Abstract
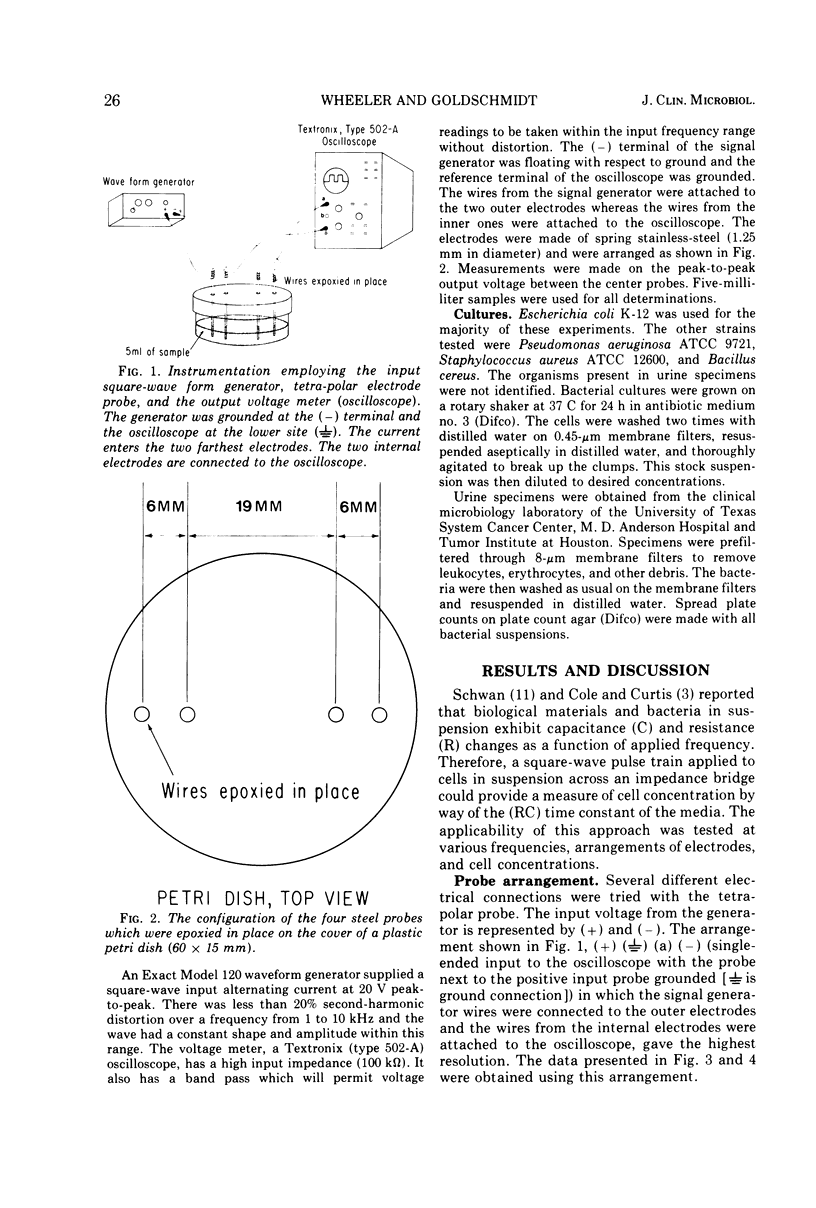
An instrument was developed to measure the concentration of bacterial suspensions by their electrical characteristics. It employed a square-wave signal generator, a tetra-polar electrode probe, and a voltage detector in the form of an oscilloscope. When electrical measurements were made on washed bacteria obtained from cultures or urine specimens, there was a direct relationship between the concentration of the cells and the electrical characteristics of the system as reflected by voltage changes. As little as 10(3) organisms per ml could be detected. The resolution between readings taken on samples containing 10(3) to 10(9) cells per ml was found to be a function of the input frequency. The maximal resolution between concentration readings was obtained at a input frequency of 10 Hz. Thus, with relatively simple instrumentation, bacterial concentrations could be determined within a few minutes. This technique, therefore, eliminates the more lengthy laboratory procedures as plate counts or the accumulation of measurable metabolic changes (such as the utilization of radioactive or other substrates). This method can efficiently monitor clinical urine specimens when a bacteriuria is suspected.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRUMFITT W., PERCIVAL A. PATHOGENESIS AND LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS OF NON-TUBERCULOUS URINARY TRACT INFECTION: A REVIEW. J Clin Pathol. 1964 Sep;17:482–491. doi: 10.1136/jcp.17.5.482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEUTCH M., JESPERSEN H. G. THE DETECTION OF SIGNIFICANT BACTERIURIA. Acta Med Scand. 1964 Feb;175:191–196. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1964.tb00566.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genster H. G., Madsen P. O. Urinary tract infections following transurethral prostatectomy: with special reference to the use of antimicrobials. J Urol. 1970 Jul;104(1):163–168. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)61692-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KASS E. H. Chemotherapeutic and antibiotic drugs in the management of infections of the urinary tract. Am J Med. 1955 May;18(5):764–781. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(55)90190-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KINCAID-SMITH P., BULLEN M., FUSSELL U., MILLS J., HUSTON N. THE RELIABILITY OF SCREENING TESTS FOR BACTERIURIA IN PREGNANCY. Lancet. 1964 Jul 11;2(7350):61–62. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)90066-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAIZTEGUI J. I., BIEGELEISEN J. Z., Jr, CHERRY W. B., KASS E. H. BACTEREMIA DUE TO GRAM-NEGATIVE RODS. A CLINICAL, BACTERIOLOGIC, SEROLOGIC AND IMMUNOFLUORESCENT STUDY. N Engl J Med. 1965 Feb 4;272:222–229. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196502042720502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwan H. P. Electrode polarization impedance and measurements in biological materials. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1968 Feb 1;148(1):191–209. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1968.tb20349.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ur A. Changes in the electrical impedance of blood during coagulation. Nature. 1970 Apr 18;226(5242):269–270. doi: 10.1038/226269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


