Summary
Orphan nuclear receptors provide a unique resource for uncovering novel regulatory systems that impact human health and provide excellent drug targets for a variety of human diseases. Ligands of nuclear receptors have been used in a number of important therapeutic areas, such as breast cancers, skin disorders, and diabetes. Orphan nuclear receptors, therefore, represent a tremendous opportunity in understanding and treating human diseases. This review highlights advances and potentials of using orphan nuclear receptors, in particular PPARs, Nurr1, RORs, and TLX as targets for drug discovery in diabetes and obesity, neurodegenerative diseases, and other related disorders.
Keywords: Orphan Nuclear Receptor, ligand identification, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs), TLX, Nur-related protein 1 (Nurr1), retinoid acid receptor-related orphan receptors (RORs), diabetes and obesity, neurodegenerative diseases
Introduction
Nuclear receptors are ligand-dependent transcription factors that play important roles in a variety of biological processes, including cell proliferation, differentiation, and cellular homeostasis [1]. The primary function of nuclear receptors is to mediate transcriptional responses to hormones and other metabolic ligands. Nuclear receptors regulate many different target genes through the recruitment of a host of positive and negative regulatory proteins, referred to as coactivators or corepressors. The recruitment of coactivator complexes is a critical step in ligand-induced transcription, whereas the recruitment of corepressor complexes mediates active repression of unliganded nuclear receptors. The target genes of nuclear receptors comprise a complex genetic network, in which their coordinated activity defines the physiological hormonal responses.
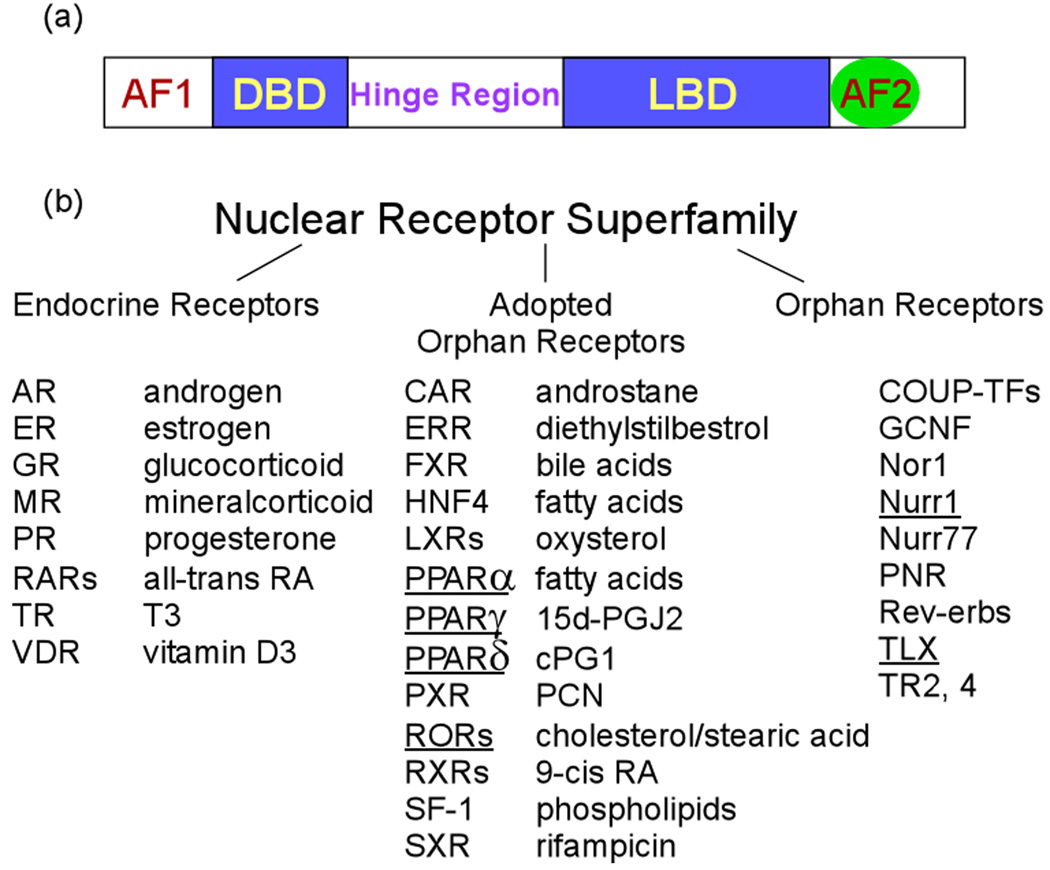
Nuclear receptors contain a number of functional domains that are defining structural features for members of the nuclear receptor superfamily. In general, the receptor structure is comprised of an amino-terminal activation domain AF-1, a DNA-binding domain (DBD), a hinge region, a conserved ligand-binding domain (LBD), and a second activation domain AF-2, which is located at the carboxy-terminal end of LBD and mediates ligand-dependent transactivation by nuclear receptors (Figure 1a). The LBD mediates nuclear localization and contains sites for coactivator and corepressor interactions. Members of the nuclear receptor superfamily include the well-known endocrine receptors, the adopted orphan receptors, for which ligands have been identified in recent years, and the orphan receptors, ligands of which have not yet been identified (Figure 1b). The identification of selective small molecule ligands is one of the major goals of orphan nuclear receptor research, which will make new therapeutic interventions available for a variety of human diseases.
Figure 1. Structure/function domains and the superfamily members of nuclear receptors.
(a) Nuclear receptor domain structure. In general, the receptor structure is comprised of an amino-terminal activation domain AF-1, DNA binding domain (DBD), a hinge region, a conserved ligand binding domain (LBD), and a variable C-terminal region with a second activation domain AF-2. (b) The nuclear receptor superfamily includes the endocrine receptors, the adopted orphan receptors, and the orphan receptors. The orphan nuclear receptors that are discussed in the review is underlined.
Ligand Identification for Orphan Nuclear Receptors
Identification of novel ligands for orphan nuclear receptors will lead to the discovery of new drugs. Because nuclear receptors are important regulators of human physiology and pathology, ligands that interact with nuclear receptors to modulate the activity of these receptors have direct implications in drug discovery. Ligands of nuclear receptors have been used in many important clinical areas. For example, estrogen receptor (ER) antagonist, tamoxifen, is used in the treatment of breast cancers. Retinoic acid receptor (RAR) agonists, retinoids, are used in the treatment of skin disorders [2]. PPARγ serves as another excellent example of drug targets. Thiazolidinediones (TZDs), ligands of PPARγ, are widely used in the treatment of type II diabetes [3]. In addition to ligands that bind directly to the conserved ligand binding pocket, compounds that target regions outside of the LBD in the receptor may also regulate receptor-cofactor interactions and receptor functions, thus serve as potential drugs for related diseases. One such example is Nurr1 agonist, 6-mercaptopurine (6-MP) that activates Nurr1 through its AF1 domain [4].
Attempts to identify ligands for orphan receptors have been conducted using a variety of methods. The most frequently used approach is cell-based assays using cultured mammalian cells transfected with a receptor construct and a reporter gene. Nuclear receptor LBD fused to Gal4 DBD is often used as the receptor. The transfected cells are treated with candidate ligands and assayed for the activity of the reporter gene product. Using this strategy, ligands have been ientified for retinoid acid receptors (RARs), retinoid X receptors (RXRs), peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs), liver X receptors (LXRs), farnesoid X receptor (FXR), pregnane X receptor (PXR), steroid and xenobiotic receptor (SXR), and constitutive androstane receptor (CAR) [5,6].
The most straightforward methods for ligand identification are those based on direct binding, in which the target protein is immobilized on a solid support. Cell lysates or mixtures of compounds containing possible ligands are passed over the immobilized target protein. After extensive washes, the putative ligand is eluted and characterized by analytical methods such as mass spectrometry. The ligand-dependent nuclear receptor-coactivator interactions have also been used for ligand screening. Examples of this strategy include fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) assay [7], in which ligand-induced receptor-coactivator interactions lead to energy transfer between their tags, fluorescent proteins such as CFP and YFP. The resulting fluorescent intensity change can be detected by fluorescence microscopy. The AlphaScreen assay (Amplified Luminescent Proximity Homogenous Assay) is also based on ligand-dependent interactions between receptors and coactivators [8]. In this assay the receptor is conjugated to a donor bead and the coactivator to a receptor bead. When a ligand-dependent interaction between a receptor and its coactivator brings their conjugated beads into proximity, singlet oxygen generated by the donor beads initiates a luminescence or fluorescence cascade in the nearby acceptor beads, leading to a highly amplified signal in the 520–620 nm range. This assay has been used to screen for phospholipid ligands that regulate SF-1/coactivator interactions [9].
Structures of orphan nuclear receptor LBDs have also helped to identify ligands of these receptors. To date, crystal structures of LBD have been reported for most of the nuclear receptors [10]. The structure of the LBD provides a detailed picture of its ligand binding pocket, which greatly facilitates designing pharmacologically active ligands for the receptors. Structure ligands, small molecules that are found in the ligand binding pocket of receptors in crystal structures, have been identified for orphan receptors, including RORs, HNFα, SF-1 and IRH-1. For example, cholesterol was identified as a ligand for RORα in a structural analysis [11]. One obvious aim for the near future is to elucidate the structures of LBD for the remaining orphan nuclear receptors. These studies will provide new insights into ligand-mediated regulation of nuclear receptors and help to identify ligands for the remaining orphan receptors. The identification of ligands will in turn lead to discovery and design of new drugs.
Virtual screening of molecular compound libraries has recently emerged as a powerful method for drug discovery [12,13]. Based on the crystal structure of the target protein and high-throughput molecular docking using compound database, virtual screening allows for scanning a large number of compounds with reasonable accuracy and speed. It has been used to identify RAR and TR antagonists [14,15] and to screen for selective estrogen receptor (ER) modulators [16]. Computer-aided high throughput docking provides a rapid and economic approach for orphan nuclear receptor ligand screening and proves to be a valuable tool for drug discovery.
PPARs, Drug Targets for Diabetes and Obesity
Since their discovery, PPARs have received attention as potential pharmacologic targets for combating diabetes and obesity because of their important roles in cell metabolism regulation. There are three members of the PPAR family: PPARα, PPARγ, and PPARδ. PPARα is most prominently expressed in the liver, kidney, heart, skeletal muscle and brown adipose tissue. In addition to its activation in response to peroxisome proliferators, PPARα is also activated by a variety of medium- and long-chain fatty acids and has been shown to stimulate lipid metabolism by the induction of peroxisomal β-oxidation and fatty acid ω-hydroxylation [17]. Mice lacking functional PPARα are incapable of responding to peroxisome proliferators and fail to induce expression of a variety of genes required for the metabolism of fatty acids [18]. For a long time, the PPARα-activating fibrates, a class of amphipathic carboxylic acids, have been used in the treatment of dyslipidemia. In dyslipidemic patients, these drugs improve the plasma lipid profile by lowering triglyceride, and to a lesser extent, low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol levels and by increasing high-density-lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol levels [19]. These effects are achieved by a variety of mechanisms, such as an increase in lipoprotein lipase expression, reduction of apolipoprotein CIII expression, inhibition of triglyceride synthesis and very-low-density lipoprotein production.
PPARγ is abundantly expressed in adipose tissue and has been shown to play a central role in adipogenesis [20,21]. The PPARγ-null mice are embryonic lethal due in part to disrupted placental function [21]. Rescue of the placental defect results in lipid dystrophy and neonatal death [22,23]. PPARγ has been shown to be activated by 15-deoxy-(12, 14)-prostaglandin J2 (15d-PGJ2) or its synthetic analog thiazolidinediones (TZDs) [24,25]. TZDs represent the best studied class of PPARγ agonists and are used clinically as insulin sensitizing drugs for the treatment of type 2 diabetes [3]. Activation of PPARγ by TZDs induces genes involved in adipocyte differentiation and lipogenesis, which are thought to be responsible for the insulin-sensitizing actions of these drugs. An unwanted side effect of TZD is weight gain. Partial PPARγ agonists, compounds that selectively activate PPARγ glycemic control function with weaker adipogenic potential, are being developed now to avoid the adverse side effect [26]. PPARγ antagonists that promote glycemic control and decrease adiposity will also become valuable tools for drug discovery in diabetes and obesity.
PPARδ is widely expressed at relatively high levels in brain, macrophages, lung, adipose tissue and skeletal muscle [27]. Recent data in transgenic mouse models have implicated PPARδ in regulation of energy expenditure as well as glucose and lipid metabolism, highlighting the potential use of PPARδ modulators as therapeutic agents for type II diabetes and obesity [28]. Muscle-specific expression of an activated form of PPARδ (VP-PPARδ) in mice resulted in resistance to diet-induced obesity, increased metabolic rate and lipid utilization, and decreased intramyocellular triglyceride levels [29]. In addition, there was an increase in the type I muscle fibers, which correlated with increased exercise endurance in transgenic mice. Mice expressing VP-PPARδ in adipose tissue had reduced white adipose tissue mass along with increased energy expenditure and lipid utilization [30]. These mice were resistant to diet-induced obesity and hyperlipidemia. PPARδ agonists have validated this receptor as a therapeutic target for the treatment of obesity and diabetes. Treatment of obese, insulin-resistant monkeys and diabetic rodent models with GW501516, a potent and selective synthetic PPARδ agonist, lowered fasting insulin and triglyceride levels and increased HDL cholesterol levels [31], supporting the idea that PPARδ is an important drug target for the treatment of diabetes and obesity.
Recently, the concept of the selective peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor modulators (SPPARM) was introduced [19]. SPPARM is a new pharmacological approach that is based on selective receptor-cofactor interactions and differential target gene regulation. It encompasses the principle of chemical alteration of PPAR-specific ligands to create compounds that selectively activate specific PPAR functions. For example, selective PPARγ modulation could lead to potent insulin sensitization without adverse effects such as weight gain [32]. Several compounds have now been identified as SPPARMs, and some of them are already in clinical testing [32–35]. In addition, pan-agonists combining PPARα, γ, and δ agonism have the potential to improve insulin resistance and dyslipidemia without causing weight gain. These compounds have recently entered clinical trials [28]. The development of SPPARMs and pan-PPAR agonists will contribute significantly to drug discovery in diabetes and obesity.
Nurr1, Drug Target for Parkinson’s Disease (PD)
The NR4A subfamily of nuclear receptors comprises three members, Nurr1, Nur77, and Nor1 [36–38]. They largely function as immediate-early genes, the expression and activation of which is regulated in a cell-type specific manner in response to a range of signals, such as mitogenic and apoptotic stimuli [39]. Nurr1 is expressed predominantly in the central nervous system (CNS), especially in substantia nigra, ventral tegmental area, midbrain and limbic areas [40]. Several lines of evidence have indicated that Nurr1 is essential for the development, migration, and survival of dopaminergic neurons [41]. As Parkinson’s disease results from the loss of dopaminergic neurons, the prospect of using Nurr1 as a drug target for PD is promising.
Experimental studies in Nurr1 knockout mice indicated that Nurr1 deficiency resulted in impaired dopaminergic function and increased vulnerability to apoptosis in midbrain dopaminergic neurons that degenerate in PD. Mutations in Nurr1 gene have been associated with PD [42]. Decreased Nurr1 expression was found in PD midbrains, particularly in neurons containing Lewy bodies, abnormal aggregates of proteins that are associated with neuronal degeneration in PD brains [43]. Moreover, Nurr1 overexpression in embryonic stem cells is sufficient to generate differentiated dopaminergic neurons [44]. All these studies suggest that Nurr1 is not only essential in the development and survival of mensencephalic dopaminergic neurons, but also plays a role in the pathogenesis of PD.
For many years major efforts were put into finding ligands that bind and activate Nurr1 receptor. Although the Nurr1 ligand binding domain is folded in much the same way as in other nuclear receptors, the space that in other nuclear receptors is normally occupied by ligands is entirely filled by hydrophobic amino acid side chains in Nurr1, hence preventing ligand binding in this pocket [45]. However, a novel hydrophobic interaction surface outside of the classic ligand binding domain has been identified that could bind coactivators and could be used as a molecular target for Nurr1-activating compounds [46]. The identification of potent and selective agonists of Nurr1 will allow the development of new therapeutic interventions for CNS disorders. Recently, 6-MP was reported as a modest agonist of Nurr1, which activates Nurr1 through its amino-terminal AF1 instead of the classic ligand binding domain [4]. More Nurr1 agonists with high potency (EC50: 8–70 nM) have been identified, which can activate Nurr1 transcription activity with excellent bioavailability and can easily cross the blood-brain barrier [47]. These compounds are tested in both in vitro and in vivo PD models currently [43]. They enhance tyrosine hydroxylase and dopamine transporter expression in primary mensencephalic cultures and exert beneficial effect on dopaminergic neurons in animal models of PD [43]. These new Nurr1 agonists will have the potential to be developed into therapeutic tools for PD.
RORs, Drug Targets for CNS and Cholesterol-related Diseases
The RORs are encoded by three different genes, RORα, RORβ, and RORγ [48]. RORα is expressed in specific areas of the brain, including the Purkinje cells in the cerebellum and the suprachiasmatic nucleus of the hypothalamus. RORα is also expressed in the spleen, thymus, and macrophages. The initial studies on the in vivo function of RORα came from an animal model known as staggerer mice, which have a deletion in the RORα gene [49]. These mice exhibit ataxic phenotype resulting from a massive neurodegeneration in the cerebellum, which is caused by a developmental defect in Purkinje cells [50]. Additional phenotypes in the staggerer mice include abnormal circadian behaviors, osteoporosis, muscular atrophy, dyslipidemia, and enhanced susceptibility to atherosclerosis. RORβ is expressed specifically in areas of the CNS that are involved in the processing of sensory information and in primary components of the mammalian circadian system, including the suprachiasmatic nuclei, the pineal gland, and the retina. The expression profile suggests a role for RORβ in the processing of sensory information and in the circadian rhythm [51]. RORβ knockout mice display a duck-like gait, transient male infertility, abnormal circadian behavior and retinal degeneration [52]. RORγ is found at high levels in skelekal muscle and thymocytes [53,54]. Analysis of RORγ knockout mice revealed significant roles of RORγ in both thymocyte development and lymphoid organogenesis [55].
Ligands have been identified for both RORα and RORβ but no ligands have been described for RORγ. Studies of the RORβ LBD structure revealed the presence of a relatively large ligand binding pocket [56]. Stearic acid was found in the ligand pocket of RORβ in a crystal structure but was not able to activate RORβ in a reporter assay, arguing against it to be a real RORβ ligand [56]. All-trans retinoic acids (ATRA) have been proposed as RORβ ligand after a co-crystal complex was reported [57]. RORβ transactivation was strongly inhibited by retinoids, suggesting that ATRA acts as an antagonist for the constitutively active RORβ. This finding suggests that retinoids can become valuable tools for drug discovery in RORβ-related CNS diseases.
The pineal gland hormone melatonin, a drug that has been used to treat sleep disorders, was reported as a natural ligand for RORα [58]. The human 5-lipoxygenase was shown to be the first RORα/melatonin-responding gene [59]. More recently, cholesterol was identified as being a ligand for RORα [11]. Cholesterol is an important membrane component of mammalian cells and a biosynthetic precursor of the corticosteroid and sex steroid hormones [60]. Depleting cellular cholesterol led to a reduction in RORα activity, whereas addition of cholesterol or its analogs reactivated its activity. Interestingly, RORα has been shown to directly regulate transcription of apolipopoprotein A-I, a key component of HDL particles that transport cholesterol. These data together suggest that RORα senses cholesterol levels and regulates cholesterol flux [60]. The fact that changes in cholesterol levels are capable of modulating the transcriptional activity of RORα suggests that cholesterol is a “real” ligand rather than just a structural cofactor of RORα [11]. RORα could play a key role in the regulation of cholesterol homeostasis and thus represents an important drug target in cholesterol-related diseases. The identification of RORα as a cholesterol “receptor” will significantly aid the hunting for pharmacologically active synthetic RORα ligands for the discovery and design of new drugs in RORα-related diseases.
TLX, Potential Drug Target for Neurodegenerative Diseases
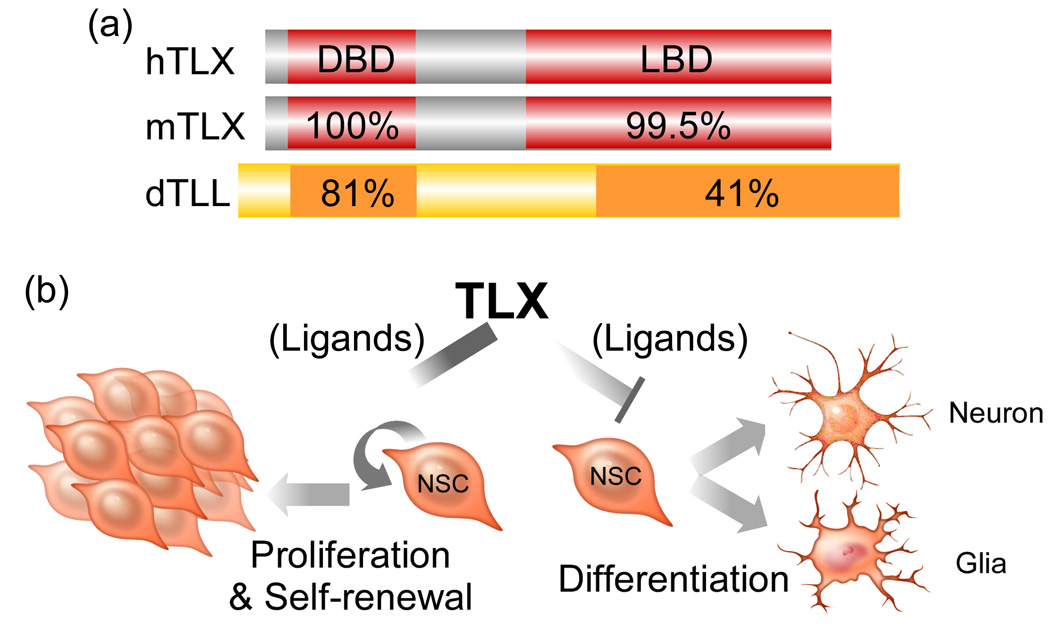
Orphan receptor TLX is specifically expressed in the brain and plays an important role in vertebrate brain functions [61,62]. The human and mouse TLX are highly conserved and they are homologous to the Drosophila tailless (Figure 2a). TLX knockout mice are viable and appear normal at birth, although the TLX gene has been shown to be required for the formation of superficial cortical layers in embryonic brains [63], to regulate the timing of neurogenesis in the cortex [64] and control patterning of lateral telencephalic progenitor domains during development [65]. Mature TLX knockout mice have significantly reduced cerebral hemispheres [61] and severe retinopathies [66–69]. Behaviorally, adult TLX mutants exhibit increased aggressiveness, decreased copulation, progressively violent behavior, late onset epilepsy and reduced learning abilities [61].
Figure 2. Orphan nuclear receptor TLX.
(a) Structure/function domains and sequence homology of human (h), mouse (m) TLX, and Drosophila Tailless (dTLL). b A model of TLX-mediated neural stem cell (NSC) maintenance and self-renewal. TLX stimulates NSC proliferation and self-renewal and inhibits NSC differentiation to maintain NSCs in the undifferentiated and self-renewable state. Ligands of TLX can modulate these events through regulating TLX activity.
We have shown that TLX is an essential regulator of neural stem cell maintenance and self-renewal in the adult brain [62]. TLX maintains adult neural stem cells in the undifferentiated and self-renewable state (Figure 2b). The TLX-expressing cells isolated from adult TLX-heterozygote brains can proliferate, self-renew and differentiate into all neural cell types in vitro. By contrast, TLX-null cells isolated from the brains of adult TLX-knockout mice fail to proliferate. Reintroducing TLX into TLX-null cells rescues their ability to proliferate and self-renew [62]. In vivo, TLX mutant mice show a loss of cell proliferation and reduced neural precursors in the neurogenic areas of adult brains. TLX represses the expression of astrocyte markers, such as GFAP, in neural stem cells, suggesting that transcriptional repression is crucial in maintaining the undifferentiated state of neural stem cells. Similarly, the Drosophila tailless acts as a dedicated repressor in the early Drosophila embryo to support normal embryonic development and establish accurate patterns of gene expression [70].
In addition to its function in neural stem cells in the brain, TLX is a key component of retinal development and is essential for vision [66]. TLX is expressed in retinal progenitor cells in the neuroblastic layer during the period of retinal layer formation and is critical for controlling the generation of appropriate numbers of retinal progenies [67]. The TLX knockout neural retinas were significantly thinner than that of wild-type littermates during development [68]. In the postnatal mouse retina, TLX is strongly expressed in the proangiogenic astrocytes and acts as a proangiogenic switch in response to hypoxia [69].
Given the essential role of TLX in regulating the maintenance and self-renewal of adult neural stem cells, ligands of TLX will be important modulators of neurogenesis and neuronal regeneration. Identification of either endogenous ligands using purified TLX LBD and brain extracts or synthetic ligands using cell-based assays with Gal4 TLX LBD will provide potential pharmacological tools for neurodegeneration. Ligands of TLX can lead to enhanced neurogenesis in normal brains and increased neuroregeneration in neurodegenerative brains. The role of TLX in retinal progenitor cells suggests that TLX is also an important drug target for retinodegeneration. In summary, ligand screening for TLX provides a future direction for drug discovery in neudegenerative diseases.
Conclusions
The search for ligands of orphan nuclear receptors has led to the discovery of many signaling pathways and revealed a direct link of nuclear receptors to human diseases such as diabetes, obesity, and neurodegenerative diseases. Ligand identification of orphan receptors will lead to the discovery of novel hormone response systems and open many new therapeutic avenues for a variety of human diseases. Identification of compounds with selective activities for specific orphan receptors is of clinical and pharmacological importance and promises a bountiful harvest in the near future.
Acknowledgements
I apologize to colleagues whose work could not be cited due to space limitations. I thank Drs. Kamil Alzayady and Chunnian Zhao for their comments on this manuscript. This work was supported by the Whitehall Foundation, the Margaret E. Early Medical Research Trust, the Sidney Kimmel Foundation, and NIH NINDS.
References
- 1.Evans RM. The nuclear receptor superfamily: a rosetta stone for physiology. Mol Endocrinol. 2005;19(6):1429–1438. doi: 10.1210/me.2005-0046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Enmark E, Gustafsson JA. Orphan nuclear receptors--the first eight years. Mol Endocrinol. 1996;10(11):1293–1307. doi: 10.1210/mend.10.11.8923456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Yki-Jarvinen H. Thiazolidinediones. N Engl J Med. 2004;351(11):1106–1118. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra041001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ordentlich P, et al. Identification of the antineoplastic agent 6-mercaptopurine as an activator of the orphan nuclear hormone receptor Nurr1. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(27):24791–24799. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M302167200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Mangelsdorf DJ, Evans RM. The RXR heterodimers and orphan receptors. Cell. 1995;83(6):841–850. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90200-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Blumberg B, Evans RM. Orphan nuclear receptors--new ligands and new possibilities. Genes Dev. 1998;12(20):3149–3155. doi: 10.1101/gad.12.20.3149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Boute N, et al. The use of resonance energy transfer in high-throughput screening: BRET versus FRET. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2002;23(8):351–354. doi: 10.1016/s0165-6147(02)02062-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Xu HE, et al. Structural basis for antagonist-mediated recruitment of nuclear co-repressors by PPARalpha. Nature. 2002;415(6873):813–817. doi: 10.1038/415813a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Li Y, et al. Crystallographic identification and functional characterization of phospholipids as ligands for the orphan nuclear receptor steroidogenic factor-1. Mol Cell. 2005;17(4):491–502. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2005.02.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ingraham HA, Redinbo MR. Orphan nuclear receptors adopted by crystallography. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2005;15(6):708–715. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2005.10.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kallen JA, et al. X-ray structure of the hRORalpha LBD at 1.63 A: structural and functional data that cholesterol or a cholesterol derivative is the natural ligand of RORalpha. Structure. 2002;10(12):1697–1707. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(02)00912-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lyne PD. Structure-based virtual screening: an overview. Drug Discov Today. 2002;7(20):1047–1055. doi: 10.1016/s1359-6446(02)02483-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Klebe G. Virtual ligand screening: strategies, perspectives and limitations. Drug Discov Today. 2006;11(13–14):580–594. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2006.05.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Schapira M, et al. Discovery of diverse thyroid hormone receptor antagonists by high-throughput docking. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100(12):7354–7359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1131854100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Schapira M, et al. Rational discovery of novel nuclear hormone receptor antagonists. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97(3):1008–1013. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.3.1008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Yang JM, Shen TW. A pharmacophore-based evolutionary approach for screening selective estrogen receptor modulators. Proteins. 2005;59(2):205–220. doi: 10.1002/prot.20387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Forman BM, et al. Hypolipidemic drugs, polyunsaturated fatty acids, and eicosanoids are ligands for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors alpha and delta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997;94(9):4312–4317. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.9.4312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Lee SS, et al. Targeted disruption of the alpha isoform of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gene in mice results in abolishment of the pleiotropic effects of peroxisome proliferators. Mol Cell Biol. 1995;15(6):3012–3022. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.6.3012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Gilde AJ, et al. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors at the crossroads of obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;48(9 Suppl):A24–A32. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Tontonoz P, et al. Stimulation of adipogenesis in fibroblasts by PPAR gamma 2, a lipid-activated transcription factor. Cell. 1994;79(7):1147–1156. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90006-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Barak Y, et al. PPAR gamma is required for placental, cardiac, and adipose tissue development. Mol Cell. 1999;4(4):585–595. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80209-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Rosen ED, et al. PPAR gamma is required for the differentiation of adipose tissue in vivo and in vitro. Mol Cell. 1999;4(4):611–617. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80211-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kubota N, et al. PPAR gamma mediates high-fat diet-induced adipocyte hypertrophy and insulin resistance. Mol Cell. 1999;4(4):597–609. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80210-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Forman BM, et al. 15-Deoxy-delta 12, 14-prostaglandin J2 is a ligand for the adipocyte determination factor PPAR gamma. Cell. 1995;83(5):803–812. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90193-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Kliewer SA, et al. A prostaglandin J2 metabolite binds peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma and promotes adipocyte differentiation. Cell. 1995;83(5):813–819. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90194-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Rocchi S, et al. A unique PPARgamma ligand with potent insulin-sensitizing yet weak adipogenic activity. Mol Cell. 2001;8(4):737–747. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(01)00353-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Willson TM, et al. The PPARs: from orphan receptors to drug discovery. J Med Chem. 2000;43(4):527–550. doi: 10.1021/jm990554g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Tobin JF, Freedman LP. Nuclear receptors as drug targets in metabolic diseases: new approaches to therapy. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2006;17(7):284–290. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2006.07.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Wang YX, et al. Regulation of muscle fiber type and running endurance by PPARdelta. PLoS Biol. 2004;2(10):e294. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0020294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Wang YX, et al. Peroxisome-proliferator-activated receptor delta activates fat metabolism to prevent obesity. Cell. 2003;113(2):159–170. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(03)00269-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Leibowitz MD, et al. Activation of PPARdelta alters lipid metabolism in db/db mice. FEBS Lett. 2000;473(3):333–336. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(00)01554-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Schupp M, et al. Molecular characterization of new selective peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma modulators with angiotensin receptor blocking activity. Diabetes. 2005;54(12):3442–3452. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.54.12.3442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Misra P, et al. PAT5A: a partial agonist of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma is a potent antidiabetic thiazolidinedione yet weakly adipogenic. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2003;306(2):763–771. doi: 10.1124/jpet.103.049791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Bruemmer D, et al. A non-thiazolidinedione partial peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma ligand inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell growth. Eur J Pharmacol. 2003;466(3):225–234. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(03)01556-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Minoura H, et al. Ameliorating effect of FK614, a novel nonthiazolidinedione peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma agonist, on insulin resistance in Zucker fatty rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 2005;519(1–2):182–190. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2005.05.042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Milbrandt J. Nerve growth factor induces a gene homologous to the glucocorticoid receptor gene. Neuron. 1988;1(3):183–188. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90138-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Law SW, et al. Identification of a new brain-specific transcription factor, NURR1. Mol Endocrinol. 1992;6(12):2129–2135. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.12.1491694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Ohkura N, et al. Molecular cloning of a novel thyroid/steroid receptor superfamily gene from cultured rat neuronal cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994;205(3):1959–1965. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.2900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Martinez-Gonzalez J, Badimon L. The NR4A subfamily of nuclear receptors: new early genes regulated by growth factors in vascular cells. Cardiovasc Res. 2005;65(3):609–618. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2004.10.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Zetterstrom RH, et al. Cellular expression of the immediate early transcription factors Nurr1 and NGFI-B suggests a gene regulatory role in several brain regions including the nigrostriatal dopamine system. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1996;41(1–2):111–120. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(96)00074-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Zetterstrom RH, et al. Dopamine neuron agenesis in Nurr1-deficient mice. Science. 1997;276(5310):248–250. doi: 10.1126/science.276.5310.248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Le WD, et al. Mutations in NR4A2 associated with familial Parkinson disease. Nat Genet. 2003;33(1):85–89. doi: 10.1038/ng1066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Jankovic J, et al. The role of Nurr1 in the development of dopaminergic neurons and Parkinson's disease. Prog Neurobiol. 2005;77(1–2):128–138. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2005.09.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Kim JH, et al. Dopamine neurons derived from embryonic stem cells function in an animal model of Parkinson's disease. Nature. 2002;418(6893):50–56. doi: 10.1038/nature00900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Wang Z, et al. Structure and function of Nurr1 identifies a class of ligand-independent nuclear receptors. Nature. 2003;423(6939):555–560. doi: 10.1038/nature01645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Codina A, et al. Identification of a novel co-regulator interaction surface on the ligand binding domain of Nurr1 using NMR footprinting. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(51):53338–53345. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M409096200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Dubois C, et al. Identification of a potent agonist of the orphan nuclear receptor Nurr1. ChemMedChem. 2006;1(9):955–958. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.200600078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Giguere V. Orphan nuclear receptors: from gene to function. Endocr Rev. 1999;20(5):689–725. doi: 10.1210/edrv.20.5.0378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Hamilton BA, et al. Disruption of the nuclear hormone receptor RORalpha in staggerer mice. Nature. 1996;379(6567):736–739. doi: 10.1038/379736a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Sidman RL, et al. Staggerer, a new mutation in the mouse affecting the cerebellum. Science. 1962;137:610–612. doi: 10.1126/science.137.3530.610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Schaeren-Wiemers N, et al. The expression pattern of the orphan nuclear receptor RORbeta in the developing and adult rat nervous system suggests a role in the processing of sensory information and in circadian rhythm. Eur J Neurosci. 1997;9(12):2687–2701. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1997.tb01698.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Andre E, et al. Disruption of retinoid-related orphan receptor beta changes circadian behavior, causes retinal degeneration and leads to vacillans phenotype in mice. Embo J. 1998;17(14):3867–3877. doi: 10.1093/emboj/17.14.3867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Hirose T, et al. ROR gamma: the third member of ROR/RZR orphan receptor subfamily that is highly expressed in skeletal muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994;205(3):1976–1983. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.2902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Ortiz MA, et al. TOR: a new orphan receptor expressed in the thymus that can modulate retinoid and thyroid hormone signals. Mol Endocrinol. 1995;9(12):1679–1691. doi: 10.1210/mend.9.12.8614404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Sun Z, et al. Requirement for RORgamma in thymocyte survival and lymphoid organ development. Science. 2000;288(5475):2369–2373. doi: 10.1126/science.288.5475.2369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Stehlin C, et al. X-ray structure of the orphan nuclear receptor RORbeta ligand-binding domain in the active conformation. Embo J. 2001;20(21):5822–5831. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.21.5822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Stehlin-Gaon C, et al. All-trans retinoic acid is a ligand for the orphan nuclear receptor ROR beta. Nat Struct Biol. 2003;10(10):820–825. doi: 10.1038/nsb979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Becker-Andre M, et al. Pineal gland hormone melatonin binds and activates an orphan of the nuclear receptor superfamily. J Biol Chem. 1994;269(46):28531–28534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Steinhilber D, et al. The nuclear receptor for melatonin represses 5-lipoxygenase gene expression in human B lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 1995;270(13):7037–7040. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.13.7037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Willson TM. RORalpha: an orphan nuclear receptor on a high-cholesterol diet. Structure. 2002;10(12):1605–1606. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(02)00916-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Monaghan AP, et al. Defective limbic system in mice lacking the tailless gene. Nature. 1997;390(6659):515–517. doi: 10.1038/37364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Shi Y, et al. Expression and function of orphan nuclear receptor TLX in adult neural stem cells. Nature. 2004;427(6969):78–83. doi: 10.1038/nature02211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Land PW, Monaghan AP. Expression of the transcription factor, tailless, is required for formation of superficial cortical layers. Cereb Cortex. 2003;13(9):921–931. doi: 10.1093/cercor/13.9.921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Roy K, et al. The Tlx gene regulates the timing of neurogenesis in the cortex. J Neurosci. 2004;24(38):8333–8345. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1148-04.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Stenman JM, et al. Tlx controls proliferation and patterning of lateral telencephalic progenitor domains. J Neurosci. 2003;23(33):10568–10576. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-33-10568.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Yu RT, et al. The orphan nuclear receptor Tlx regulates Pax2 and is essential for vision. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97(6):2621–2625. doi: 10.1073/pnas.050566897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Miyawaki T, et al. Tlx, an orphan nuclear receptor, regulates cell numbers and astrocyte development in the developing retina. J Neurosci. 2004;24(37):8124–8134. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2235-04.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Zhang CL, et al. Nuclear receptor TLX prevents retinal dystrophy and recruits the corepressor atrophin1. Genes Dev. 2006;20(10):1308–1320. doi: 10.1101/gad.1413606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Uemura A, et al. Tlx acts as a proangiogenic switch by regulating extracellular assembly of fibronectin matrices in retinal astrocytes. J Clin Invest. 2006;116(2):369–377. doi: 10.1172/JCI25964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Moran E, Jimenez G. The tailless nuclear receptor acts as a dedicated repressor in the early Drosophila embryo. Mol Cell Biol. 2006;26(9):3446–3454. doi: 10.1128/MCB.26.9.3446-3454.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]