Abstract
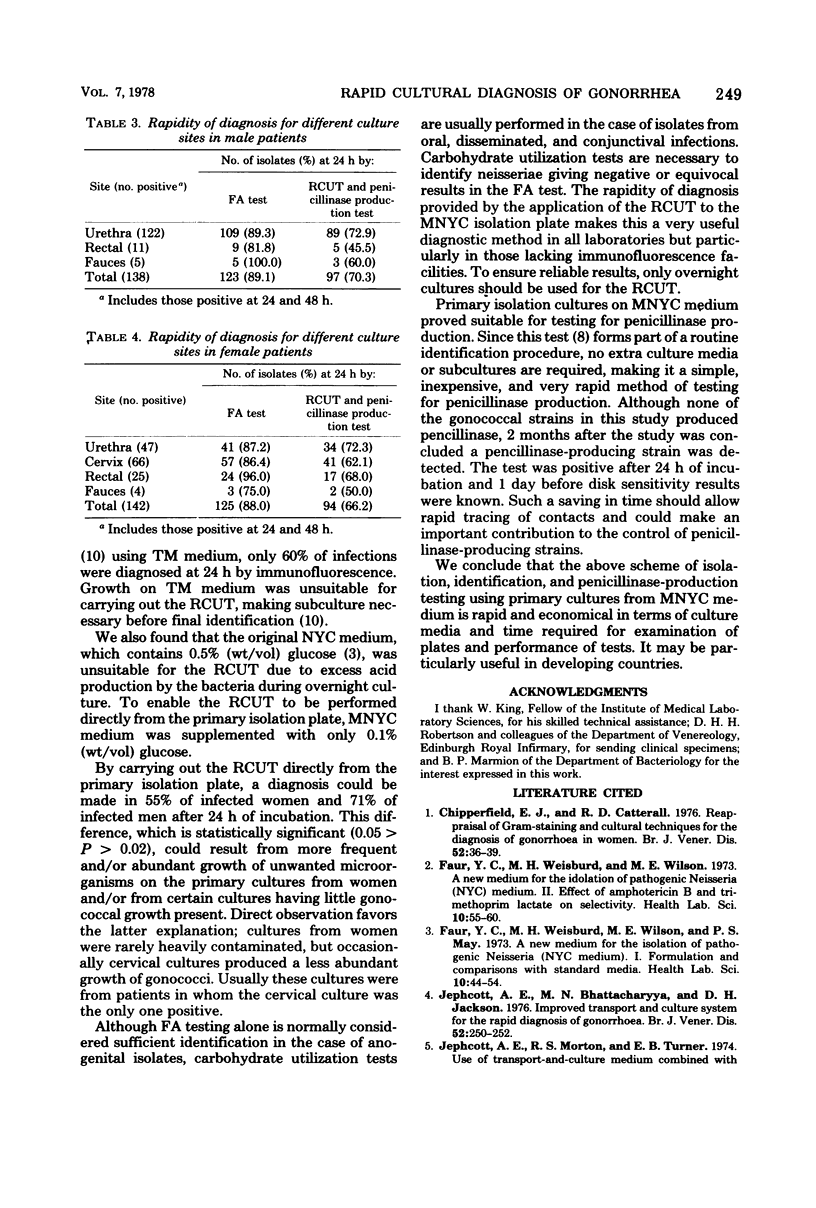
The fluorescent-antibody test, rapid carbohydrate utilization test (RCUT), and a test for penicillinase production were performed on the bacterial growth from primary cultures on modified New York City medium. Of 134 gonococcal infections in men, 88.8% were diagnosed by the fluorescent-antibody test and 70.9% by the RCUT after incubation for 24 h; the corresponding figures for 75 infections in women were 86.7 and 54.7%, respectively. After incubation for 48 h, 100% of infections were diagnosed by the fluorescent-antibody test, wherease 88.8% of infected males and 86.7% of females were also diagnosed by the RCUT. Primary isolation cultures on modified New York City medium proved suitable for determining the ability of strains to produce penicillinase by a modified RCUT procedure. The method of isolation and identification by using primary cultures from modified New York City medium is both rapid and economical. The rapidity of diagnosis provided by the RCUT makes this a very useful diagnostic method, particularly in laboratories lacking immunofluorescence equipment. Since the penicillinase production test forms part of a routine identification procedure, no extra culture media or subcultures are required. The rapidity of this test should make it of value in tracing contacts of patients infected with penicillinase-producing strains.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chipperfield E. J., Catterall R. D. Reappraisal of Gram-staining and cultural techniques for the diagnosis of gonorrhoea in women. Br J Vener Dis. 1976 Feb;52(1):36–39. doi: 10.1136/sti.52.1.36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faur Y. C., Weisburd M. H., Wilson M. E. A new medium for the isolation of pathogenic Neisseria (NYC medium). II. Effect of amphotericin B and trimethoprim lactate on selectivity. Health Lab Sci. 1973 Apr;10(2):55–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faur Y. C., Weisburd M. H., Wilson M. E., May P. S. A new medium for the isolation of pathogenic Neisseria (NYC medium). I. Formulation and comparisons with standard media. Health Lab Sci. 1973 Apr;10(2):44–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jephcott A. E., Bhattacharyya M. N., Jackson D. H. Improved transport and culture system for the rapid diagnosis of gonorrhoea. Br J Vener Dis. 1976 Aug;52(4):250–252. doi: 10.1136/sti.52.4.250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock H. M. Evaluation of methods for the rapid identification of Neisseria gonorrhoeae in a routine clinical laboratory. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Jul;4(1):19–21. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.1.19-21.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson A. E. The sensitivity of gonococci to penicillin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1977 May;3(3):197–198. doi: 10.1093/jac/3.3.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young H. Cultural diagnosis of gonorrhoea with modified New York City (MNYC) medium. Br J Vener Dis. 1978 Feb;54(1):36–40. doi: 10.1136/sti.54.1.36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young H., Paterson I. C., McDonald D. R. Rapid carbohydrate utilization test for the identification of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Br J Vener Dis. 1976 Jun;52(3):172–175. doi: 10.1136/sti.52.3.172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young H. Screening Neisseriae for penicillinase production. Lancet. 1977 May 7;1(8019):1014–1015. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)92323-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



