Abstract
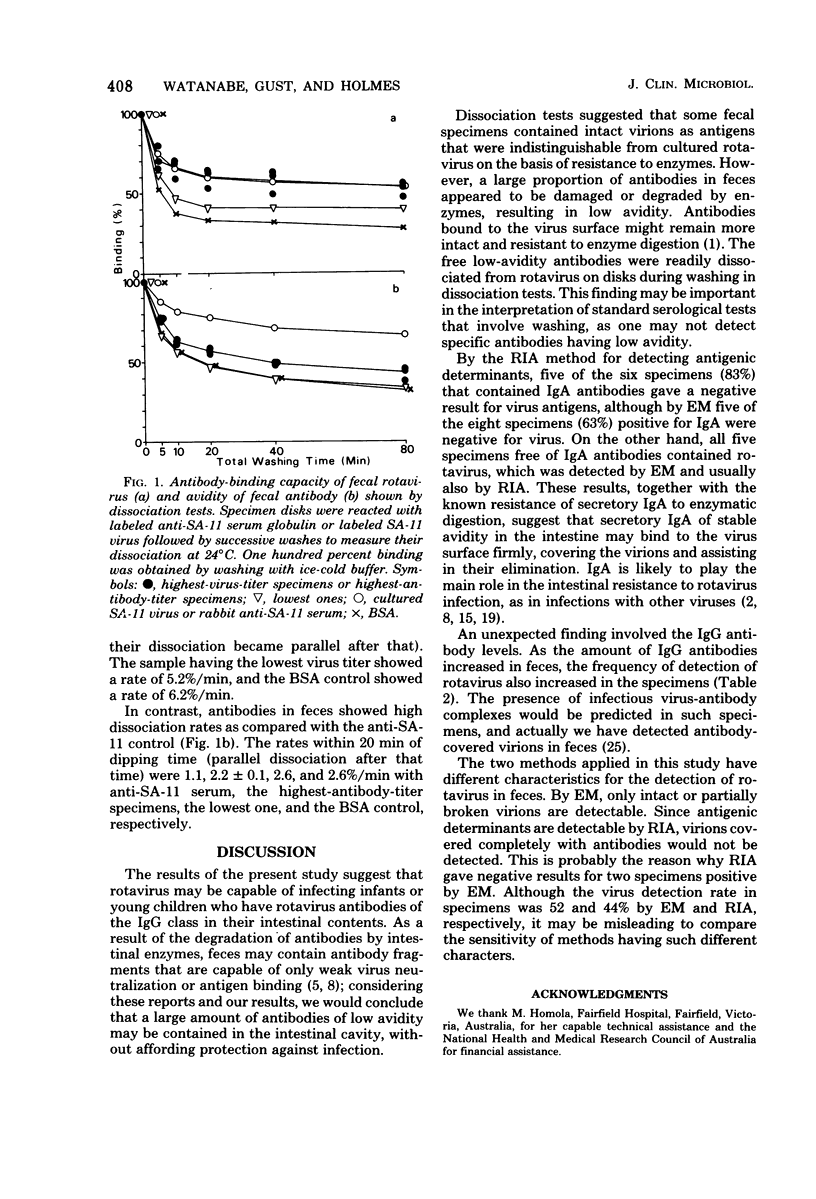
Rotavirus and its antibody were detected by paper disk solid-phase radioimmunoassay or electron microscopy in feces of infants and young children with acute diarrhea. The fecal specimens in which rotavirus was detectable often contained a high titer of antibodies, which were shown by radioimmunoassay to belong mainly to the immunoglobulin G class. Rotavirus was rarely detected in the specimens containing immunoglobulin A antibodies. By dissociation tests carried out by radioimmunoassay, it was shown that the rotavirus particles in some specimens had the same antibody-binding capacity as did cultured simian rotavirus (SA-11), but antibodies in feces usually had low avidity, probably resulting from enzymatic digestion.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blank S. E., Leslie G. A., Clem L. W. Antibody affinity and valence in viral neutralization. J Immunol. 1972 Mar;108(3):665–673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohl E. H., Saif L. J. Passive immunity in transmissible gastroenteritis of swine: immunoglobulin characteristics of antibodies in milk after inoculating virus by different routes. Infect Immun. 1975 Jan;11(1):23–32. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.1.23-32.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson G. P., Bishop R. F., Townley R. R., Holmes I. H. Importance of a new virus in acute sporadic enteritis in children. Lancet. 1975 Feb 1;1(7901):242–246. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91140-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flewett T. H., Bryden A. S., Davies H., Woode G. N., Bridger J. C., Derrick J. M. Relation between viruses from acute gastroenteritis of children and newborn calves. Lancet. 1974 Jul 13;2(7872):61–63. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91631-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haneberg B., Endresen C. Fragments of immunoglobulins in human faeces. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1976 Feb;84(1):31–36. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1976.tb03596.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalica A. R., Purcell R. H., Sereno M. M., Wyatt R. G., Kim H. W., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. A microtiter solid phase radioimmunoassay for detection of the human reovirus-like agent in stools. J Immunol. 1977 Apr;118(4):1275–1279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapikian A. Z., Kim H. W., Wyatt R. G., Cline W. L., Arrobio J. O., Brandt C. D., Rodriguez W. J., Sack D. A., Chanock R. M., Parrott R. H. Human reovirus-like agent as the major pathogen associated with "winter" gastroenteritis in hospitalized infants and young children. N Engl J Med. 1976 Apr 29;294(18):965–972. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197604292941801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller R., Dwyer J. E. Neutralization of poliovirus by IgA coproantibodies. J Immunol. 1968 Aug;101(2):192–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konno T., Imai A., Suzuki H., Ishida N. Letter: Mercaptoethanol-sensitive antibody to reovirus-like agents in acute epidemic gastroenteritis. Lancet. 1975 Dec 27;2(7948):1312–1312. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)90654-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAFFERTY K. J. THE INTERACTION BETWEEN VIRUS AND ANTIBODY. I. KINETIC STUDIES. Virology. 1963 Sep;21:61–75. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90305-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- M Neill T. A. The neutralization of pox viruses. I. Evidence for antibody interference. J Hyg (Lond) 1968 Dec;66(4):541–548. doi: 10.1017/s002217240002828x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mach J. P., Pahud J. J. Secretory IgA, a major immunoglobulin in most bovine external secretions. J Immunol. 1971 Feb;106(2):552–563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middleton P. J., Holdaway M. D., Petric M., Szymanski M. T., Tam J. S. Solid-phase radioimmunoassay for the detection of rotavirus. Infect Immun. 1977 May;16(2):439–444. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.2.439-444.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogra P. L. Immunologic aspects of hepatitis-associated antigen and antibody in human body fluids. J Immunol. 1973 May;110(5):1197–1205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogra P. L., Wallace R. B., Umana G., Ogra S. S., Grant D. K., Morag A. Implications of secretory immune system in viral infections. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1974;45(0):271–282. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-4550-3_33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pahud J. J., Mach J. P. Identification of secretory IgA, free secretory piece and serum IgA in the ovine and caprine species. Immunochemistry. 1970 Aug;7(8):679–686. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(70)90174-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson M. W., Spendlove R. S., Smart R. A. Detection of neonatal calf diarrhea virus, infant reovirus-like diarrhea virus, and a coronavirus using the fluorescent virus precipitin test. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Mar;3(3):376–377. doi: 10.1128/jcm.3.3.376-377.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodger S. M., Schnagl R. D., Holmes I. H. Biochemical and biophysical characteristics of diarrhea viruses of human and calf origin. J Virol. 1975 Nov;16(5):1229–1235. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.5.1229-1235.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saif L. J., Bohl E. H., Gupta R. K. Isolation of porcine immunoglobulins and determination of the immunoglobulin classes of transmissible gastroenteritis viral antibodies. Infect Immun. 1972 Oct;6(4):600–609. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.4.600-609.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snodgrass D. R., Smith W., Gray E. W., Herring J. A. A rotavirus in lambs with diarrhoea. Res Vet Sci. 1976 Jan;20(1):113–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tufvesson B., Johnsson T. Immunoelectroosmophoresis for detection of reo-like virus: methodology and comparison with electron microscopy. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1976 Aug;84(4):225–228. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1976.tb01929.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaerman J. P., Heremans J. F. The IgA system of the guinea pig. J Immunol. 1972 Mar;108(3):637–648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker W. A., Abel S. N., Wu M., Bloch K. J. Intestinal uptake of macromolecules. V. Comparison of the in vitro uptake by rat small intestine of antigen-antibody complexes prepared in antibody or antigen excess. J Immunol. 1976 Sep;117(3):1028–1032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker W. A., Isselbacher K. J., Bloch K. J. Intestinal uptake of macromolecules. II. Effect of parenteral immunization. J Immunol. 1973 Jul;111(1):221–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe H., Holmes I. H. Filter paper solid-phase radioimmunoassay for human rotavirus surface immunoglobulins. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Oct;6(4):319–324. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.4.319-324.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe H., Kobayashi K. Peculiar secretory IgA system identified in chickens. J Immunol. 1974 Nov;113(5):1405–1409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilsnack R. E., Blackwell J. H., Parker J. C. Identification of an agent of epizootic diarrhea of infant mice by immunofluorescent and complement-fixation tests. Am J Vet Res. 1969 Jul;30(7):1195–1204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woode G. N., Bridger J., Hall G. A., Jones J. M., Jackson G. The isolation of reovirus-like agents (rota-viruses) from acute gastroenteritis of piglets. J Med Microbiol. 1976 May;9(2):203–209. doi: 10.1099/00222615-9-2-203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H., Kim H. W., Clem T., Wyatt R. G., Kalica A. R., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for detection of human reovirus-like agent of infantile gastroenteritis. Lancet. 1977 Aug 6;2(8032):263–267. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)90951-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


