Abstract
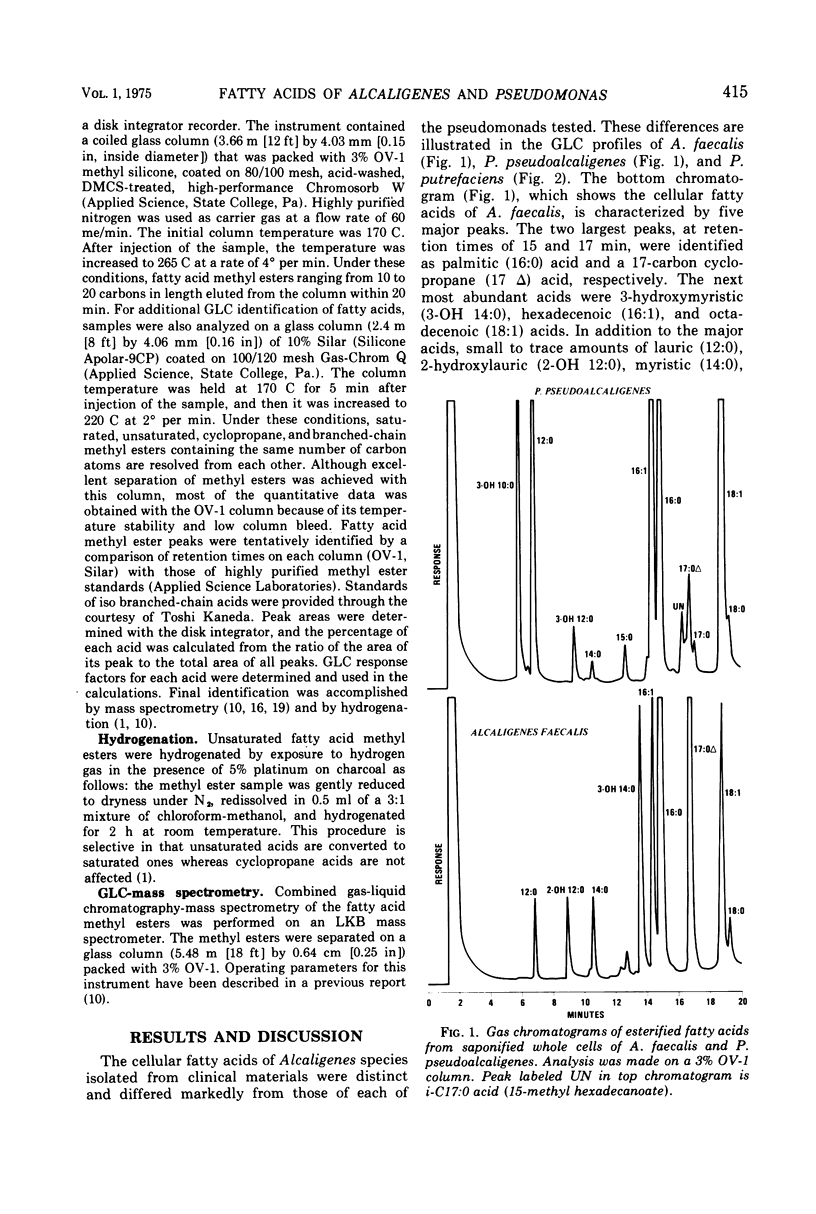
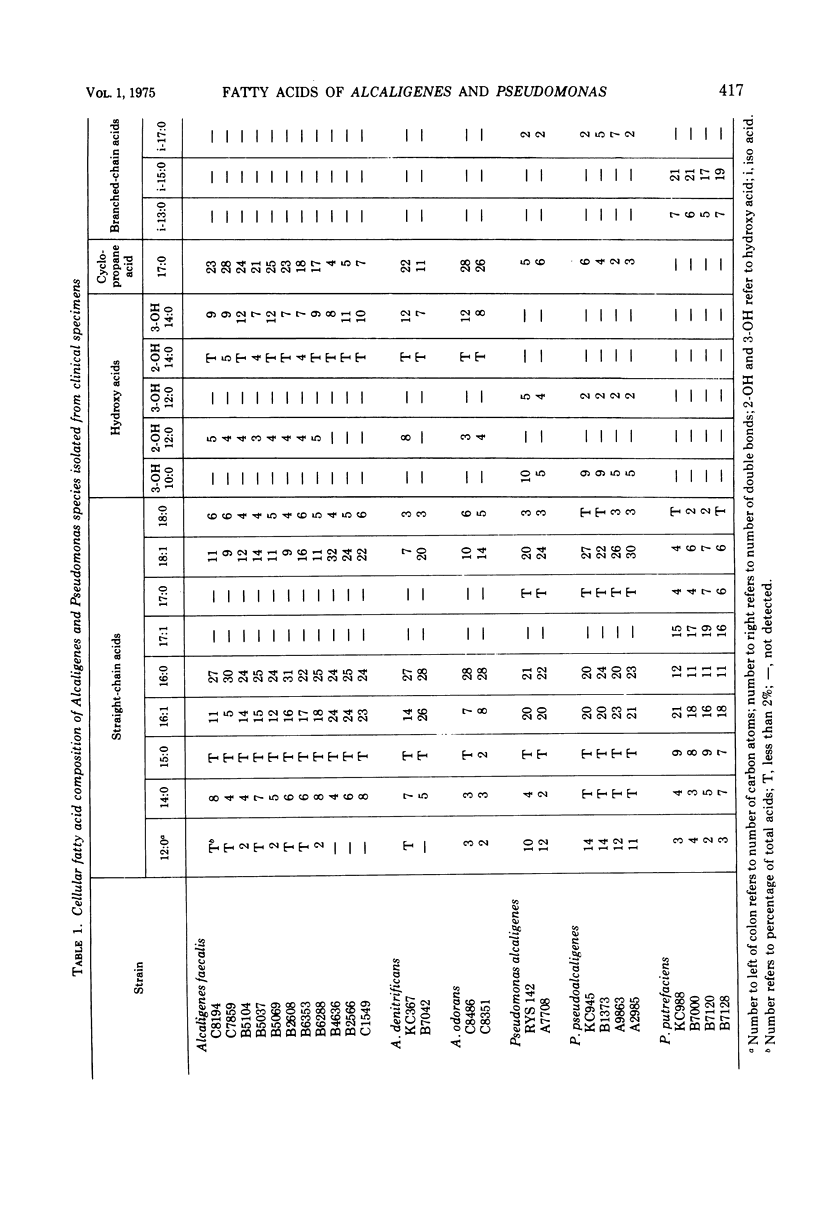
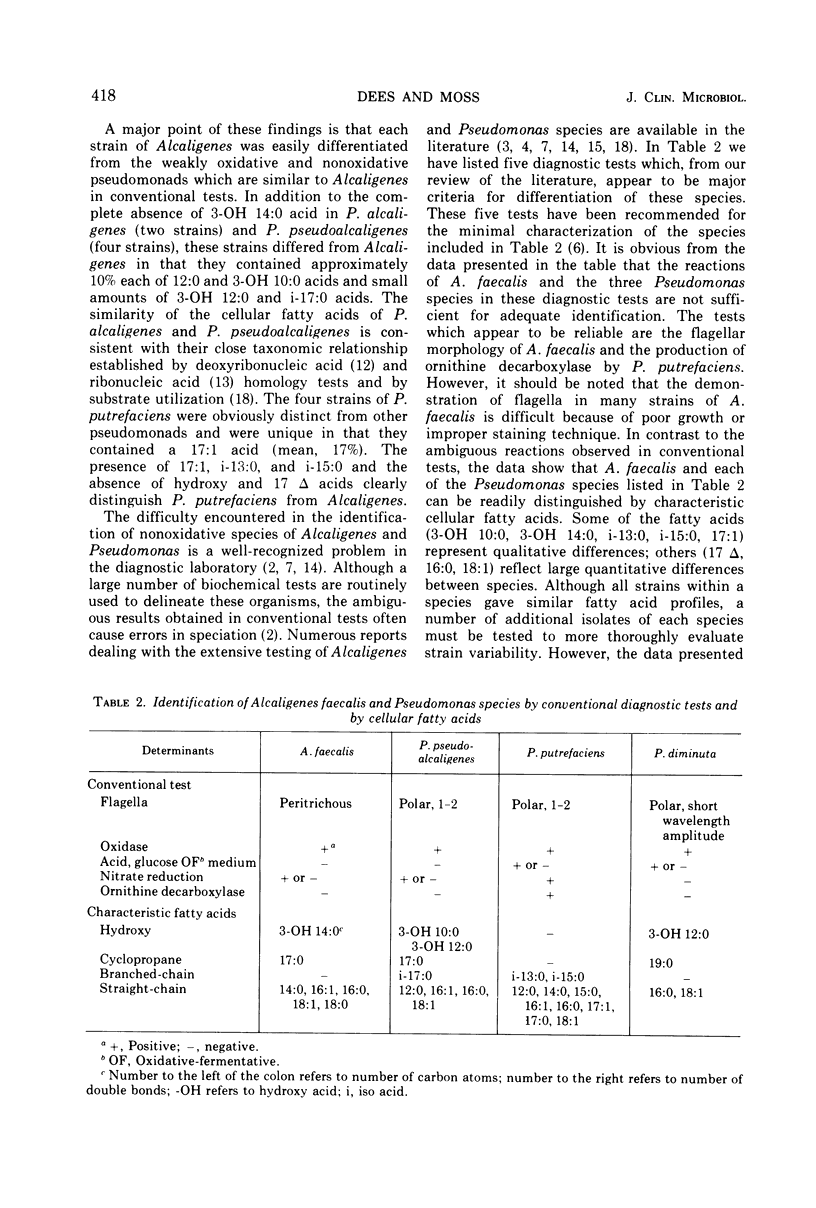
The cellular fatty acid composition of 25 clinical isolates of Alcaligenes and Pseudomonas was determined by gas-liquid chromatography (GLC). The GLC fatty acid profiles of three species of Pseudomonas were markedly different from those of Alcaligenes. The most significant differences were the presence and relative amounts of hydroxy, branched-chain, and cyclopropane fatty acids. One of the major fatty acids in A. faecalis was a 17-carbon cyclopropane (17 delta) acid, whereas a 15-carbon branched-chain acid (13-methyl tetradecanoate) characterized isolates of P. putrefaciens. The determination of these fatty acids by GLC provides a rapid and specific means of distinguishing clinical isolates of Pseudomonas and Alcaligenes.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brian B. L., Gardner E. W. A simple procedure for detecting the presence of cyclopropane fatty acids in bacterial lipids. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Apr;16(4):549–552. doi: 10.1128/am.16.4.549-552.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilardi G. L. Infrequently encountered Pseudomonas species causing infection in humans. Ann Intern Med. 1972 Aug;77(2):211–215. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-77-2-211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilardi G. L. Nonfermentative gram-negative bacteria encountered in clinical specimens. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1973;39(2):229–242. doi: 10.1007/BF02578855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilardi G. L. Practical schema for the identification of nonfermentative gram negative bacteria encountered in medical bacteriology. Am J Med Technol. 1972 Mar;38(3):65–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock I. C., Humphreys G. O., Meadow P. M. Characterisation of the hydroxy acids of Pseudomonas aeruginosa 8602. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Mar 10;202(2):389–391. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(70)90204-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Key B. A., Gray G. W., Wilkinson S. G. The purification and chemical composition of the lipopolysaccharide of Pseudomonas alcaligenes. Biochem J. 1970 Dec;120(3):559–566. doi: 10.1042/bj1200559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüderitz O., Staub A. M., Westphal O. Immunochemistry of O and R antigens of Salmonella and related Enterobacteriaceae. Bacteriol Rev. 1966 Mar;30(1):192–255. doi: 10.1128/br.30.1.192-255.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss C. W., Samuels S. B., Liddle J., McKinney R. M. Occurrence of branched-cahin hydroxy fatty acids in Pseudomonas maltophilia. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jun;114(3):1018–1024. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.3.1018-1024.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss C. W., Samuels S. B., Weaver R. E. Cellular fatty acid composition of selected Pseudomonas species. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Oct;24(4):596–598. doi: 10.1128/am.24.4.596-598.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palleroni N. J., Ballard R. W., Ralston E., Doudoroff M. Deoxyribonucleic acid homologies among some Pseudomonas species. J Bacteriol. 1972 Apr;110(1):1–11. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.1.1-11.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickett M. J., Pedersen M. M. Salient features of nonsaccharolytic and weakly saccharolytic nonfermentative rods. Can J Microbiol. 1970 Jun;16(6):401–409. doi: 10.1139/m70-069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RYHAGE R., STENHAGEN E. Mass spectrometry in lipid research. J Lipid Res. 1960 Oct;1:361–390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley P. S., Tatum H. W., Weaver R. E. Pseudomonas putrefaciens isolates from clinical specimens. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Nov;24(5):798–800. doi: 10.1128/am.24.5.798-800.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuels S. B., Moss C. W., Weaver R. E. The fatty acids of Pseudomonas multivorans (Pseudomonas cepacia) and Pseudomonas kingii. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Feb;74(2):275–279. doi: 10.1099/00221287-74-2-275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y., Palleroni N. J., Doudoroff M. The aerobic pseudomonads: a taxonomic study. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 May;43(2):159–271. doi: 10.1099/00221287-43-2-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyrrell D. The fatty acid composition of some entomophthoraceae : II. The occurrence of branched-chain fatty acids inConidiobolus denaesporus Drechsl. Lipids. 1968 Jul;3(4):368–372. doi: 10.1007/BF02530941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


