Abstract
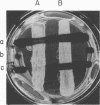
A study of 27 clinical specimens from which Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Candida albicans were isolated simultaneously indicated that 44% of the gonococcal isolates were resistant to inhibition by the C. albicans with which they were found and an additional 33% were totally resistant to inhibition by all C. albicans tested. All 27 C. albicans showed inhibitory activity against standard indicator strains of N. gonorrhoeae.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Geizer E. Antibacterial substances produced by different bacteria inhibiting the growth of Neisseria gonorrhoea (preliminary report). J Hyg Epidemiol Microbiol Immunol. 1968;12(2):241–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hipp S. S., Lawton W. D., Chen N. C., Gaafar H. A. Inhibition of Neisseria gonorrhoeae by a factor produced by Candida albicans. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Jan;27(1):192–196. doi: 10.1128/am.27.1.192-196.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraus S. J., Ellison N. Resistance to gonorrhea possibly mediated by bacterial interference. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Jun;27(6):1014–1016. doi: 10.1128/am.27.6.1014-1016.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maibach H. I., Strauss W. G., Shinefield H. R. Bacterial interference: relating to chronic furunculosis in man. Br J Dermatol. 1969;81(Suppl):69+–69+. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1969.tb12836.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSEBURY T., GALE D., TAYLOR D. F. An approach to the study of interactive phenomena among microorganisms indigenous to man. J Bacteriol. 1954 Feb;67(2):135–152. doi: 10.1128/jb.67.2.135-152.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]