Abstract
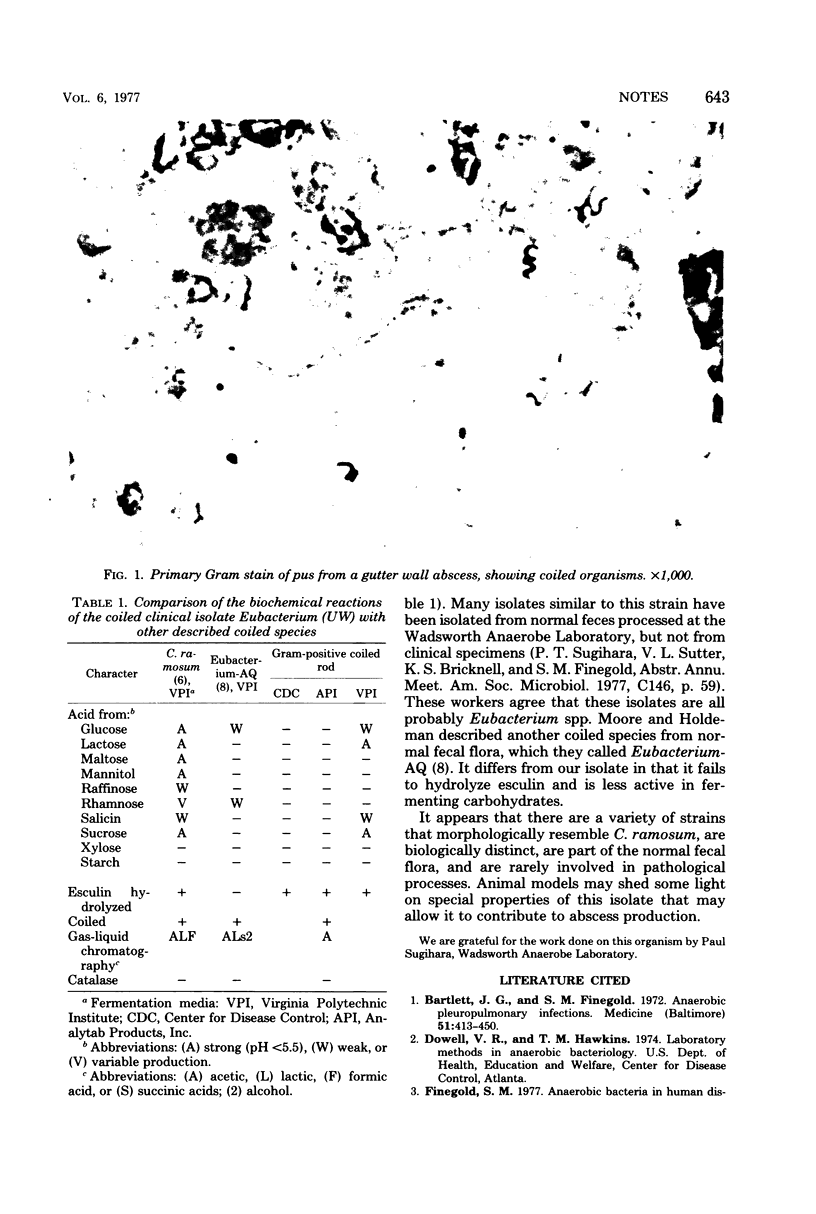
A gram-positive, nonsporing coiled rod was visible on Gram stain and isolated in pure culture from 20 ml of pus. This organism differs from previously described species in that it produces only acetic acid from glucose metabolism, hydrolyzes esculin, and has less fermentative activity in carbohydrates.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartlett J. G., Finegold S. M. Anaerobic pleuropulmonary infections. Medicine (Baltimore) 1972 Nov;51(6):413–450. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197211000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore H. B., Sutter V. L., Finegold S. M. Comparison of three procedures for biochemical testing of anaerobic bacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Jan;1(1):15–24. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.1.15-24.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore W. E., Holdeman L. V. Human fecal flora: the normal flora of 20 Japanese-Hawaiians. Appl Microbiol. 1974 May;27(5):961–979. doi: 10.1128/am.27.5.961-979.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sans M. D., Crowder J. G. Subacute bacterial endocarditis caused by Eubacterium aerofaciens: report of a case. Am J Clin Pathol. 1973 Apr;59(4):576–580. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/59.4.576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



