Abstract
Use of an antigen consisting of purified isolated nuclei from a mixture of human cytomegalovirus-infected and uninfected fibroblasts in a 2:1 ratio is a simple and reliable method for eliminating nonspecific fluorescence associated with the presence of Fc-immunoglobulin G receptors in the cytoplasm of infected cells. The specificity obtained with this antigen on 100 normal human sera was 99, 100, and 98% when compared with microneutralization, anticomplement immunofluorescence, and conventional indirect fluorescent-antibody assays, respectively. Also, 95% of the antibody titers obtained with the nuclear antigen had a perfect correlation with or were within a fourfold-dilution difference of the antibody levels obtained by anticomplement immunofluorescence and the conventional indirect fluorescent-antibody test.
Full text
PDF

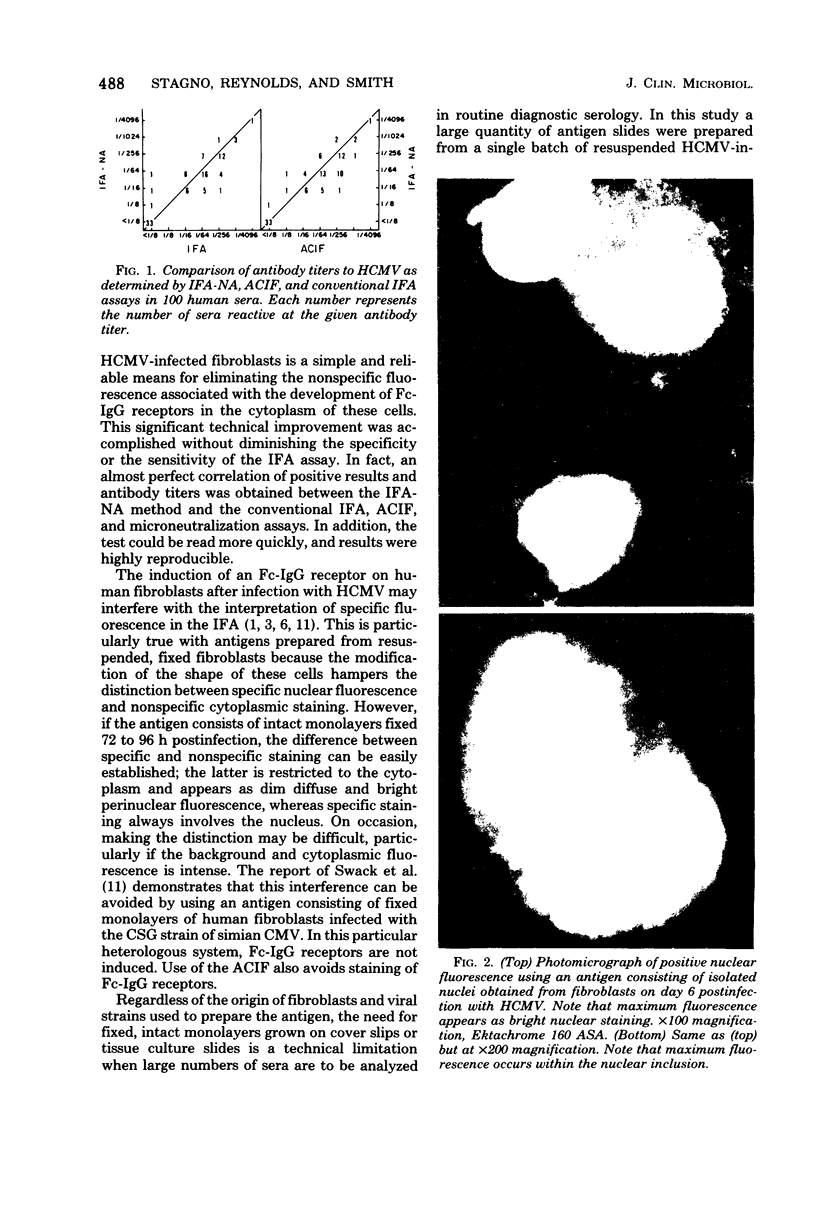

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chiba S., Striker R. L., Jr, Benyesh-Melnick M. Microculture plaque assay for human and simian cytomegaloviruses. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Apr;23(4):780–783. doi: 10.1128/am.23.4.780-783.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa T., Hornberger E., Sakuma S., Plotkin S. A. Demonstration of immunoglobulin G receptors induced by human cytomegalovirus. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Oct;2(4):332–336. doi: 10.1128/jcm.2.4.332-336.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geder L. Evidence for early nuclear antigens in cytomegalovirus-infected cells. J Gen Virol. 1976 Aug;32(2):315–319. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-32-2-315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giraldo G., Beth E., Hämmerling U., Tarro G., Kourilsky F. M. Detection of early antigens in nuclei of cells infected with cytomegalovirus or herpes simplex virus type 1 and 2 by anti-complement immunofluorescence, and use of a blocking assay to demonstrate their specificity. Int J Cancer. 1977 Jan;19(1):107–116. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910190115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller R., Peitchel R., Goldman J. N., Goldman M. An IgG-Fc receptor induced in cytomegalovirus-infected human fibroblasts. J Immunol. 1976 Mar;116(3):772–777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luka J., Siegert W., Klein G. Solubilization of the Epstein-Barr virus-determined nuclear antigen and its characterization as a DNA-binding protein. J Virol. 1977 Apr;22(1):1–8. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.1.1-8.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reedman B. M., Hilgers J., Hilgers F., Klein G. Immunofluorescence and anti-complement immunofluorescence absorption tests for quantitation of Epstein-Barr virus-associated antigens. Int J Cancer. 1975 Apr 15;15(4):566–571. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910150406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stagno S., Reynolds D. W., Tsiantos A., Fuccillo D. A., Long W., Alford C. A. Comparative serial virologic and serologic studies of symptomatic and subclinical congenitally and natally acquired cytomegalovirus infections. J Infect Dis. 1975 Nov;132(5):568–577. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.5.568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stagno S., Volanakis J. E., Reynolds D. W., Stroud R., Alford C. A. Immune complexes in congenital and natal cytomegalovirus infections of man. J Clin Invest. 1977 Oct;60(4):838–845. doi: 10.1172/JCI108838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swack N. S., Michalski F. J., Baumgarten A., Hsiung G. D. Indirect fluorescent-antibody test for human cytomegalovirus infection in the absence of interfering immunoglobulin G receptors. Infect Immun. 1977 May;16(2):522–526. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.2.522-526.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]