Abstract
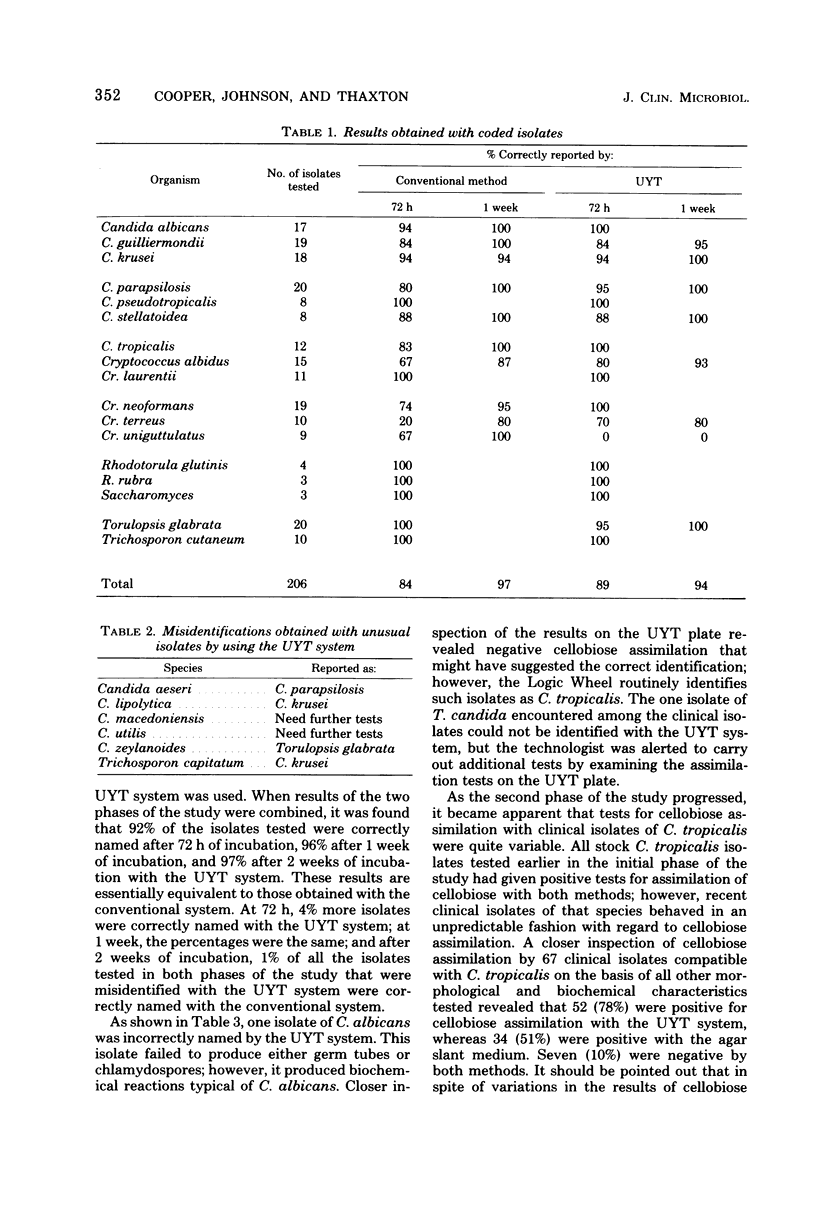
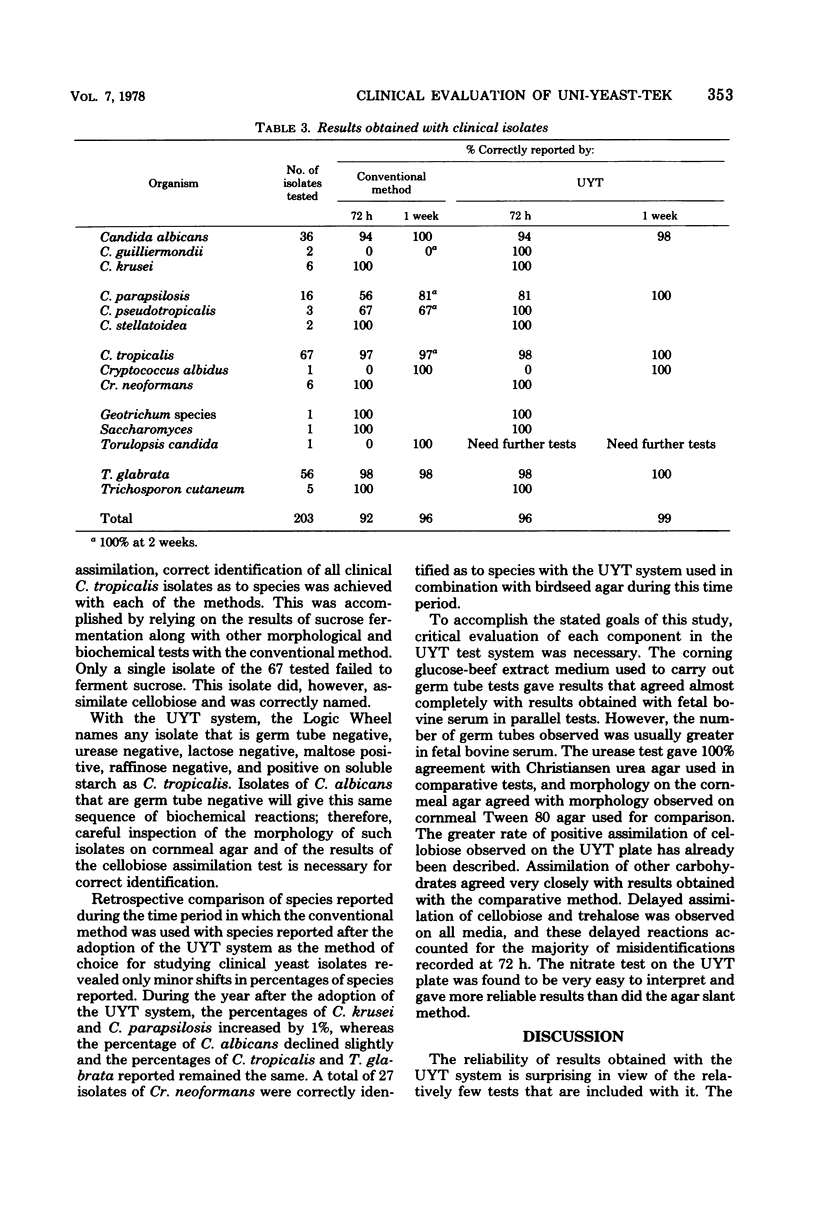
The results of over 400 tests for identification of clinical yeast isolates as to species using the Uni-Yeast-Tek (UYT) system in comparison with a more conventional system are reported. The conventional system utilized a total of 23 individual tests, including both fermentation and assimilation tests, whereas the UYT system included only 11 separate tests. In the initial phase of the study, coded unknown isolates were evaluated by each of two technologists using both methods independently. After this initial evaluation, the two methods were used in parallel for routine testing of yeast isolates as they were obtained from clinical specimens. A further evaluation of the UYT system was carried out by retrospectively analyzing the species reported from a clinical mycology laboratory during two separate time periods in which different approaches to yeast identification were employed. A total of 92% of the isolates tested with the UYT system were correctly reported within 72 h, 96% were correctly named after 1 week of incubation, and 97% were correctly reported after 2 weeks of incubation of UYT plates at 30°C when results of the two phases of the study were analyzed together. With the conventional system, 88% of the isolates were correctly reported at 72 h, 96% at 1 week, and 98% after 2 weeks of incubation of biochemical tests. Retrospective analysis of laboratory records revealed no major changes in species reported after adoption of the UYT system for routine testing of clinical isolates. The data presented in this report suggest that the UYT system can be expected to yield rapid presumptive identification of clinical yeast isolates with reasonable confidence when certain minor limitations that are discussed in the text are taken into account.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams E. D., Jr, Cooper B. H. Evaluation of a modified Wickerham medium for identifying medically important yeasts. Am J Med Technol. 1974 Sep;40(9):377–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahearn D. G., Meyer S. A., Mitchell G., Nicholson M. A., Ibrahim A. I. Sucrose-negative variants of Candida tropicalis. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Apr;5(4):494–496. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.4.494-496.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman P. I., Ahearn D. G. Evaluation of commercial systems for the identification of clinical yeast isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Jul;4(1):49–53. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.1.49-53.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman P. I., Ahearn D. G. Evaluation of the Uni-Yeast-Tek kit for the identification of medically important yeasts. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Oct;2(4):354–358. doi: 10.1128/jcm.2.4.354-358.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming W. H., Hopkins J. M., Land G. A. New culture medium for the presumptive identificaion of Candida albicans and Cryptococcus neoformans. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Feb;5(2):236–243. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.2.236-243.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haley L. D. Identification of yeasts in clinical microbiology laboratories. Am J Med Technol. 1971 Apr;37(4):125–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huppert M., Harper G., Sun S. H., Delanerolle V. Rapid methods for identification of yeasts. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Jul;2(1):21–34. doi: 10.1128/jcm.2.1.21-34.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land G. A., Vinton E. C., Adcock G. B., Hopkins J. M. Improved auxanographic method for yeast assimilations: a comparison with other approaches. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Sep;2(3):206–217. doi: 10.1128/jcm.2.3.206-217.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mickelsen P. A., McCarthy L. R., Propst M. A. Further modifications of the auxanographic method for identification of yeasts. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Mar;5(3):297–301. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.3.297-301.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts G. D., Wang H. S., Hollick G. E. Evaluation of the API 20 c microtube system for the identification of clinically important yeasts. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Mar;3(3):302–305. doi: 10.1128/jcm.3.3.302-305.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal E., Ajello L. Evaluation of a new system for the rapid identification of clinically important yeasts. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Aug;4(2):157–159. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.2.157-159.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


