Abstract
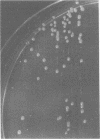
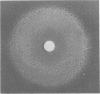
Stable dwarf forms of Staphylococcus aureus have been identified in clinical specimens as the sole or predominant isolate in eight cases. These organisms have been shown to be menadione or thiamine dependent, i.e., cultivation in the presence of one of these agents has permitted growth of colonies which appear typical of S. aureus. In vitro resistance to aminoglycosides was overcome by cultivation in the presence of menadione or thiamine. Menadione- or thiamine-requiring S. aureus can be considered as causative agents in severe human infections. Special care must be taken if they are to be identified in pathological specimens. Their antibiotic sensitivity testing should be done comparatively on supplemented and nonsupplemented media.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acar J. F., Goldstein F., Chabbert Y. A. Synergistic activity of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole on gram-negative bacilli: observations in vitro and in vivo. J Infect Dis. 1973 Nov;128(Suppl):470–p. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.supplement_3.s470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Annear D. I. The effect of temperature on resistance of Staphylococcus aureus to methicillin and some other antibioics. Med J Aust. 1968 Mar 16;1(11):444–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAIRD-PARKER A. C. A classification of micrococci and staphylococci based on physiological and biochemical tests. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Mar;30:409–427. doi: 10.1099/00221287-30-3-409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARBOUR R. G. H. The development of resistance to streptomycin by Staphylococcus pyogenes. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1950 Jul;28(4):415–420. doi: 10.1038/icb.1950.42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BONIFAS V. Détermination de l'association synergique binaire d'antibiotes et de sulfamides. Experientia. 1952 Jun 15;8(6):234–235. doi: 10.1007/BF02170729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borderon E., Horodniceanu T., Buissiere J., Barthez J. P. Mutants déficients à colonies naines de Escherichia coli: étude d'une souche thiamine-déficiente isolée d'une uroculture. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1977 May-Jun;128A(4):413–417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borderon E., Horodniceanu T. Mutants déficients à colonies naines de Staphylococcus: étude de trois souches isolées chez des malades porteurs d'ostéosynthèses. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1976 May-Jun;127(4):503–514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin Y. M., Harmon S. A. Genetic studies of kanamycin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Jpn J Microbiol. 1971 Sep;15(5):417–423. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1971.tb00599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colien F. E. A Study of Microbic Variation in a Yellow Pigment-producing Coccus. J Bacteriol. 1935 Sep;30(3):301–321. doi: 10.1128/jb.30.3.301-321.1935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE REPENTIGNY J., SONEA S., FRAPPIER A. SELECTION OF THYMINELESS MUTANTS BY GROWING STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS PATHOGENIC STRAINS IN THE PRESENCE OF AMINOPTERIN AND THYMINE OR THYMIDINE. Rev Can Biol. 1964 Dec;23:451–454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DYE W. E. An agar diffusion method for studying the bacteriostatic action of combinations of antimicrobial agents. Antibiot Annu. 1955;3:374–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devriese L. A. Hemin-dependent mutants isolated from methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1973;39(1):33–40. doi: 10.1007/BF02578839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ericsson H. M., Sherris J. C. Antibiotic sensitivity testing. Report of an international collaborative study. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1971;217(Suppl):1+–1+. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAUSE G. F., KOCHETKOVA G. V., VLADIMIROVA G. B. Biochemical changes accompanying impaired respiration in staphylococci. Nature. 1961 Jun 10;190:978–980. doi: 10.1038/190978a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOUDIE J. G., GOUDIE R. B. Recurrent infections by a stable dwarf-colony variant of Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Pathol. 1955 Nov;8(4):284–287. doi: 10.1136/jcp.8.4.284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godeau P., Pechère J. C., Sicard D. Evolution de la sensibilité à la gentamycine d'une endocardite aiguë à staphylocoque post-abortum. Ann Med Interne (Paris) 1972 Mar;123(3):225–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALE J. H. Studies on staphylococcus mutation: a naturally occurring "G" gonidial variant and its carbon dioxide requirements. Br J Exp Pathol. 1951 Aug;32(4):307–313. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan M. L., Dye W. Growth requirements of some small-colony-forming variants of Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Oct;4(4):343–348. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.4.343-348.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacey R. W. Dwarf-colony variants of Staphylococcus aureus resistant to aminoglucoside antibiotics and to a fatty acid. J Med Microbiol. 1969 Aug;2(3):187–197. doi: 10.1099/00222615-2-3-187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musher D. M., Baughn R. E., Templeton G. B., Minuth J. N. Emergence of variant forms of Staphylococcus aureus after exposure to gentamicin and infectivity of the variants in experimental animals. J Infect Dis. 1977 Sep;136(3):360–369. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.3.360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATTE J. C., HIRSCH H., CHABBERT Y. Etude des courbes d'effet baçtériostatique des associations d'antibiotiques. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1958 May;94(5):621–635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quie P. G. Microcolonies (G-variants) of Staphylococcus aureus. Yale J Biol Med. 1969 Apr;41(5):394–403. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHERRIS J. C. Two small colony variants of Staph. aureus isolated in pure culture from closed infected lesions and their carbon dioxide requirements. J Clin Pathol. 1952 Nov;5(4):354–355. doi: 10.1136/jcp.5.4.354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasarman A., Surdeanu M., Szabados J., Greceanu V., Horodniceanu T. Menaphthone-requiring mutants of Staphylococcus aureus. Rev Can Biol. 1968 Dec;27(4):333–339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slifkin M., Merkow L. P., Kreuzberger S. A., Engwall C., Pardo M. Characterization of CO 2 dependent microcolony variants of Staphylococcus aureus. Am J Clin Pathol. 1971 Nov;56(5):584–592. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/56.5.584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sompolinsky D., Cohen M., Ziv G. Epidemiological and biochemical studies on thiamine-less dwarf-colony variants of Staphylococcus aureus as etiological agents of bovine mastitis. Infect Immun. 1974 Feb;9(2):217–228. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.2.217-228.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sompolinsky D., Ernst-Geller Z., Segal S. Metabolic disorders in thiamineless dwarf strains of Staphylococcus aureus. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Aug;48(2):205–213. doi: 10.1099/00221287-48-2-205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sompolinsky D., Gluskin I., Ziv G. Pantothenate-requiring dwarf colony variants of Staphylococcus aureus as the etiological agent in bovine mastitis. J Hyg (Lond) 1969 Sep;67(3):511–516. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400041930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suganuma A. Fine structure of Staphylococcus aureus. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Jul 23;128(1):26–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb11627.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swingle E. L. Studies on Small Colony Variants of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1935 May;29(5):467–489. doi: 10.1128/jb.29.5.467-489.1935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Săsărman A., Surdeanu M., Portelance V., Dobardzic R., Sonea S. Classification of vitamin K-deficient mutants of Staphylococcus aureus. J Gen Microbiol. 1971 Feb;65(2):125–130. doi: 10.1099/00221287-65-2-125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS M. E. Studies on a CO2-dependent staphylococcus. J Clin Pathol. 1955 Nov;8(4):288–291. doi: 10.1136/jcp.8.4.288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WISE R. I., SPINK W. W. The influence of antibiotics on the origin of small colonies (G variants) of Micrococcus pyogenes var. aureus. J Clin Invest. 1954 Dec;33(12):1611–1622. doi: 10.1172/JCI103041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WISE R. I. Small colonies (G variants) of staphylococci: isolation from cultures and infections. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1956 Aug 31;65(3):169–174. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1956.tb36636.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson S. G., Sanders C. C. Selection and characterization of strains of Staphylococcus aureus displaying unusual resistance to aminoglycosides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Sep;10(3):519–525. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.3.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YEGIAN D., GALLO G., TOLL M. W. Kanamycin resistant staphylococcus mutant requiring heme for growth. J Bacteriol. 1959 Jul;78(1):10–12. doi: 10.1128/jb.78.1.10-12.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youmans G. P., Delves E. The Effect of Inorganic Salts on the Production of Small Colony Variants by Staphylococcus Aureus. J Bacteriol. 1942 Jul;44(1):127–136. doi: 10.1128/jb.44.1.127-136.1942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]