, J. J. Letesson, and X. De Bolle. 2006. NnrA is required for full virulence and regulates several Brucella melitensis denitrification genes. J. Bacteriol. 188:1615-1619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Hall-Stoodley, L., J. W. Costerton, and P. Stoodley. 2004. Bacterial biofilms: from the natural environment to infectious diseases. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2:95-108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hassett, D. J., J. Cuppoletti, B. Trapnell, S. V. Lymar, J. J. Rowe, S. S. Yoon, G. M. Hilliard, K. Parvatiyar, M. C. Kamani, D. J. Wozniak, S. H. Hwang, T. R. McDermott, and U. A. Ochsner. 2002. Anaerobic metabolism and quorum sensing by Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms in chronically infected cystic fibrosis airways: rethinking antibiotic treatment strategies and drug targets. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 54:1425-1443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Hauser, A. R., and J. N. Engel. 1999. Pseudomonas aeruginosa induces type-III-secretion-mediated apoptosis of macrophages and epithelial cells. Infect. Immun. 67:5530-5537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Henry, Y., and A. Guissani. 1999. Interactions of nitric oxide with hemoproteins: roles of nitric oxide in mitochondria. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 55:1003-1014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hueck, C. J. 1998. Type III protein secretion systems in bacterial pathogens of animals and plants. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 62:379-433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hutchison, M. L., and J. R. Govan. 1999. Pathogenicity of microbes associated with cystic fibrosis. Microbes Infect. 1:1005-1014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Jeng, B. H., and S. D. McLeod. 2003. Microbial keratitis. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 87:805-806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Körner, H., H. J. Sofia, and W. G. Zumft. 2003. Phylogeny of the bacterial superfamily of Crp-Fnr transcription regulators: exploiting the metabolic spectrum by controlling alternative gene programs. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 27:559-592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Lee, V. T., R. S. Smith, B. Tummler, and S. Lory. 2005. Activities of Pseudomonas aeruginosa effectors secreted by the type III secretion system in vitro and during infection. Infect. Immun. 73:1695-1705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Liberati, N. T., J. M. Urbach, S. Miyata, D. G. Lee, E. Drenkard, G. Wu, J. Villanueva, T. Wei, and F. M. Ausubel. 2006. An ordered, nonredundant library of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain PA14 transposon insertion mutants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103:2833-2838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Middlebrook, J. L., and R. B. Dorland. 1977. Response of cultured mammalian cells to the exotoxins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Corynebacterium diphtheriae: differential cytotoxicity. Can. J. Microbiol. 23:183-189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Miyata, S., M. Casey, D. W. Frank, F. M. Ausubel, and E. Drenkard. 2003. Use of the Galleria mellonella caterpillar as a model host to study the role of the type III secretion system in Pseudomonas aeruginosa pathogenesis. Infect. Immun. 71:2404-2413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Montie, T. C., D. Doyle-Huntzinger, R. C. Craven, and I. A. Holder. 1982. Loss of virulence associated with absence of flagellum in an isogenic mutant of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the burned-mouse model. Infect. Immun. 38:1296-1298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ohman, D. E., J. C. Sadoff, and B. H. Iglewski. 1980. Toxin A-deficient mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA103: isolation and characterization. Infect. Immun. 28:899-908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Pavlovskis, O. R., and F. B. Gordon. 1972. Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin: effect on cell cultures. J. Infect. Dis. 125:631-636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Preston, M. J., P. C. Seed, D. S. Toder, B. H. Iglewski, D. E. Ohman, J. K. Gustin, J. B. Goldberg, and G. B. Pier. 1997. Contribution of proteases and LasR to the virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa during corneal infections. Infect. Immun. 65:3086-3090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Rahme, L. G., E. J. Stevens, S. F. Wolfort, J. Shao, R. G. Tompkins, and F. M. Ausubel. 1995. Common virulence factors for bacterial pathogenicity in plants and animals. Science 268:1899-1902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Ratnaningsih, E., S. Dharmsthiti, V. Krishnapillai, A. Morgan, M. Sinclair, and B. W. Holloway. 1990. A combined physical and genetic map of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO. J. Gen. Microbiol. 136(Pt. 12):2351-2357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Rinaldo, S., G. Giardina, M. Brunori, and F. Cutruzzola. 2006. N-oxide sensing and denitrification: the DNR transcription factors. Biochem. Soc Trans. 34:185-187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Rinderknecht, H., M. C. Geokas, P. Silverman, and B. J. Haverback. 1968. A new ultrasensitive method for the determination of proteolytic activity. Clin. Chim. Acta 21:197-203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Rodionov, D. A., I. L. Dubchak, A. P. Arkin, E. J. Alm, and M. S. Gelfand. 2005. Dissimilatory metabolism of nitrogen oxides in bacteria: comparative reconstruction of transcriptional networks. PLoS Comput. Biol. 1:e55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Schreiber, K., N. Boes, M. Eschbach, L. Jaensch, J. Wehland, T. Bjarnsholt, M. Givskov, M. Hentzer, and M. Schobert. 2006. Anaerobic survival of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by pyruvate fermentation requires an Usp-type stress protein. J. Bacteriol. 188:659-668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Smith, R. S., and B. H. Iglewski. 2003. P. aeruginosa quorum-sensing systems and virulence. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 6:56-60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Spickett, C. M., A. R. Pitt, N. Morrice, and W. Kolch. 2006. Proteomic analysis of phosphorylation, oxidation and nitrosylation in signal transduction. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1764:1823-1841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Stewart, V. 2003. Nitrate- and nitrite-responsive sensors NarX and NarQ of proteobacteria. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 31:1-10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Toder, D. S., M. J. Gambello, and B. H. Iglewski. 1991. Pseudomonas aeruginosa LasA: a second elastase under the transcriptional control of lasR. Mol. Microbiol. 5:2003-2010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Tsuchiya, S., M. Yamabe, Y. Yamaguchi, Y. Kobayashi, T. Konno, and K. Tada. 1980. Establishment and characterization of a human acute monocytic leukemia cell line (THP-1). Int. J. Cancer 26:171-176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Tucker, N. P., B. D'Autreaux, F. K. Yousafzai, S. A. Fairhurst, S. Spiro, and R. Dixon. 2008. Analysis of the nitric oxide-sensing non-heme iron center in the NorR regulatory protein. J. Biol. Chem. 283:908-918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Van Alst, N. E., K. F. Picardo, B. H. Iglewski, and C. G. Haidaris. 2007. Nitrate sensing and metabolism modulate motility, biofilm formation, and virulence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect. Immun. 75:3780-3790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Wagner, V. E., R. J. Gillis, and B. H. Iglewski. 2004. Transcriptome analysis of quorum-sensing regulation and virulence factor expression in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Vaccine 22(Suppl. 1):S15-S20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Yahr, T. L., J. Goranson, and D. W. Frank. 1996. Exoenzyme S of Pseudomonas aeruginosa is secreted by a type III pathway. Mol. Microbiol. 22:991-1003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Yahr, T. L., and M. C. Wolfgang. 2006. Transcriptional regulation of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa type III secretion system. Mol. Microbiol. 62:631-640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Zumft, W. G. 1997. Cell biology and molecular basis of denitrification. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 61:533-616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]