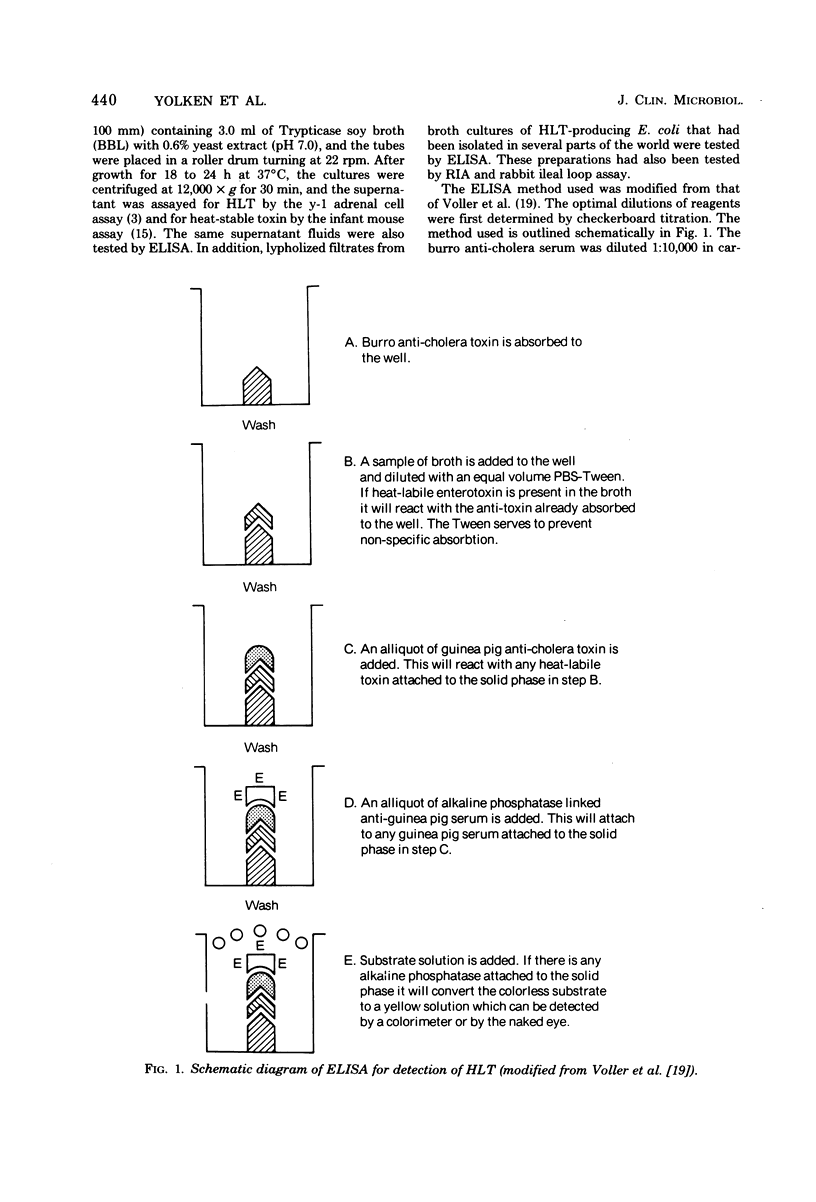
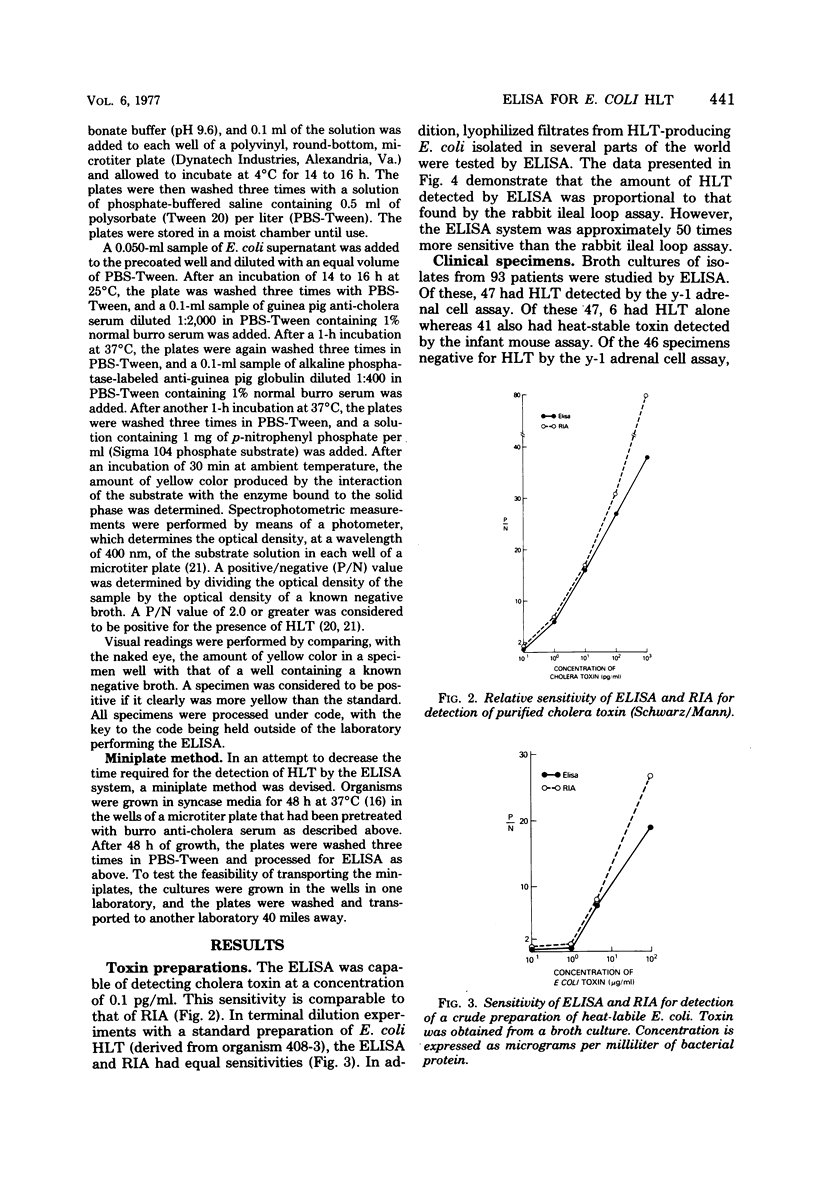
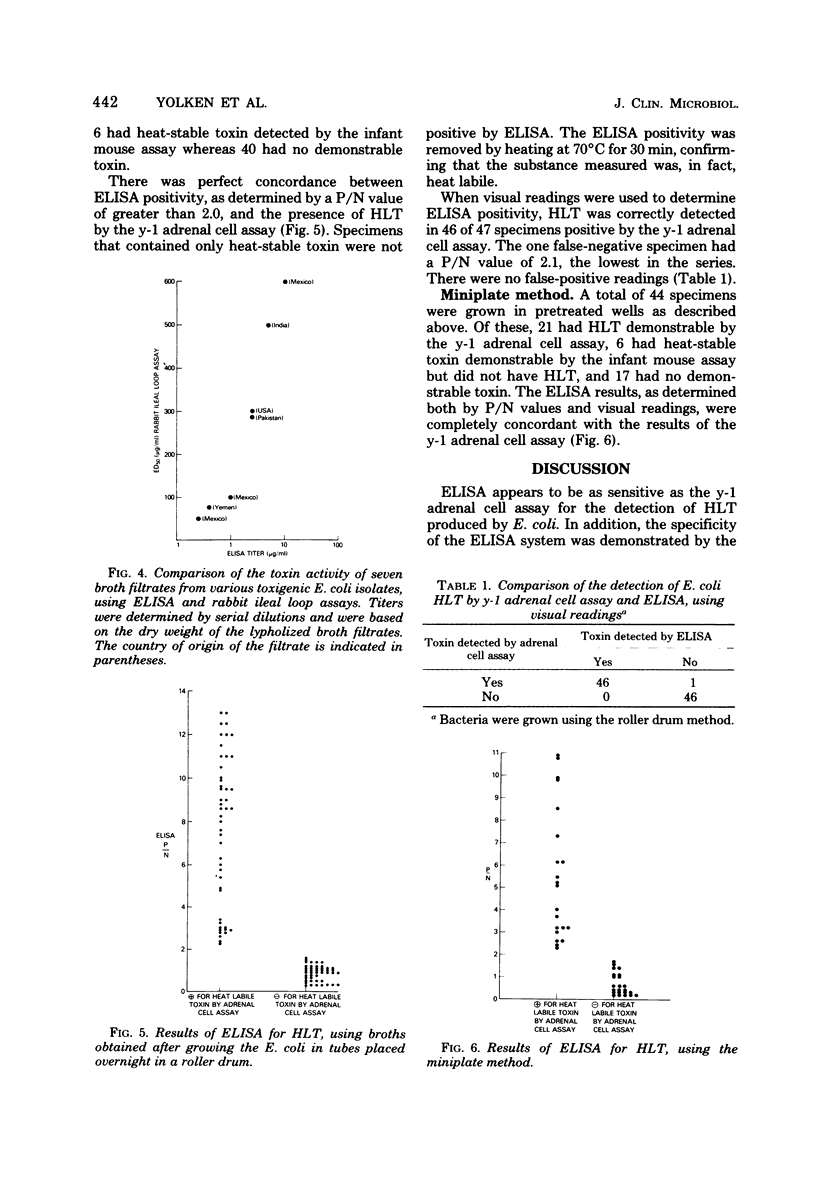
Abstract
The development of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for the detection of heat-labile Escherichia coli enterotoxin is described. The assay, which is based on the immunological similarity between Vibrio cholerae toxin and heat-labile E. coli enterotoxin, is similar in design to a radioimmunoassay but utilizes enzyme-labeled rather than radioactive isotope-labeled reagents. The ELISA system is as sensitive as both radioimmunoassay and the y-1 adrenal cell assay for the detection of heat-labile E. coli enterotoxin but requires neither radioactive reagents nor tissue culture techniques. The ELISA is easy to perform and is adaptable for use in small laboratories.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DE S. N., BHATTACHARYA K., SARKAR J. K. A study of the pathogenicity of strains of Bacterium coli from acute and chronic enteritis. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1956 Jan;71(1):201–209. doi: 10.1002/path.1700710126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donta S. T., Smith D. M. Stimulation of steroidogenesis in tissue culture by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and its neutralization by specific antiserum. Infect Immun. 1974 Mar;9(3):500–505. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.3.500-505.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Jr, Evans D. G. Direct serological assay for the heat-labile enterotoxin of Escherichia coli, using passive immune hemolysis. Infect Immun. 1977 May;16(2):604–609. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.2.604-609.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Jr, Evans D. G., Gorbach S. L. Production of vascular permeability factor by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from man. Infect Immun. 1973 Nov;8(5):725–730. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.5.725-730.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Jr, Evans D. G. Inhibition of immune hemolysis: serological assay for the heat-labile enterotoxin of Excherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Jan;5(1):100–105. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.1.100-105.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer J. J., Davis B. R., Cherry W. B., Brenner D. J., Dowell V. R., Jr, Balows A. "Enteropathogenic serotypes" of Escherichia coli which really are not. J Pediatr. 1977 Jun;90(6):1047–1051. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(77)80617-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gangarosa E. J., Merson M. H. Epidemiologic assessment of the relevance of the so-called enteropathogenic serogroups of Escherichia coli in diarrhea. N Engl J Med. 1977 May 26;296(21):1210–1213. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197705262962106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbach S. L., Khurana C. M. Toxigenic Escherichia coli: a cause of infantile diarrhea in Chicago. N Engl J Med. 1972 Oct 19;287(16):791–795. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197210192871603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg H. B., Sack D. A., Rodriguez W., Sack R. B., Wyatt R. G., Kalica A. R., Horswood R. L., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. Microtiter solid-phase radioimmunoassay for detection of Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1977 Sep;17(3):541–545. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.3.541-545.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Brunton L. L., Schnaitman T. C., Rebhun L. I., Gilman A. G. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate and alteration of Chinese hamster ovary cell morphology: a rapid, sensitive in vitro assay for the enterotoxins of Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1974 Aug;10(2):320–327. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.2.320-327.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Svennerholm A. M. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays for cholera serology. Infect Immun. 1973 May;7(5):759–763. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.5.759-763.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacks T. M., Wu B. J. Biochemical properties of Escherichia coli low-molecular-weight, heat-stable enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1974 Feb;9(2):342–347. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.2.342-347.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack D. A., Sack R. B. Test for enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli using Y-1 adrenal cells in miniculture. Infect Immun. 1975 Feb;11(2):334–336. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.2.334-336.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B. Human diarrheal disease caused by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:333–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.002001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith N. W., Sack R. B. Immunologic cross-reactions of enterotoxins from Escherichia coli and Vibrio cholerae. J Infect Dis. 1973 Feb;127(2):164–170. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.2.164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolters G., Kuijpers L., Kacaki J., Schuurs A. Solid-phase enzyme-immunoassay for detection of hepatitis B surface antigen. J Clin Pathol. 1976 Oct;29(10):873–879. doi: 10.1136/jcp.29.10.873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H., Kim H. W., Clem T., Wyatt R. G., Kalica A. R., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for detection of human reovirus-like agent of infantile gastroenteritis. Lancet. 1977 Aug 6;2(8032):263–267. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)90951-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


