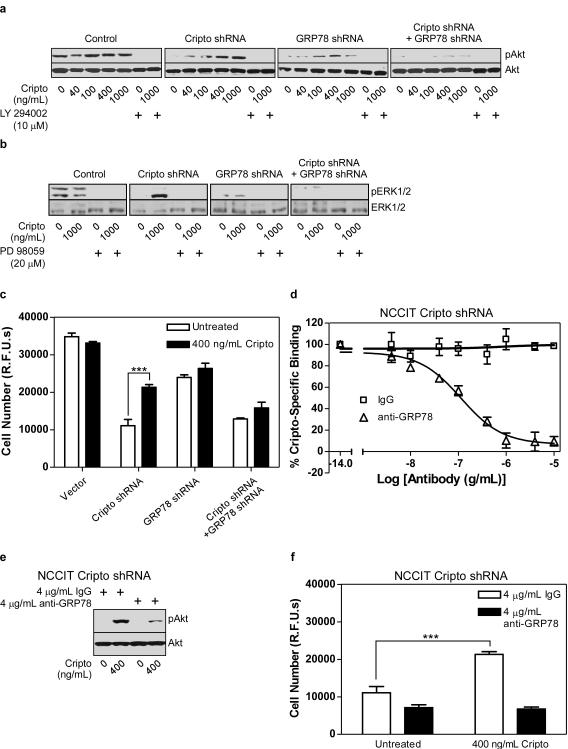
Figure 3. Cripto signaling via cell surface GRP78 promotes MAPK/PI3K signaling and mitogenesis in NCCIT cells.
NCCIT cells stably expressing the indicated shRNAs were serum starved and then treated with the indicated doses of soluble Cripto and either the PI3K inhibitor (LY2940002) (a) or the MEK1/2 inhibitor (PD98059) (b) as indicated. Cell lysates were subjected to Western blotting using anti-phospho-Akt (pAkt) and Akt (a) or phospho-ERK1/2 (pERK1/2) and ERK1/2 antibodies (b) as indicated. (c) The same NCCIT cells were treated with Cripto as indicated, grown for 8 days and then cell number was measured using the CyQuant proliferation assay kit. (d) NCCIT cells infected with Cripto shRNA were subjected to 125I-Cripto binding in the presence of a range of doses of anti-GRP78 or IgG control. Cripto specific binding represents the amount of 125I-Cripto binding that is blocked by an excess of unlabeled soluble Cripto. NCCIT cells infected with Cripto shRNA were (e) serum-starved and then treated with the indicated dose of soluble Cripto after pretreatment with the indicated dose of IgG or anti-GRP78 or (f) treated with soluble Cripto following pretreatment with IgG control or anti-GRP78 as indicated. Cells were grown for an additional 8 days and proliferation was measured using the CyQuant proliferation assay kit. *p<0.01; ***p<0.001.