Abstract
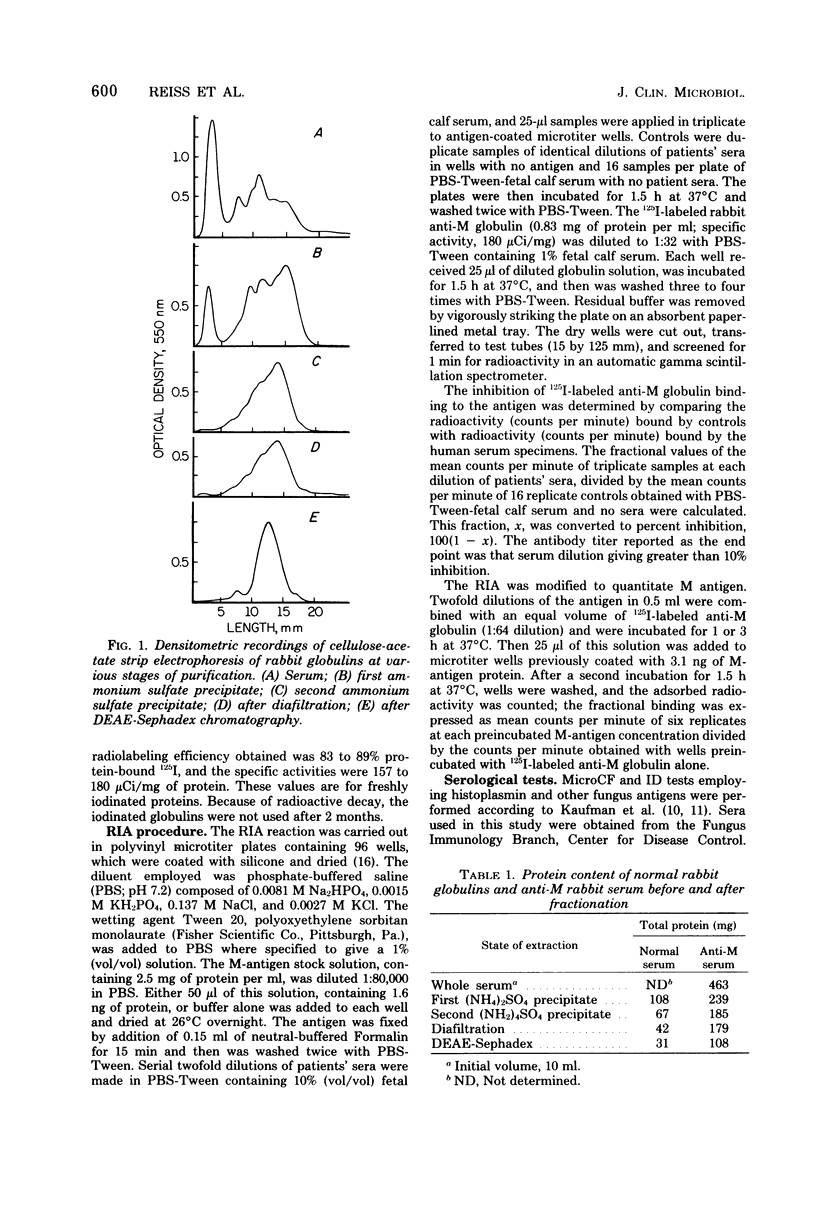
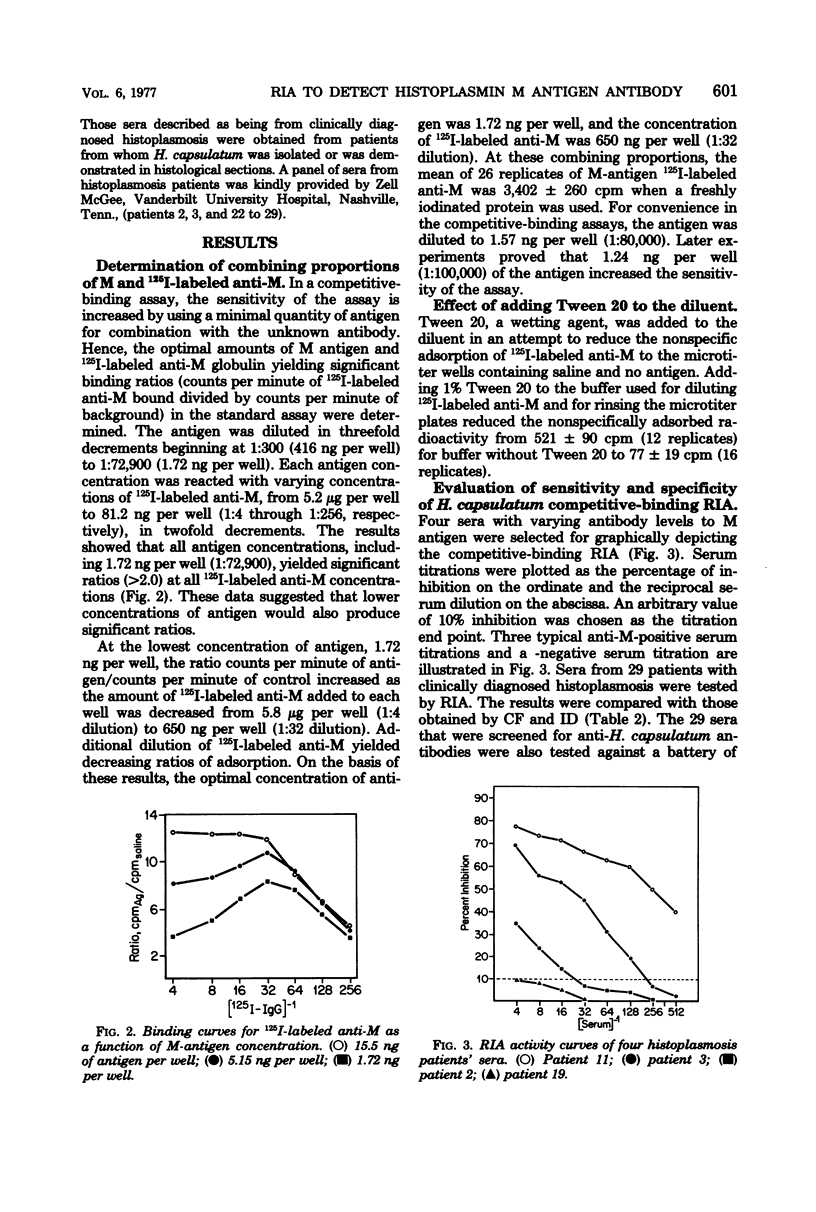
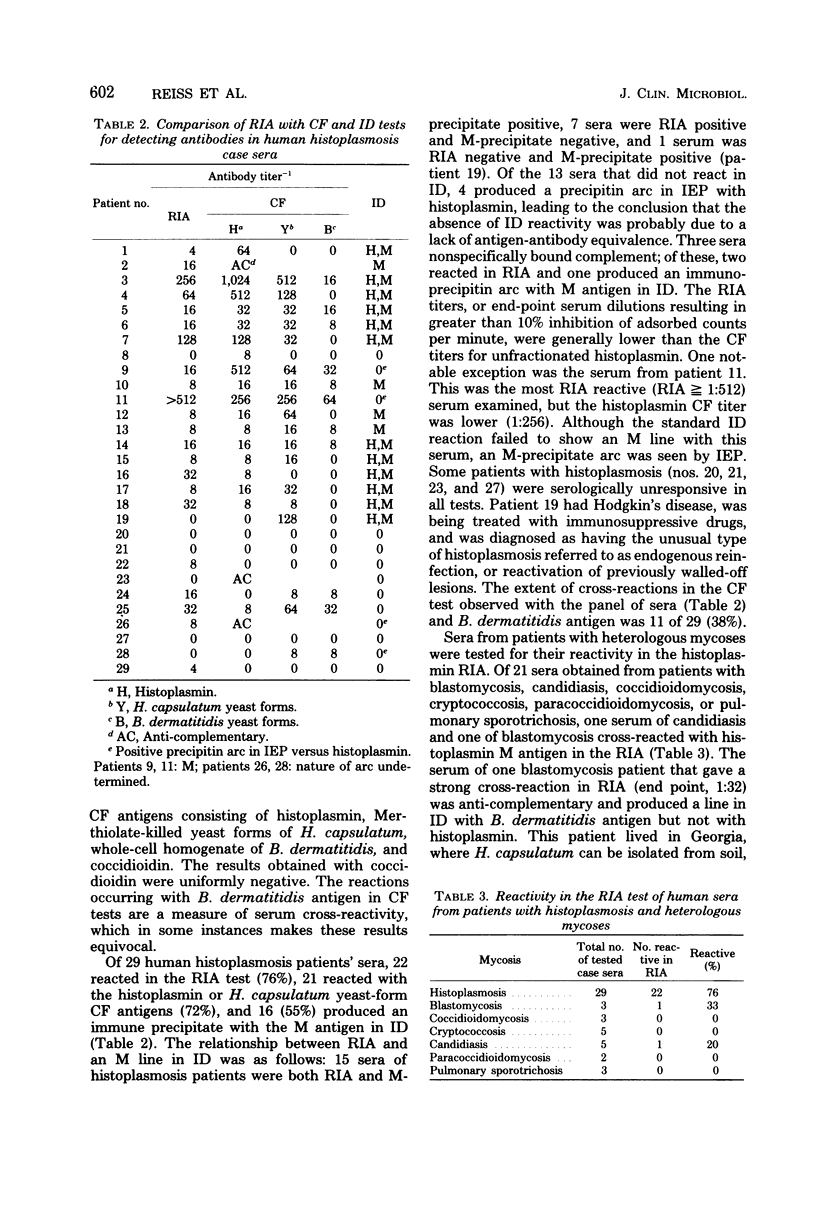
A radioimmunoassay (RIA) was designed and compared with complement fixation and immunodiffusion tests for their relative ability to detect antibodies in sera of histoplasmosis patients. M antigen, purified from histoplasmin, was fixed to microtiter wells as the solid phase, and specific rabbit 125I-labeled anti-M globulin was the source of indicator antibodies. The optimal concentrations for the competitive-binding assay were 1.6 ng per well for M antigen and 650 ng per well for the 125I-labeled anti-M globulin. A panel of sera from 29 histoplasmosis patients and from patients with other mycoses was screened for RIA activity and in complement fixation and immunodiffusion tests that used histoplasmin and Histoplasma capsulatum yeast-form antigens. The sera of 22 histoplasmosis patients reacted in the RIA, 21 in the complement fixation, and 16 in the immunodiffusion tests. Sera of patients with other mycotic infections did not react in the RIA, with the exception of those of one blastomycosis patient and one candidiasis patient. The RIA could be modified to quantitate M antigen; as little as 125 pg could be detected. The evaluation of this panel of histoplasmosis patients' sera showed that the RIA was about equivalent in sensitivity to the complement fixation test. Some advantages of the RIA over the complement fixation test were that RIA was less prone to cross-reactions and gave better quantitation of low-titered sera. The RIA was a 1-day test, was not hindered by the anti-complementary activity of some sera, and could be modified to quantitate minute amounts of M antigen.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauman D. S., Smith C. D. Comparison of immunodiffusion and complement fixation tests in the diagnosis of histoplasmosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Aug;2(2):77–80. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley G., Pine L., Reeves M. W., Moss C. W. Purification, composition, and serological characterization of histoplasmin-H and M antigens. Infect Immun. 1974 May;9(5):870–880. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.5.870-880.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green J. H., Harrell W. K., Gray S. B., Johnson J. E., Bolin R. C., Gross H., Malcolm G. B. H and M antigens of Histoplasma capsulatum: preparation of antisera and location of these antigens in yeast-phase cells. Infect Immun. 1976 Sep;14(3):826–831. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.3.826-831.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEINER D. C. Diagnosis of histoplasmosis using precipitin reactions in agargel. Pediatrics. 1958 Oct;22(4 Pt 1):616–627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebert G. A., Pelham P. L., Pittman B. Determination of the optimal ammonium sulfate concentration for the fractionation of rabbit, sheep, horse, and goat antisera. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Jan;25(1):26–36. doi: 10.1128/am.25.1.26-36.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson H. D., Ziegler D. W. Criteria for preparing, evaluating, and standardizing iodinated globulins for radioimmunoassay procedures. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Dec;28(6):935–942. doi: 10.1128/am.28.6.935-942.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman L., Clark M. J. Value of the concomitant use of complement fixation and immunodiffusion tests in the diagnosis of coccidioidomycosis. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Oct;28(4):641–643. doi: 10.1128/am.28.4.641-643.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleger B., Kaufman L. Detection and identification of diagnostic Histoplasma capsulatum precipitates by counterelectrophoresis. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Sep;26(3):231–238. doi: 10.1128/am.26.3.231-238.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purcell R. H., Wong D. C., Moritsugu Y., Dienstag J. L., Routenberg J. A., Boggs J. D. A microtiter solid-phase radioimmunoassay for hepatitis A antigen and antibody. J Immunol. 1976 Feb;116(2):349–356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler D. W., Hutchinson H. D., Koplan J. P., Nakano J. H. Detection by radioimmunoassay of antibodies in human smallpox patients and vaccinees. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Mar;1(3):311–317. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.3.311-317.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


