Abstract
Objective
To estimate the frequency, duration, and clinical importance of postherpetic neuralgia after a single episode of herpes zoster.
Design
Prospective cohort study with long term follow up.
Setting
Primary health care in Iceland.
Participants
421 patients with a single episode of herpes zoster.
Main outcome measures
Age and sex distribution of patients with herpes zoster, point prevalence of postherpetic neuralgia, and severity of pain at 1, 3, 6, and 12 months and up to 7.6 years after the outbreak of zoster.
Results
Among patients younger than 60 years, the risk of postherpetic neuralgia three months after the start of the zoster rash was 1.8% (95% confidence interval 0.59% to 4.18%) and pain was mild in all cases. In patients 60 years and older, the risk of postherpetic neuralgia increased but the pain was usually mild or moderate. After three months severe pain was recorded in two patients older than 60 years (1.7%, 2.14% to 6.15%). After 12 months no patient reported severe pain and 14 patients (3.3%) had mild or moderate pain. Seven of these became pain free within two to seven years, and five reported mild pain and one moderate pain after 7.6 years of follow up. Sex was not a predictor of postherpetic neuralgia. Possible immunomodulating comorbidity (such as malignancy, systemic steroid use, diabetes) was present in 17 patients.
Conclusions
The probability of longstanding pain of clinical importance after herpes zoster is low in an unselected population of primary care patients essentially untreated with antiviral drugs.
Introduction
Evidence is still limited about the clinical course of herpes zoster. Antiviral drugs are commonly considered to alter the course of the disease, reducing both pain in the acute phase and the risk of postherpetic neuralgia long term. Furthermore, studies on the efficacy of pain relief (including both for acute pain and for postherpetic neuralgia) have been difficult to interpret since the analyses do not include patient reports of the severity or clinical importance of the pain.1,2,3
Few large scale prospective studies have been carried out on herpes zoster.4–9 None of these fulfils the criteria for an inception cohort—that is, to include only individuals with a first episode of zoster, as repeated episodes may have a different course from the first.10,11 We have found that the clinical course of herpes zoster is usually benign and without complications in patients in primary care under the age of 60.8 We now provide long term follow up data on the clinical course of herpes zoster on the basis of an inception cohort in patients in primary care.
Participants and methods
The collection of the data (January 1990 to June 1995) has been described elsewhere.8 Sixty two selected general practices, 36 urban and 26 rural, representing a population of 100 000 people (more than a third of the Icelandic population) enrolled all patients with acute zoster in their practice. To be eligible to participate, the general practitioners had to have a computerised medical record system for registration of all patient contacts.
Each general practitioner contacted the principal investigator (SH) when he or she clinically diagnosed herpes zoster. Exclusion criteria were: a previous episode of zoster; patient unable to give accurate information owing to cognitive impairment in the initial phase of the study; wrong or possibly wrong diagnosis as judged by the authors, on the basis of clinical information provided by the general practitioners and the patients; and patients whose general practitioner was unable to comply with the research protocol.
To estimate the completeness of enrolment, records of all patients in hospital who were diagnosed with zoster in all (five) relevant hospitals covering the catchment area during the study period were examined. No additional eligible cases were detected.
Outcome assessment
We collected data on the point prevalence of postherpetic neuralgia at one, three, six, and 12 months after the outbreak of the rash. These time points enabled us to compare our results with as many existing studies on herpes zoster as possible. All patients were contacted by the principal investigator (SH) and questioned systematically about the character and location of the rash, type and duration of any discomfort, systemic symptoms, treatment, and other medical disorders or drugs. The patients (or parents if the patient was a child) were asked to rank any discomfort connected to the dermatome concerned as none, mild, moderate, or severe.12 The corresponding numerical values were also defined for the patients: no pain=0, mild pain=1 to 25, moderate pain greater than 25 to 75, severe pain greater than 75 to 100. We did not use a standardised questionnaire to assess quality of life or changes in quality of life.
We attempted to contact all enrolled patients at each point of the follow up, but only those who could be reached within four weeks of the planned date of follow up were included in the point prevalence analysis at that particular time point.
The long term follow up (greater than 12 months fromherpes zoster) was conducted in two parts. Firstly, a random subsample of 183 patients, all of whom were pain free at one year follow up, were contacted by telephone in April 1997 and asked about possible recurrence of pain. Secondly, the 14 patients reporting pain at 12 months after herpes zoster were followed until January 1999 (up to 7.6 years from the start of the zoster episode). We gathered information on the clinical course of postherpetic neuralgia, with emphasis on the patient's report of the clinical importance of pain and its impact on daily life.
Statistical analysis
Point prevalence, severity, and duration of pain were analysed according to sex and age. Point prevalence was analysed by logistic regression, severity by linear regression, and duration by Cox's regression. As there was no interaction between sex and age and as sex was not a significant predictor, we present the duration as Kaplan-Meier curves for two age groups. Significance testing was two sided at the 5% level. We used the software package SPIDA.13 Relative risk and confidence intervals were calculated with CIA software.14 The study was approved by the national ethics committee.
Results
We recruited 421 patients with a first episode of zoster. End points were obtained for all patients at or close to the 12 month follow up (table 1). Of the 421 patients included, 339 were reached within the set time frame for the follow up one month after the diagnosis of zoster, 391 at three months, and 417 at 12 months. Age was a significant predictor of pain at each time point after zoster. The odds ratio per 10 years' age difference was 1.87 (95% confidence interval 1.56 to 2.23) after one month, 2.11 (1.56 to 2.84) after 3 months, 2.45 (1.50 to 4.01) after 6 months, and 2.33 (1.48 to 3.69) after 12 months. Age was also a significant predictor of severity of pain at one month (P=0.02) and duration of pain (P<0.001). Sex was not a significant predictor of postherpetic neuralgia at any point.
Table 1.
Point prevalence and severity of postherpetic neuralgia one, three, and 12 months after start of herpes zoster in different age groups
| Extent of pain | After 1 month
|
After 3 months
|
After 12 months
|
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | % (95% CI) | No | % (95% CI) | No | % (95% CI) | |||
| 0-49 years | n=196* | n=223* | n=236* | |||||
| Pain free | 185 | 94 (90.2 to 97.2) | 220 | 99 (96.1 to 99.7) | 236 | 100 (98.4 to 100) | ||
| Mild | 10 | 5 (2.5 to 9.2) | 3 | 1 (0.3 to 3.9) | 0 | 0 (0 to 1.6) | ||
| Moderate | 1 | 1 (0 to 2.8) | 0 | 0 (0 to 1.6) | 0 | 0 (0 to 1.6) | ||
| 50-59 years | n=44* | n=53* | n=54* | |||||
| Pain free | 34 | 77 (62.2 to 88.5) | 51 | 96 (87.0 to 99.5) | 52 | 96 (87.2 to 99.5) | ||
| Mild | 7 | 16 (6.7 to 30.1) | 2 | 4 (0.5 to 13.0) | 2 | 4 (0.5 to 12.8) | ||
| Moderate | 3 | 7 (1.4 to 18.7) | 0 | 0 (0 to 6.7) | 0 | 0 (0 to 6.6) | ||
| 60-69 years | n=51* | n=58* | n=67* | |||||
| Pain free | 31 | 61 (46.1 to 74.2) | 51 | 88 (76.7 to 95.0) | 64 | 96 (87.5 to 99.1) | ||
| Mild | 10 | 20 (9.8 to 33.1) | 5 | 9 (2.9 to 19.0) | 2 | 3 (0.4 to 10.4) | ||
| Moderate | 10 | 20 (9.8 to 33.1) | 1 | 2 (0 to 9.2) | 1 | 1 (0 to 8.0) | ||
| Severe | 0 | 0 (0 to 7.0) | 1 | 2 (0 to 9.2) | 0 | 0 (0 to 5.4) | ||
| ⩾70 years | n=48* | n=57* | n=60* | |||||
| Pain free | 24 | 50 (35.2 to 64.8) | 41 | 72 (58.5 to 83.0) | 51 | 85 (73.4 to 92.9) | ||
| Mild | 10 | 21 (10.5 to 35.0) | 10 | 18 (8.8 to 29.9) | 8 | 13 (5.9 to 24.6) | ||
| Moderate | 11 | 23 (12.0 to 37.3) | 5 | 9 (2.9 to 19.3) | 1 | 2 (0 to 8.9) | ||
| Severe | 3 | 6 (1.3 to 17.2) | 1 | 2 (0 to 9.4) | 0 | 0 (0 to 6.0) | ||
Owing to prospective design, only those are counted here who were reached within four weeks of planned date of follow up. Of the four patients not accounted for at 12 months, three had died and one had moved abroad.
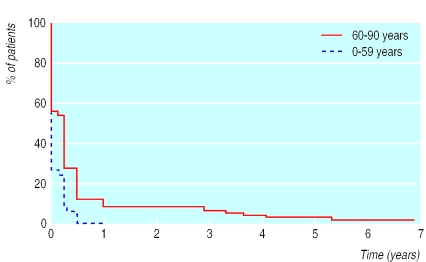
Patients younger than 60 years had a benign course (figure); only 2% (5/276; 0.59% to 4.18%) still had pain associated with zoster three months after the first outbreak, which was mild in all cases. After the age of 60 both the frequency and severity of pain increased, although moderate pain was rare after three months and severe pain uncommon at all times (table 1). The probability of having severe postherpetic neuralgia after three months in this age group was less than 7% (2/115; 2.14 to 6.15), and it was less than 3% at 12 months (0/127; 0 to 2.86).
Potentially immunomodulating comorbidity (such as malignancy, systemic steroid use, and diabetes) was present in 17 patients. Among these were four new malignancies diagnosed within six months of zoster (table 2).
Table 2.
Patients with potentially immunomodulating comorbidity and diagnoses present in cohort of 421 patients with herpes zoster
| No of patients | Diagnosis | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| 8 | Diabetes mellitus | Two patients diagnosed within two months after the outbreak of zoster |
| 2 | Hodgkin's lymphoma | Man (69 years) diagnosed three months after zoster and woman (20 years) diagnosed at the time of zoster outbreak |
| 1 | Pancreatic cancer | Woman (64 years) diagnosed five months before zoster |
| 2 | Breast cancer | Woman (55 years) diagnosed six months after zoster and woman (64 years) treated for breast cancer 2.5 years before zoster diagnosed with metastatic breast cancer three months after zoster |
| 4 | Various | Treatment with oral prednisolone >20 mg/day |
Seventeen patients (4.0%) were treated with antiviral drugs; their mean age was 60.6 years (range 43.4 to 89.3 years). Fourteen of these received doses considered subtherapeutic today (200 mg to 500 mg of aciclovir five times daily). Three patients (0.7%) were treated with therapeutic doses, one with aciclovir 800 mg five times daily and two by intravenous treatment. Of the 17 treated patients, seven had ophthalmic zoster, one oticus zoster, one suspected viral meningitis, and the remainder cutaneous zoster. None of the random subsample of 183 patients who were free of pain at 12 months reported recurrence of pain after 3.2 to 7.0 years of follow up (860 person years).
After 12 months 14 patients (3.3%) still reported mild or moderate pain; most of them (12/14) classified the discomfort as mild (table 3). One patient with mild pain was subsequently lost to follow up. Thirteen patients were followed for a mean of 6.3 years (range 3.5 to 7.6 years or 79.4 person years). Seven of these became pain free within two to seven years. Five reported mild postherpetic neuralgia, one had moderate pain, and no patient reported severe neuralgia at the end of follow up.
Table 3.
Long term follow up of patients who reported any pain 12 months or more after start of herpes zoster
| Sex (age at first episode) | Pain at 12 months | Years of follow up | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Women | |||
| 50 | Mild | 1.0 | Patient lost to follow up after 12 months |
| 56 | Mild | 5.2 | Pain free at 1.5 years |
| 68 | Moderate | 6.9 | Mild pain after 3 years until death after 6.9 years of follow up |
| 69 | Mild | 6.6 | Pain free at 3.7 years |
| 70 | Mild | 5.4 | Pain free after about 5.4 years* |
| 71 | Mild | 5.6 | Mild pain ongoing |
| 71 | Mild | 6.9 | Pain free at 6.9 years (duration, 5.9 years) |
| 74 | Mild | 3.5 | Pain free at 2.8 years |
| 80 | Mild | 6.7 | Mild pain until death after 6.7 years of follow up |
| 82 | Mild | 7.6 | Died August 1998, pain free** |
| 84 | Mild | 5.9 | Died September 1998, pain free** |
| 88 | Mild | 4.9 | Mild pain until death after 4.9 years of follow up |
| Men | |||
| 67 | Moderate | 7.0 | Moderate pain continuing |
| 72 | Mild | 6.2 | Mild pain ongoing |
Pain disappeared between December 97 and November 98 (exact time could not be recalled).
No recall owing to dementia; from interval follow up duration estimated at 5 years.
Resident in nursing house owing to dementia (pain free at 3.3 years).
Discussion
This is the first comprehensive, prospective follow up study of an unselected inception cohort of essentially untreated patients with herpes zoster. To our knowledge, this study has the longest follow up to date. The study shows that the clinical course of herpes zoster is relatively benign and that postherpetic neuralgia rarely affects daily life. When it occurs, neuralgia can last for years, but it may disappear after several years.
Strengths and weaknesses of the study
The main strengths of our study are its prospective design, its well defined target population, and access to computerised medical records. Telephone follow up by only one investigator guaranteed uniform data collection and led to a high response rate at each point of follow up. Use of antiviral drugs for herpes zoster had not gained much interest among general practitioners in Iceland at the time of the study, a fact which made it easier to study the clinical course of the disease.
A potential weakness of our study is that the diagnosis was based on clinical judgment. The presence of herpes zoster was not confirmed by diagnostic tests unless the clinician deemed it useful for the care of the patient. However, the clinicaldiagnosis of zoster is usually straightforward and accepted as such in all clinical trials assessing the effect of antiviral drugs. The methods utilised in our study reflect the reality of everyday practice, an approach that has recently been advocated by experts in evidence based medicine.15
Strengths and weaknesses in relation to other studies
Basic knowledge of the clinical course of zoster diagnosed by a doctor—treated symptomatically if necessary but not by antiviral drugs—is scanty. The use of different variables to follow the course of zoster (for example, different pain measurements, viral shedding, healing of rash) makes comparison among studies difficult. A significant difference need not be clinically important. Many studies have recorded pain simply as any pain, without differentiating severity.1–3,16 It is difficult to judge the clinical relevance of these data, and we believe that they tend to overestimate the problem of postherpetic neuralgia. As recommended by a recent consensus,1,17 we include the prevalence of clinically significant pain at three months as a primary end point.
Our results can best be compared with the placebo group in McKendrick et al's study as we used similar criteria for measuring pain.12 In McKendrick et al's study the prevalence of postherpetic neuralgia among 181 patients 60 years and older was 62.4% at one month and 24.2% at three months after zoster (compared with 44.4% and 20.0% respectively in our study).
Unanswered questions and future research
It is debatable whether antiviral therapy in acute zoster reduces the risk of postherpetic neuralgia. A recent meta-analysis suggests there might be some effect.16 Some guidelines recommend antiviral drugs in patients aged 60 or more, others in patients aged 50 or more, a recommendation that is not supported by our data.18,19 Other risk factors for postherpetic neuralgia have also been put forward: severity of pain at onset, extent of rash, severity and duration of preherpetic neuralgia, and possibly psychosocial status and sex.8,20–22 Greater prevalence of herpes zoster has been observed among women than men,8 but when correlated for age, sex was not identified as a risk factor in our study. Two studies include reports of patients who did not have pain at baseline but did develop long term pain.23,24 This did not occur in our study. One study suggests that optimal treatment of symptoms in the acute phase of zoster reduces the risk of postherpetic neuralgia.25
If zoster is to be treated appropriately, its clinical course needs to be fully understood. Existing evidence does not support the routine use of antiviral treatment in herpes zoster.
What is already known on this topic
Herpes zoster affects all age groups
The acute phase may be followed by longstanding neuralgia; antiviral drugs are commonly advocated to alleviate this phase, and they are believed to reduce the risk of postherpetic neuralgia
What this study adds
The probability of clinically important postherpetic neuralgia is low; the risk of longstanding pain has been overemphasised in trials of drug treatments
Once a patient becomes free of pain after a zoster episode, there is practically no risk of pain recurrence. Once present, neuralgia can persist for years, but spontaneous remission may occur after several years
There may be an indication for antiviral drugs in patients aged more than 60 to prevent postherpetic neuralgia, but more data on risk factors for neuralgia are needed
Supplementary Material
Figure.
Kaplan-Meier plot of duration of any pain from start of herpes zoster among patients in two age groups
Acknowledgments
We thank the general practitioners who helped with the study, Linn Getz for editing the paper, and Helgi Sigvaldason for statistical advice.
Editorial by Cunningham
Footnotes
Funding: This study was partially funded by the Icelandic College of Family Physicians and the Research Fund of the University of Iceland.
Competing interests: SH has received honoraria from GlaxoWellcome for lecturing on herpes zoster.
References
- 1.Dworkin RH, Carrington D, Cunningham A, Kost RG, Levin MJ, McKendrick MW, et al. Assessment of pain in herpes zoster: lessons learned from antiviral trials. Antiviral Res. 1997;33:73–85. doi: 10.1016/s0166-3542(96)01007-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Lydick E, Epstein RS, Himmelberger D, White CJ. Herpes zoster and quality of life: a self-limited disease with severe impact. Neurology. 1995;45 (suppl 8):52–53. doi: 10.1212/wnl.45.12_suppl_8.s52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Lancaster T, Silagy C, Gray S. Primary care management of acute herpes zoster: systematic review of evidence from randomized controlled trials. Br J Gen Pract 1995;39-45. [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 4.Sanders HWA. Herpes zoster in de huisartspraktijk. Doctoral thesis, Nijmegen: University of Nijmegen; 1968. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hope-Simpson RE. Postherpetic neuralgia. J R Coll Gen Pract. 1975;25:571–575. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Christensen P, Nørrelund N. Herpes zoster in general practice. Ugeskr Laeger. 1985;147:3401–3403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ragozzino MW, Melton LJ, Kurland LT, Chu CP, Perry HO. Risk of cancer after herpes zoster. N Engl J Med. 1982;307:393–397. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198208123070701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Helgason S, Sigurdsson JA, Gudmundsson S. The clinical course of herpes zoster: a prospective study in primary care. Eur J Gen Pract. 1996;2:12–16. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Petursson G, Helgason S, Gudmundsson S, Sigurdsson JA. Herpes zoster in children and adolescents. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1998;17:905–908. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199810000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Sackett DL, Hayens RB, Guyatt GH, Tugwell P. Boston: Little, Brown; 1991. In: Clinical epidemiology: a basic science for clinical medicine, 2nd ed; p. 318. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Hayens B, Sackett D. Purpose and procedure. Evidence-based Med. 1998;3:130–131. [Google Scholar]
- 12.McKendrick MW, McGill JI, Wood MJ. Lack of effect of acyclovir on postherpetic neuralgia. BMJ. 1989;298:431. doi: 10.1136/bmj.298.6671.431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Gebsky V, Seung D, McNeil D, Linn D. SPIDA user's manual, version 6. NSW, Australia: Statistical Computing Laboratory, Macquarie University; 1992. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Gardner MJ, Altman D. Statistics with confidence. London: BMJ Publishing Group; 1989. Confidence Interval Analysis (CIA) [Google Scholar]
- 15.Knottnerus JA, Dinant GJ. Medicine based evidence, a prerequisite for evidence based medicine: further research methods must find ways of accommodating clinical reality, not ignoring it. BMJ. 1997;315:1109–1110. doi: 10.1136/bmj.315.7116.1109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Jackson JL, Gibbons R, Meyer G, Inouye L. The effect of treating herpes zoster with oral acyclovir in preventing postherpetic neuralgia. A meta-analysis. Arch Intern Med. 1997;157:909–912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kay R. Some fundamental statistical concepts in clinical trials and their application in herpes zoster. Antivir Chem Chemother. 1995;6(suppl 1):28–33. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Johnson RW. Current and future management of herpes zoster. Antivir Chem Chemother. 1997;8(suppl 1):19–31. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kost RG, Straus SE. Postherpetic neuralgia—pathogenesis, treatment, and prevention. N Engl J Med. 1996;335:32–42. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199607043350107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Beutner KR, Friedman DJ, Forszpaniak C, Andersen PL, Wood MJ. Valaciclovir compared with acyclovir for improved therapy for herpes zoster in immunocompetent adults. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1995;39:1546–1553. doi: 10.1128/aac.39.7.1546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Dworkin RH, Hartstein G, Rosner HL, Walther RR, Sweeney EW, Brand L. A high-risk method for studying psychosocial antecedents of chronic pain: the prospective investigation of herpes zoster. J Abnorm Psychol. 1992;101:200–205. doi: 10.1037//0021-843x.101.1.200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Bowsher D. The lifetime occurrence of herpes zoster and prevalence of post-herpetic neuralgia: a retrospective survey in an elderly population. Eur J Pain. 1999;3:335–342. doi: 10.1053/eujp.1999.0139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Huff JC, Bean B, Balfour HH, Laskin OL, Connor JD, Corey L, et al. Therapy of herpes zoster with oral acyclovir. Am J Med. 1988;85(suppl 2A):84–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Harding SP, Porter SM. Oral acyclovir in herpes zoster ophthalmicus. Curr Eye Res. 1991;10(suppl):177–182. doi: 10.3109/02713689109020376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.McQuay HJ. Antidepressants and chronic pain. Effective analgesia in neuropathic pain and other syndromes. BMJ. 1997;314:763–764. doi: 10.1136/bmj.314.7083.763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.