Abstract
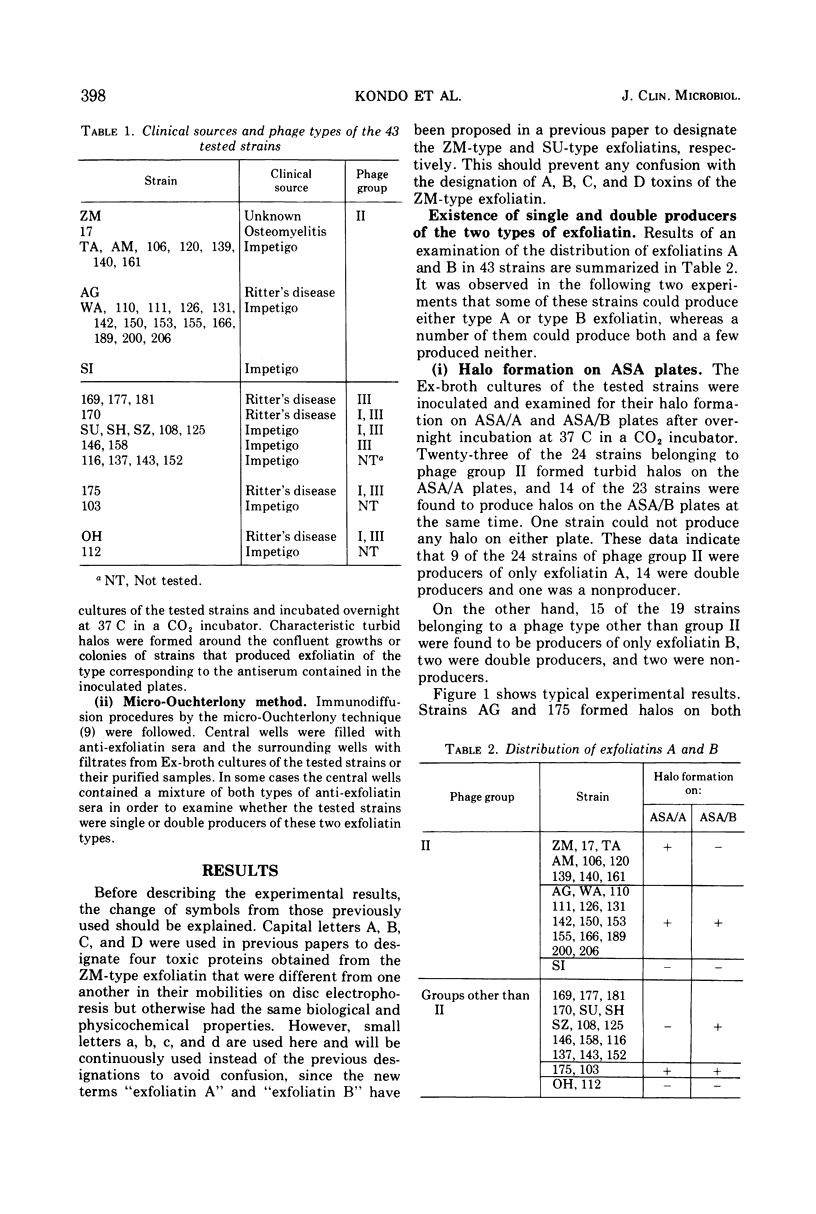
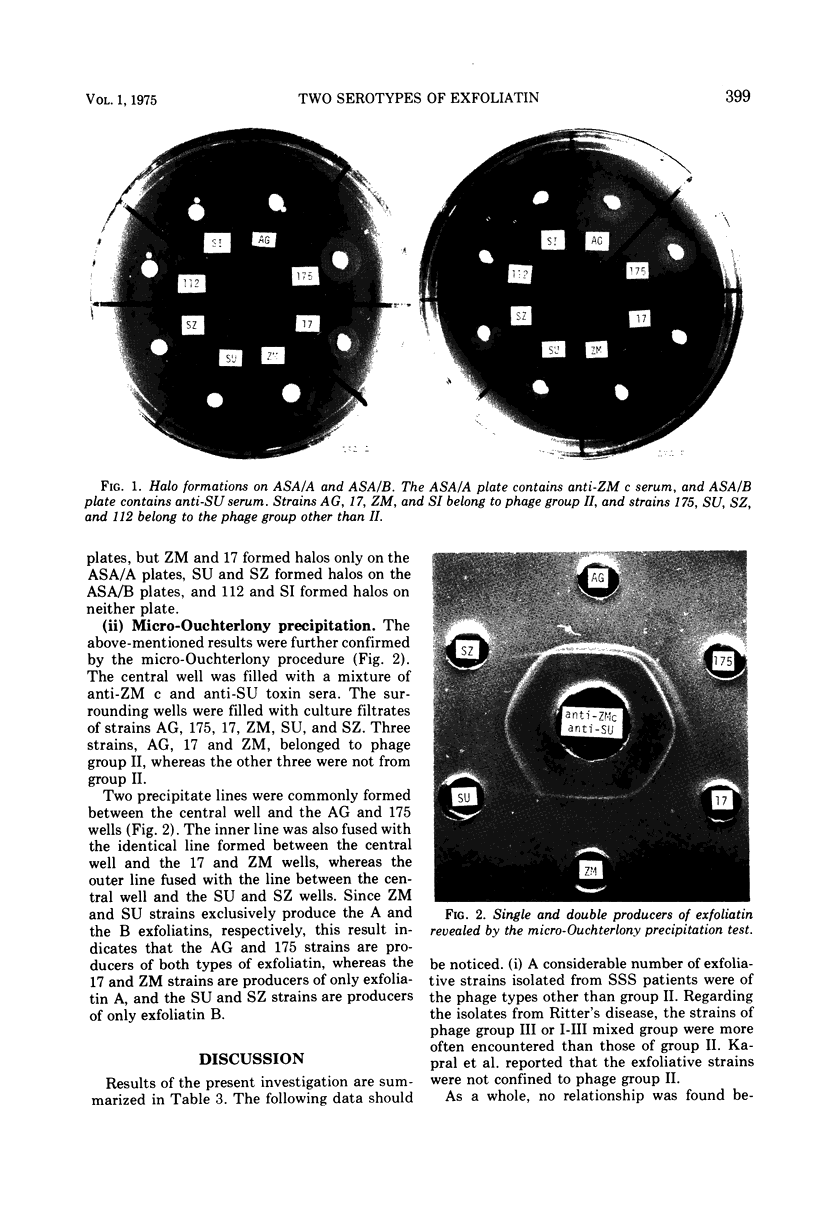
Two serotypes of exfoliatin, A and B, previously reported by Kondo et al. (1974) were examined for their presence in 43 strains of Staphylococcus aureus, most of which were isolated from patients with Ritter's disease and impetigo. The tested strains consisted of 24 strains of phage group II and 19 strains not of phage group II. Twenty-four strains were found to produce an exfoliatin of either type A or type B, but 16 strains produced both types and 3 strains produced neither. No relationship was found between the serotype of an exfoliatin and the phage type of the exfoliative strain, although the single producers of exfoliatin A were all found to belong to phage group II and those of exfoliatin B to the other phage group.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arbuthnott J. P., Kent J., Lyell A., Gemmell C. G. Toxic epidermal necrolysis produced by an extracellular product of Staphylococcus aureus. Br J Dermatol. 1971 Aug;85(2):145–149. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1971.tb07200.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapral F. A., Miller M. M. Product of Staphylococcus aureus responsible for the scalded-skin syndrome. Infect Immun. 1971 Nov;4(5):541–545. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.5.541-545.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo I., Sakurai S., Sarai Y. New type of exfoliatin obtained from staphylococcal strains, belonging to phage groups other than group II, isolated from patients with impetigo and Ritter's disease. Infect Immun. 1974 Oct;10(4):851–861. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.4.851-861.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo I., Sakurai S., Sarai Y. Purification of exfoliatin produced by Staphylococcus aureus of bacteriophage group 2 and its physicochemical properties. Infect Immun. 1973 Aug;8(2):156–164. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.2.156-164.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melish M. E., Glasgow L. A. The staphylococcal scalded-skin syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1970 May 14;282(20):1114–1119. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197005142822002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melish M. E., Glasgow L. A., Turner M. D. The staphylococcal scalded-skin syndrome: isolation and partial characterization of the exfoliative toxin. J Infect Dis. 1972 Feb;125(2):129–140. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.2.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren R., Rogolsky M., Wiley B. B., Glasgow L. A. Effect of ethidium bromide on elimination of exfoliative toxin and bacteriocin production in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jun;118(3):980–985. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.3.980-985.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]