Abstract
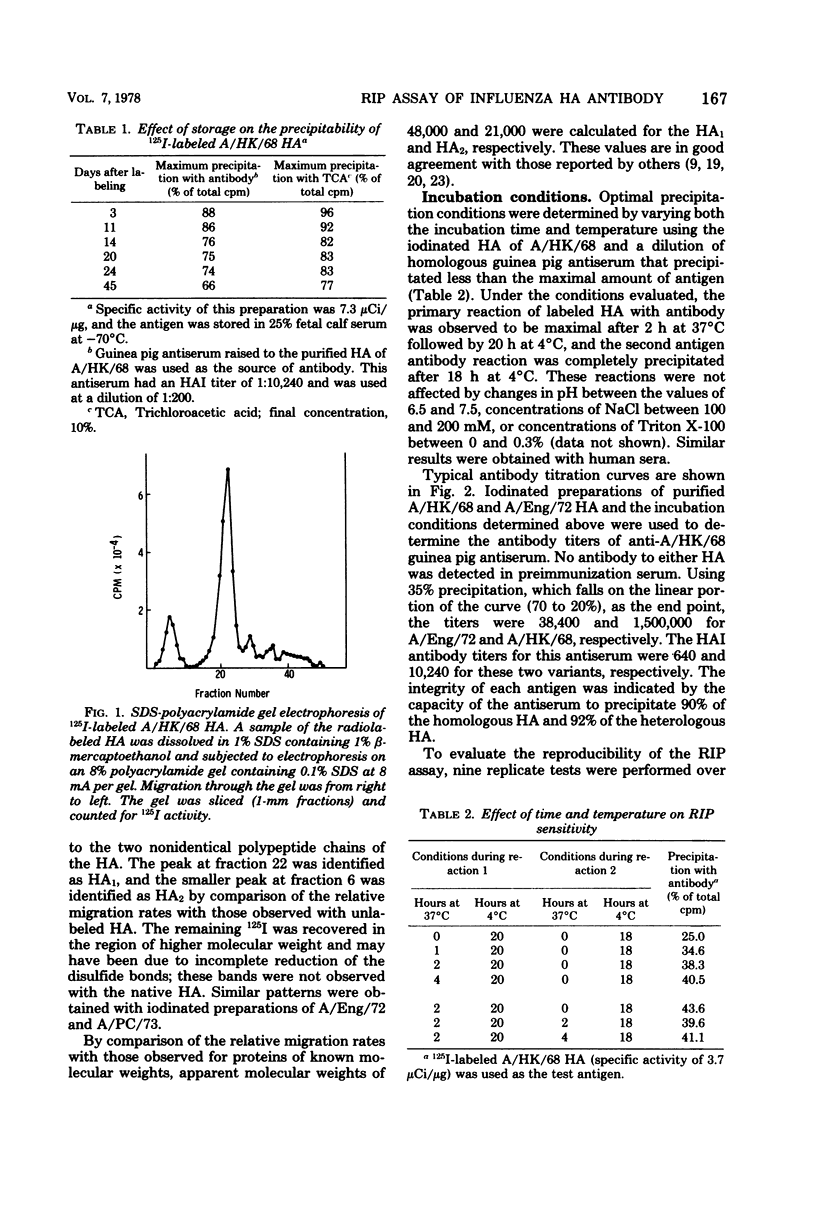
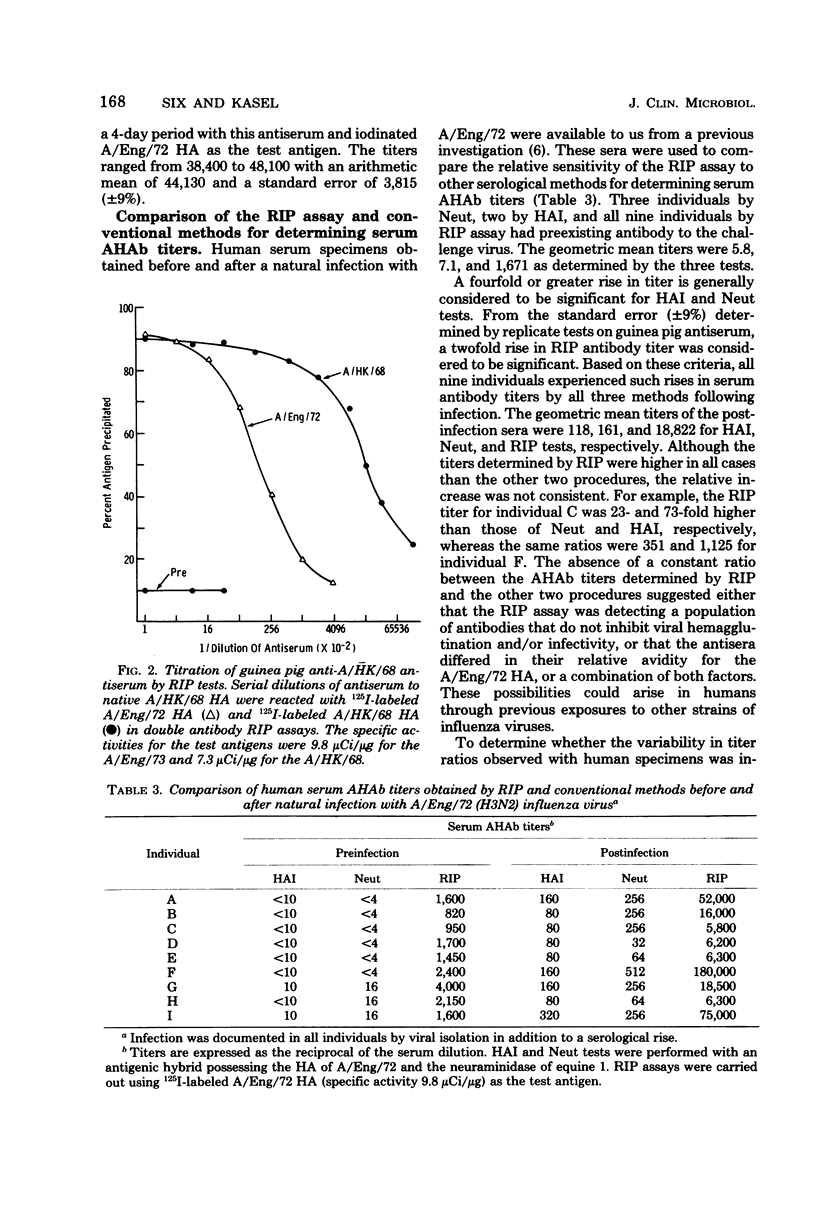
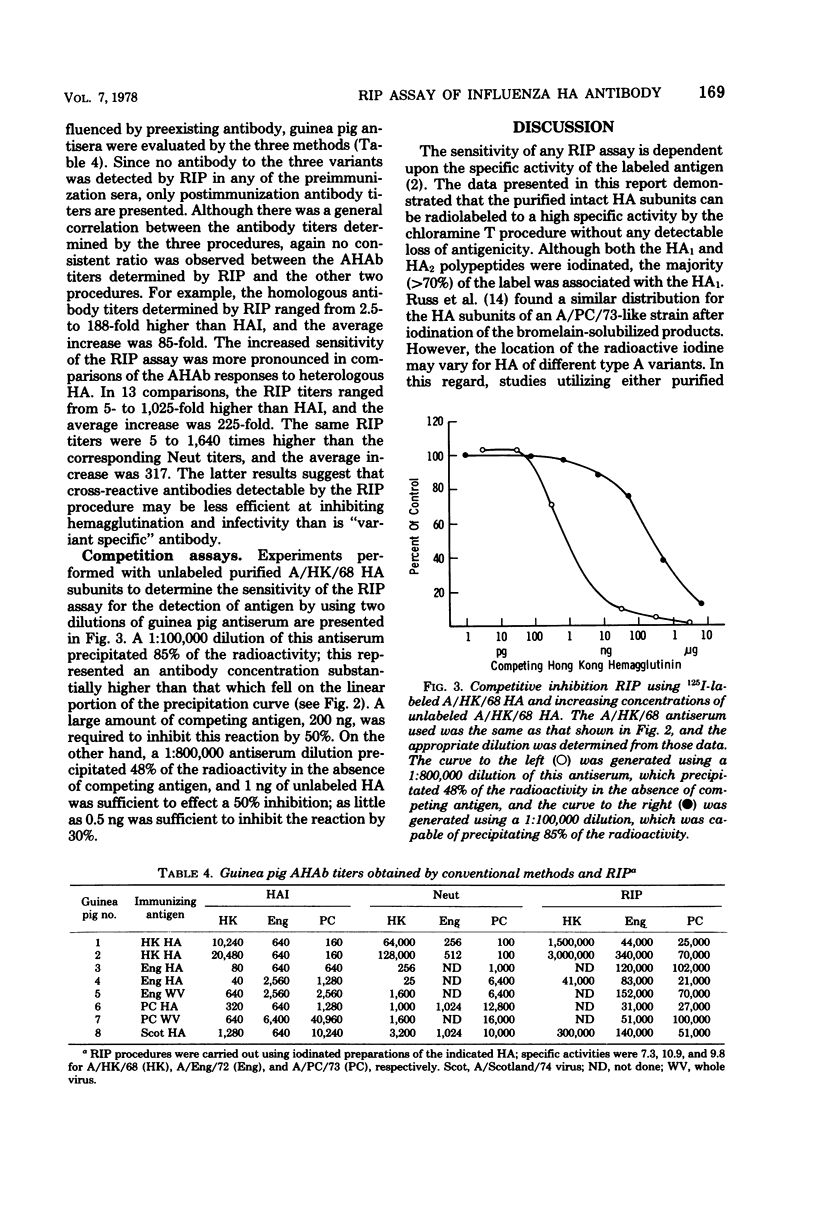
A double-antibody radioimmunoprecipitation (RIP) assay has been developed to provide a sensitive and specific measure of antibody to hemagglutinins of H3N2 influenza viruses. Chloramine T was used to radiolabel purified hemagglutinins to high specific activity without loss of antigenicity. The purity of the labeled hemagglutinin was confirmed by sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, which also established that both the HA1 and HA2 polypeptides were iodinated. Radiolabeled hemagglutinins with a specific activity that did not exceed 12 μCi/μg of protein could be maintained for up to 30 days at −70°C in the presence of supplemental protein. The RIP assay was compared with conventional methods, hemagglutination inhibition and viral neutralization tests, using H3N equine 1 hybrid viruses for determining serum antihemagglutinin antibody titers. The geometric mean titers for human convalescent sera after infection with A/England/72 virus were 118, 161, and 18,822 for hemagglutination inhibition, viral neutralization, and RIP tests, respectively, and the three tests demonstrated significant rises in antihemagglutinin antibody titers with equal efficiency. In general, a positive correlation existed between antihemagglutinin antibody titers determined by these three procedures; however, the antibody level determined by RIP assay for each individual could not be related to hemagglutination inhibition or viral neutralization titers by a constant factor. A similar lack of a constant relationship was found by using hyperimmune guinea pig antisera, which suggests that the RIP assay can detect antibody populations that exhibit differing efficiencies for inhibition of viral hemagglutination and replication.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berson S. A., Yalow R. S. General principles of radioimmunoassay. Clin Chim Acta. 1968 Sep;22(1):51–69. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(68)90247-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boche R. D., Quilligan J. J., Jr Adsorption to glass and specific antibody inhibition of iodine-125 labeled influenza virus. J Immunol. 1966 Dec;97(6):942–950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daugharty H., Warfield D. T., Davis M. L. Solid-phase radioimmunoassay of total and influenza-specific immunoglobulin G. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Feb;23(2):360–367. doi: 10.1128/am.23.2.360-367.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerhard W., Braciale T. J., Klinman N. R. The analysis of the monoclonal immune response to influenza virus. I. Production of monoclonal anti-viral antibodies in vitro. Eur J Immunol. 1975 Oct;5(10):720–725. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830051013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg S. B., Couch R. B., Kasel J. A. An outbreak of an influenza type A variant in a closed population: The effect of homologous and heterologous antibody on infection and illness. Am J Epidemiol. 1974 Sep;100(3):209–215. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAVER W. G. STRUCTURAL STUDIES ON THE PROTEIN SUBUNITS FROM THREE STRAINS OF INFLUENZA VIRUS. J Mol Biol. 1964 Jul;9:109–124. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80094-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laver W. G., Downie J. C., Webster R. G. Studies on antigenic variation in influenza virus. Evidence for multiple antigenic determinants on the hemagglutinin subunits of A-Hong Kong-68 (H3 N2) virus and the A-England-72 strains. Virology. 1974 May;59(1):230–244. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90218-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laver W. G. Separation of two polypeptide chains from the hemagglutinin subunit of influenza virus. Virology. 1971 Jul;45(1):275–288. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90134-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laver W. G., Webster R. G. Studies on the origin of pandemic influenza. II. Peptide maps of the light and heavy polypeptide chains from the hemagglutinin subunits of A 2 influenza viruses isolated before and after the appearance of Hong Kong influenza. Virology. 1972 May;48(2):445–455. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90055-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEVER J. L. Application of a microtechnique to viral serological investigations. J Immunol. 1962 Mar;88:320–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schieble J. H., Cottam D. Solid-phase radioimmunoassay as a method for evaluating antigenic differences in type A influenza viruses. Infect Immun. 1977 Jan;15(1):66–71. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.1.66-71.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. V., Dreesman G. R., Spira G., Kasel J. A. Radioimmunoassay of human serum antibody specific for adenovirus type 5-purified fiber. J Immunol. 1975 Jul;115(1):124–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skehel J. J., Waterfield M. D. Studies on the primary structure of the influenza virus hemagglutinin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):93–97. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley P., Crook N. E., Streader L. G., Davidson B. E. The polypeptides of influenza virus. 8. Large-scale purification of the hemagglutinin. Virology. 1973 Dec;56(2):640–645. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90066-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley P., Haslam E. A. The polypeptides of influenza virus. V. Localization of polypeptides in the virion by iodination techniques. Virology. 1971 Dec;46(3):764–773. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90078-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udenfriend S., Stein S., Böhlen P., Dairman W., Leimgruber W., Weigele M. Fluorescamine: a reagent for assay of amino acids, peptides, proteins, and primary amines in the picomole range. Science. 1972 Nov 24;178(4063):871–872. doi: 10.1126/science.178.4063.871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward C. W., Dopheide A. A. Size and chemical composition of influenza virus hemagglutinin chains. FEBS Lett. 1976 Jun 15;65(3):365–368. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80148-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


