Abstract
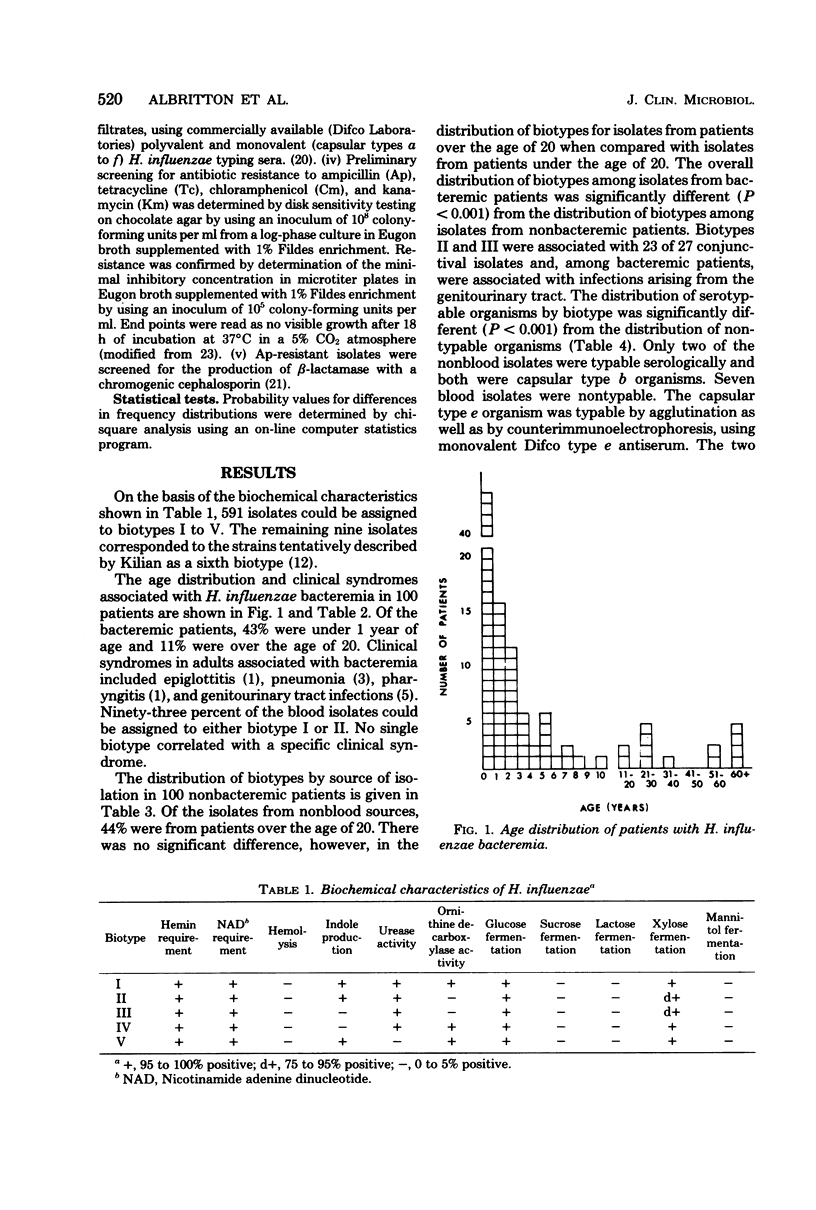
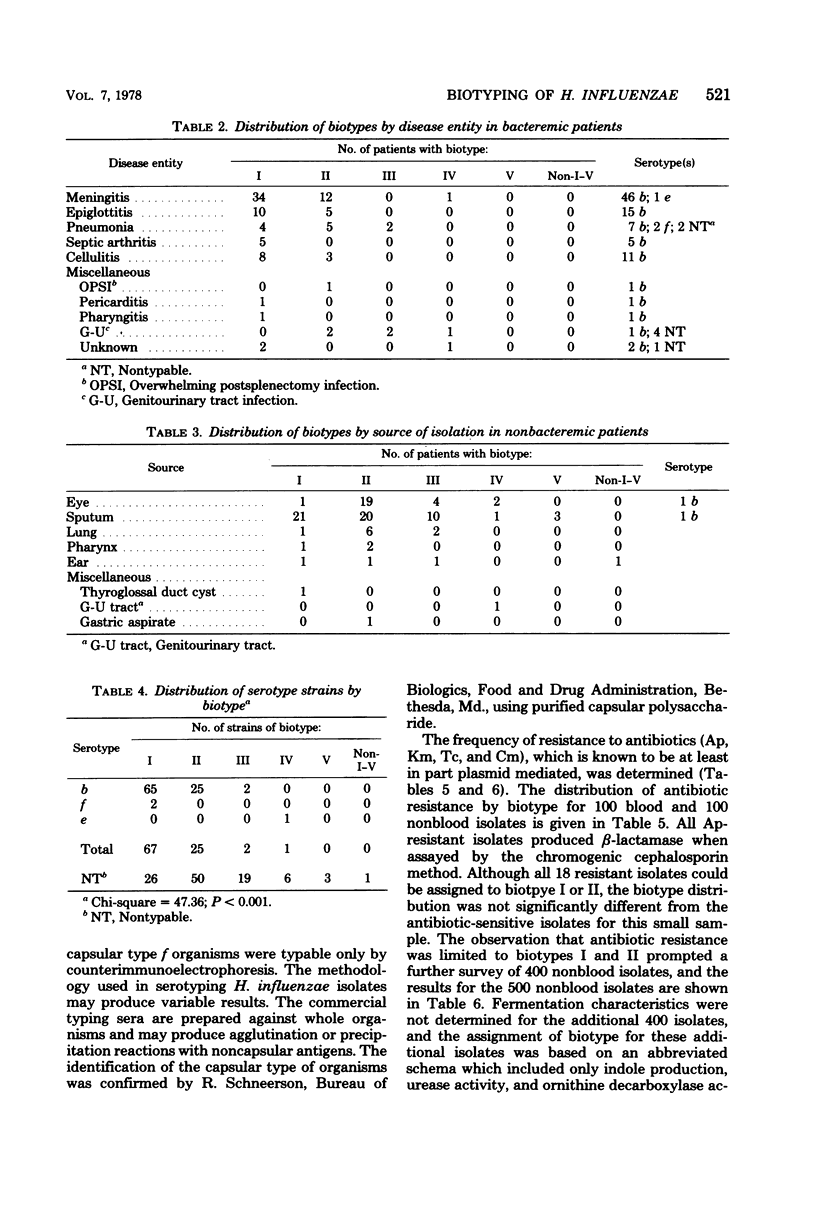
Based on a limited number of biochemical properties, a system for biotyping Haemophilus influenzae (M. Kilian, Acta Pathol. Microbiol, Scand. Sect. B82:835-842, 1976) was used to analyze the relationship of biotype to source of infection and antibiotic resistance for 600 clinical strains. The distribution of biotypes from bacteremic patients was significantly different (P less than 0.001) from the distribution of biotypes from nonbacteremic patients. Although there appeared to be a correlation between biotype and source of isolation, no single biotype correlated with a specific clinical syndrome in bacteremic patients. The frequency of resistance to antibiotics (ampicillin, tetracycline, chloramphenicol, and kanamycin), which was known to be at least in part plasmid mediated, was determined. Of the 600 isolates, 43 were resistant to at least one antibiotic (30 were ampicillin resistant, 11 were tetracycline resistant, 1 was ampicillin-tetracycline resistant, and 1 was tetracycline-chloramphenicol resistant). Of these 43 resistant isolates, 42 were either biotype I or II. This distribution of biotypes among antibiotic-resustant isolates was significantly different from the overall distribution of biotypes (P is less than 0.001).
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bruun B., Friis-Moller A. Ampicllin sensitivity and biotypes of recent Danish isolates of Haemophilus influenzae. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1976 Aug;84(4):201–204. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1976.tb01926.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck L. L., Douglas G. W. Meningitis due to Haemophilus influenzae type e. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Oct;4(4):381–381. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.4.381-381.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapkin M. S., Wilson M. E., Shrager S. M., Rubin R. H. Bacteremic hemophilus influenzae type B cellulitis in the adult. Am J Med. 1977 Sep;63(3):449–452. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(77)90284-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elwell L. P., Saunders J. R., Richmond M. H., Falkow S. Relationships among some R plasmids found in Haemophilus influenzae. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jul;131(1):356–362. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.1.356-362.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett E. D., Rham A. E., Jr, Adaniya R., Stevens D. L., McNitt T. R. Haemophilus influenzae pneumonia in adults. JAMA. 1977 Jul 25;238(4):319–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honig P. J., Pasquariello P. S., Jr, Stool S. E. H. influenzae pneumonia in infants and children. J Pediatr. 1973 Aug;83(2):215–219. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80478-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khuri-Bulos N., McIntosh K. Neonatal Haemophilus influenzae infection. Report of eight cases and review of the literature. Am J Dis Child. 1975 Jan;129(1):57–62. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1975.02120380037009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilian M. A rapid method for the differentiation of Haemophilus strains. The porphyrin test;. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1974 Dec;82(6):835–842. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1974.tb02381.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilian M. A taxonomic study of the genus Haemophilus, with the proposal of a new species. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Mar;93(1):9–62. doi: 10.1099/00221287-93-1-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilian M., Mordhorst C. H., Dawson C. R., Lautrop H. The taxonomy of haemophili isolated from conjunctivae. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1976 Jun;84(3):132–138. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1976.tb01915.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEIDY G., HAHN E., ZAMENHOF S., ALEXANDER H. E. Biochemical aspects of virulence of Hemophilus influenzae. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Nov 21;88:1195–1202. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb20109.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin D. C., Schwarz M. I., Matthay R. A., LaForce F. M. Bacteremic hemophilus influenzae pneumonia in adults. A report of 24 cases and a review of the literature. Am J Med. 1977 Feb;62(2):219–224. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(77)90317-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund M. E., Blazevic D. J. Rapid speciation of Haemophilus with the porphyrin production test versus the satellite test for X. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Feb;5(2):142–144. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.2.142-144.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marraro R. V., McCleskey F. K., Mitchell J. L. Pneumonia due to Haemophilus influenzae (H. aegyptius) biotype 3. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Aug;6(2):172–173. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.2.172-173.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGowan J. E., Jr, Klein J. O., Bratton L., Barnes M. W., Finland M. Meningitis and bacteremia due to Haemophilus influenzae: occurrence and mortality at Boston City Hospital in 12 selected years, 1935-1972. J Infect Dis. 1974 Aug;130(2):119–124. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.2.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myhre E. B. Typing of Haemophilus influenzae by counterimmunoelectrophoresis. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1974 Apr;82(2):164–166. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1974.tb02308.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C. H., Morris A., Kirby S. M., Shingler A. H. Novel method for detection of beta-lactamases by using a chromogenic cephalosporin substrate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Apr;1(4):283–288. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.4.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd J. K., Bruhn F. W. Severe Haemophilus influenzae infections. Am J Dis Child. 1975 May;129(5):607–611. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1975.02120420047016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van A. D., Goldstein F., Acar J. F., Bouanchaud D. H. A transferable kanamycin resistance plasmid isolated from Haemophilus influenzae. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1975 Apr;126(3):397–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Klingeren B., van Embden J. D., Dessens-Kroon M. Plasmid-mediated chloramphenicol resistance in Haemophilus influenzae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Mar;11(3):383–387. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.3.383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


