Abstract
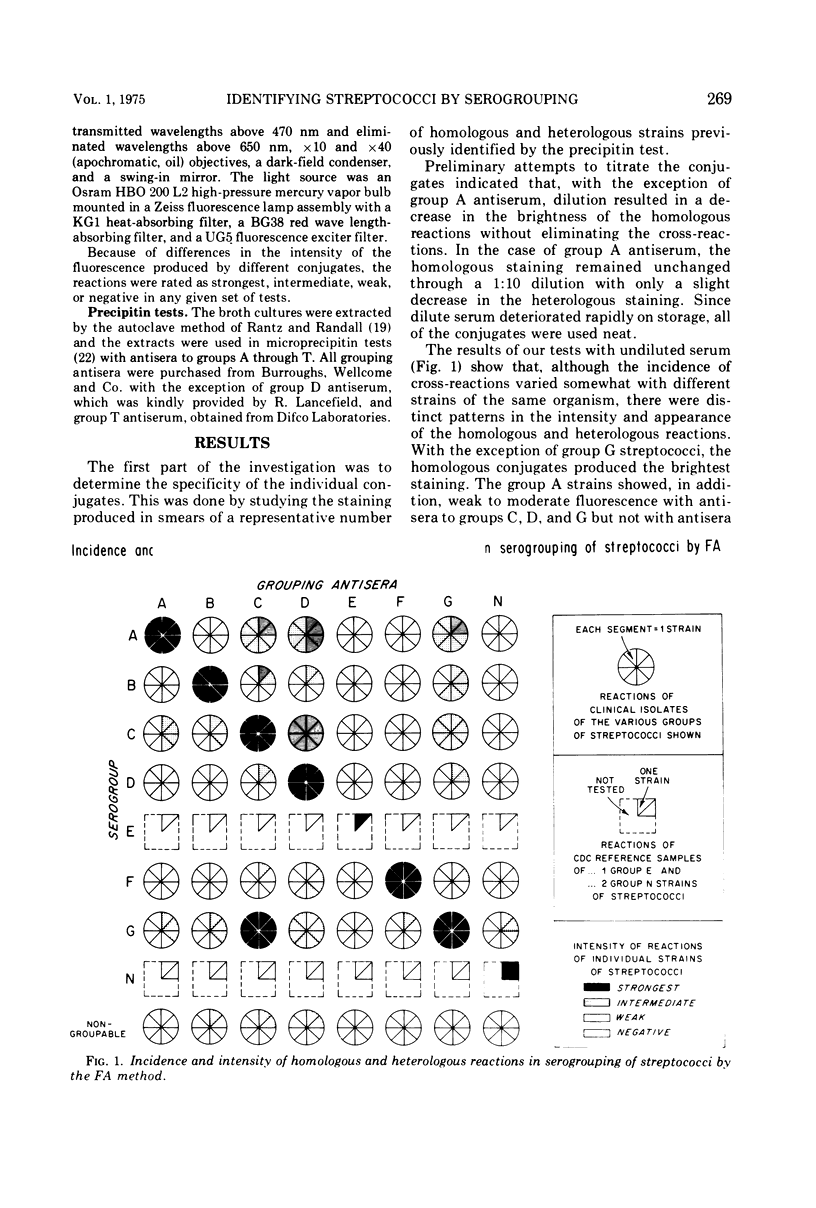
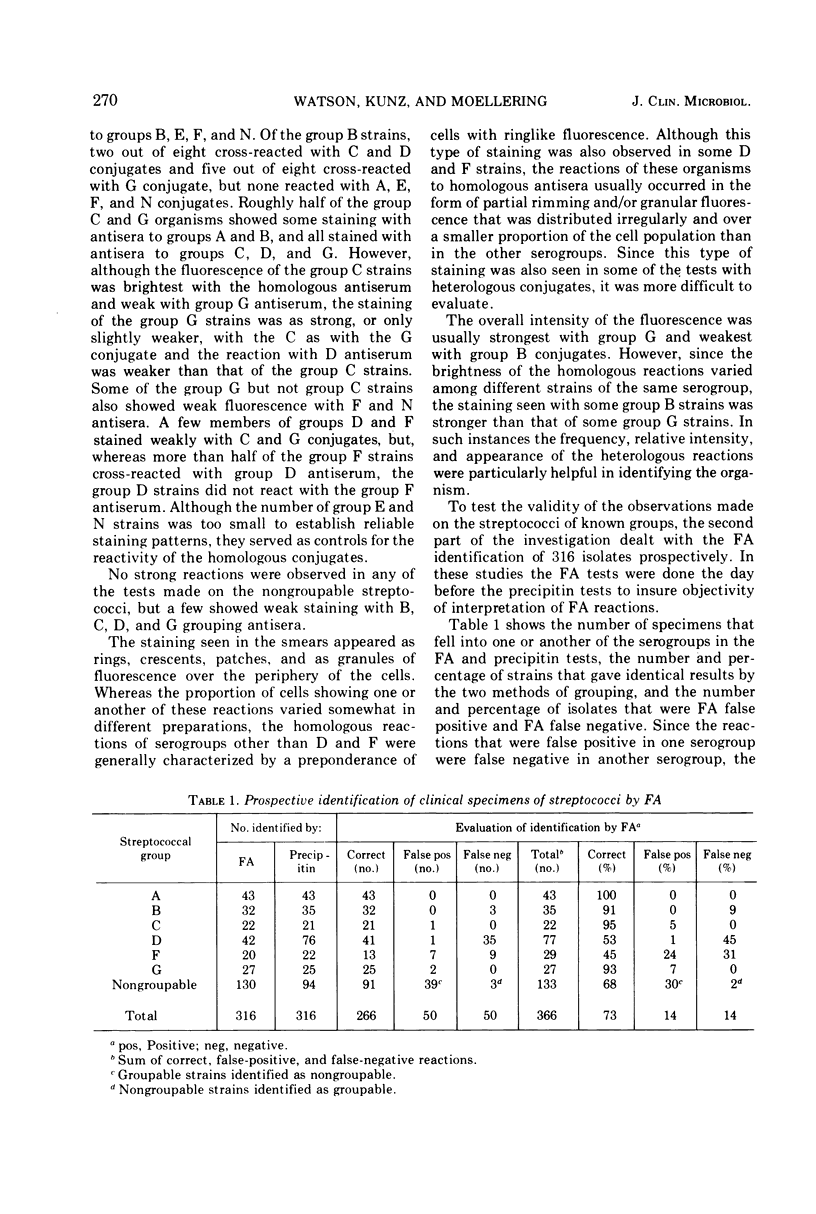
This paper deals with the fluorescent antibody (FA) method for identifying six commonly occuring and two rare groups of streptococci by using commercially prepared (Difco) conjugates. We have shown that group-specific FA produced frequent cross-reactions with heterologous groups of organisms. These reactions varied with different strains of the same serogroup. Nonetheless, there was distinct overall patterns in the intensity and appearance of the homologous and heterologous reactions. When monitored by the precipitin test with Rantz and Randall extracts, these patterns led to the correct identification of 90 to 100% of specimens of serogroup A, B, C, and G streptococci. Many members of groups D and F also showed distinctive reaction patterns. However, there was a significant number of strains of both groups D and F that either failed to strain or stained poorly with the homologous conjugate. As a result, the identification of these serogroups by FA was less reliable.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chitwood L. A., Jennings M. B., Riley H. D., Jr Time, cost, and efficacy study of identifying group A streptococci with commercially available reagents. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Aug;18(2):193–197. doi: 10.1128/am.18.2.193-197.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEIBEL R. H. THE GROUP D STREPTOCOCCI. Bacteriol Rev. 1964 Sep;28:330–366. doi: 10.1128/br.28.3.330-366.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feingold D. S., Stagg N. L., Kunz L. J. Extrarespiratory streptococcal infections. Importance of the various serologic groups. N Engl J Med. 1966 Aug 18;275(7):356–361. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196608182750704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebert G. A., Pittman B., Cherry W. B. Factors affecting the degree of nonspecific staining given by fluorescein isothiocyanate labelled globulins. J Immunol. 1967 Jun;98(6):1204–1212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebert G. A., Pittman B., Cherry W. B. The definition and application of evaluation techniques as a guide for the improvement of fluorescent antibody reagents. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Jun 21;177:54–69. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb35033.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JONES D., SHATTOCK P. M. The location of the group antigen of group D Streptococcus. J Gen Microbiol. 1960 Oct;23:335–343. doi: 10.1099/00221287-23-2-335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCARTY M. The lysis of group A hemolytic streptococci by extracellular enzymes of Streptomyces albus. II. Nature of the cellular substrate attacked by the lytic enzymes. J Exp Med. 1952 Dec;96(6):569–580. doi: 10.1084/jem.96.6.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOODY M. D., ELLIS E. C., UPDYKE E. L. Staining bacterial smears with fluorescent antibody. IV. Grouping streptococci with fluorescent antibody. J Bacteriol. 1958 May;75(5):553–560. doi: 10.1128/jb.75.5.553-560.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel M. F., Krause R. M. Immunochemical studies on the group and type antigens of group F streptococci and the identification of a grouplike carbohydrate in a type II strain with an undesignated group antigen. J Exp Med. 1967 Jun 1;125(6):1075–1089. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.6.1075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel M. F., van Vonno J., Krause R. M. Studies on the chemical structure and the antigenic determinant of type II antigen of group F streptococci. J Immunol. 1969 Jan;102(1):215–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlova M. T., Beauvais E., Brezenski F. T., Litsky W. Fluorescent-antibody techniques for the identification of group D streptococci: direct staining method. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Mar;23(3):571–577. doi: 10.1128/am.23.3.571-577.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman B., Herbert G. A., Cherry W. B., Taylor G. C. The quantitation of nonspecific staining as a guide for improvement of fluorescent antibody conjugates. J Immunol. 1967 Jun;98(6):1196–1203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANTZ L. A., RANDALL E. Use of autoclaved extracts of hemolytic streptococci for serological grouping. Stanford Med Bull. 1955 May;13(2):290–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REDYS J. J., ROSS M. R., BORMAN E. K. Inhibition of commonantigen fluorescence in grouping streptococci by the fluorescent antibody method. J Bacteriol. 1960 Dec;80:823–829. doi: 10.1128/jb.80.6.823-829.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romero R., Wilkinson H. W. Identification of group B streptococci by immunofluorescence staining. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Aug;28(2):199–204. doi: 10.1128/am.28.2.199-204.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


