Abstract
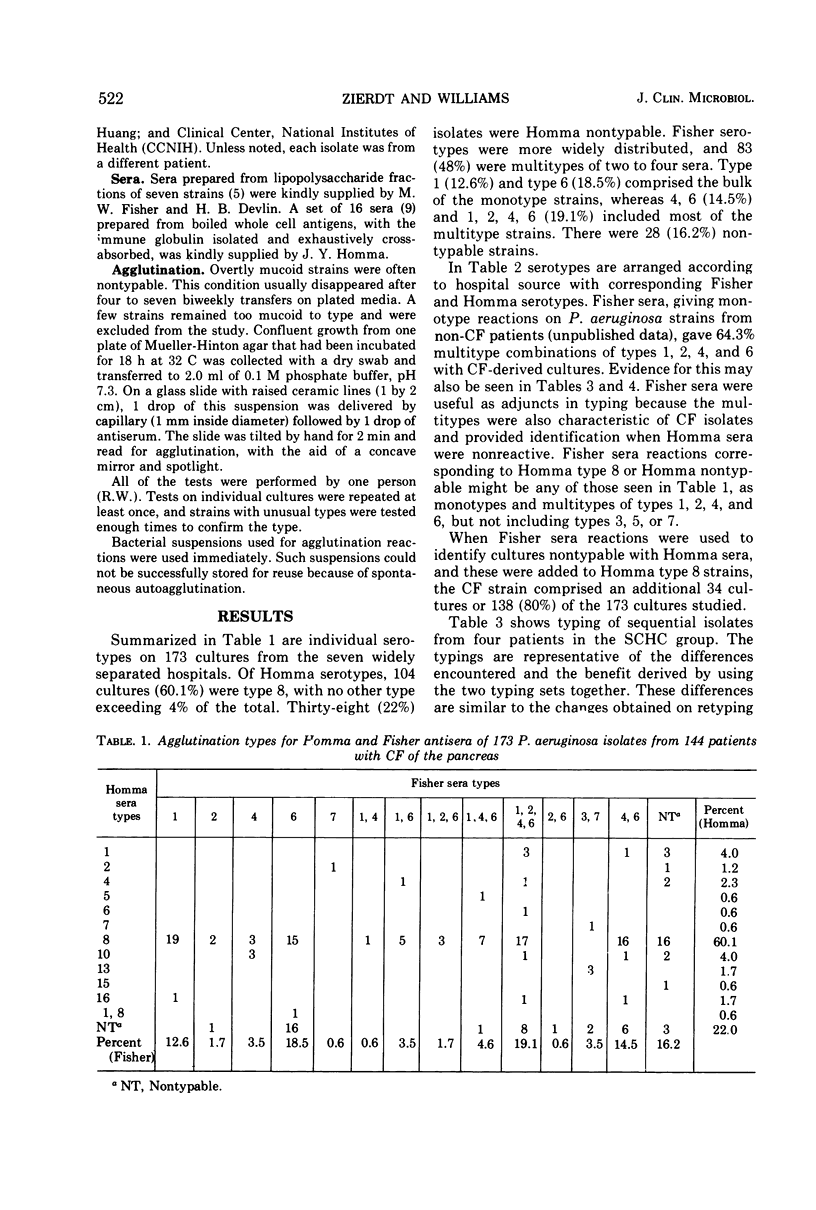
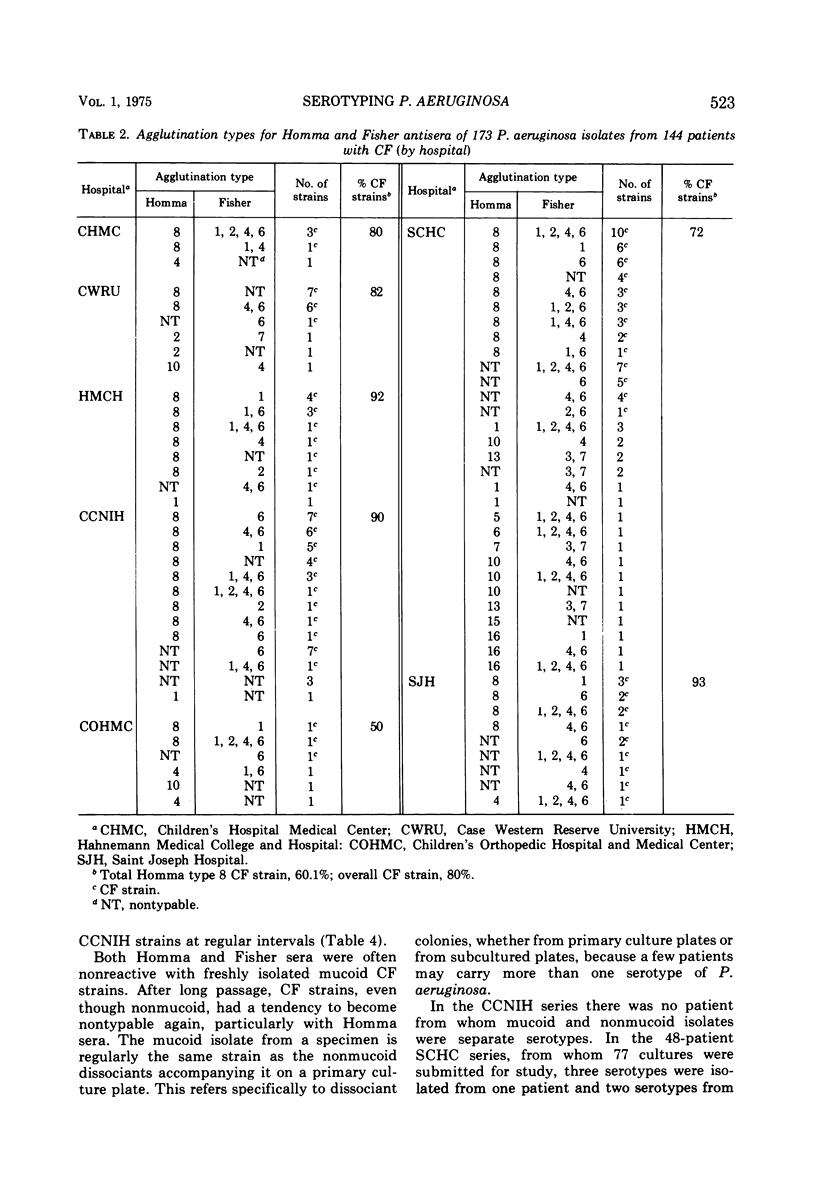
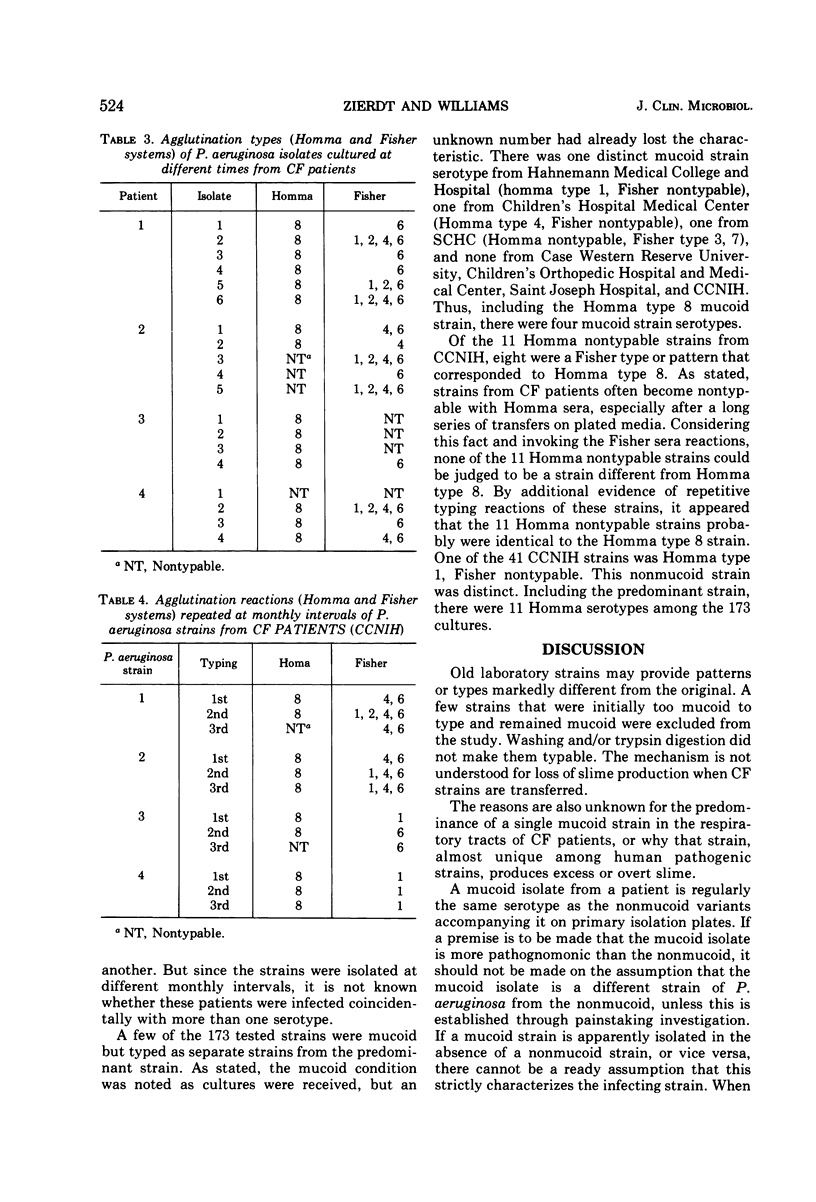
Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates (173) from 144 patients with cystic fibrosis (CF) of the pancreas in seven hospitals were serotyped with the agglutination systems of Homma (1974) and Fisher et al. (1969). The two systems were complementary. Strains from CF patients were much less likely to furnish a stable type on repetitive typing tests than strains from other patients. This was related to the frequent occurrence of mucoid P. aeruginosa strains. The 173 strains were divided among 11 Homma serotypes. A single Homma type (type 8) capable of mucoid growth comprised 104 (60%) CF strains. Eight serotypes were detected in 77 strains from 48 CF patients in one hospital; three strains were detected in one hospital CF unit; and two strains were detected in each of five hospital CF units. The CF serotype comprised from 50 to 93% of CF strians inthe seven hospitals. These P. aeruginosa strains dissociated in vivo as judged by mucoid and nonmucoid colonies on primary culture plates and continued to dissociate during subcultures. Both colony type were the same serotype. The tendency to regard colonial phenotypes (mucoid, nonmucoid, rough) as separate strians was erroneous. Repetitive typing with the two systems gave better results than a single system. The mucoid P. aeruginosa strain is probably spread from patient to patient, rather than acquiring its mucoid characteristic de novo in the CF patient. It is not known why the mucoid CF strain has a peculiar predilection for CF patients, nor why it generally loses the quality in culture but retains it indefinitely in the patient.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CETIN E. T., TOERECI K., ANG O. ENCAPSULATED PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA (PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA MUCOSUS) STRAINS. J Bacteriol. 1965 May;89:1432–1433. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.5.1432-1433.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chadwick P. the significance of pattern variations in pyocine typing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Can J Microbiol. 1972 Jul;18(7):1153–1158. doi: 10.1139/m72-177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doggett R. G. Incidence of mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa from clinical sources. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Nov;18(5):936–937. doi: 10.1128/am.18.5.936-937.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elston H. R., Hoffman K. C. Increasing incidence of encapsulated Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains. Am J Clin Pathol. 1967 Nov;48(5):519–523. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/48.5_ts.519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher M. W., Devlin H. B., Gnabasik F. J. New immunotype schema for Pseudomonas aeruginosa based on protective antigens. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):835–836. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.835-836.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto S., Enomoto S., Takahashi Y., Motomatsu R. Slime production by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. I. Conditions for slime production by the cellophane plate method. Jpn J Microbiol. 1971 Jul;15(4):317–324. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1971.tb00587.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma J. Y. Serological typing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and several points to be considered. Jpn J Exp Med. 1974 Feb;44(1):1–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma J. Y., Shionoya H., Yamada H., Enomoto M., Miyao K. Changes in serotype of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Jpn J Exp Med. 1972 Apr;42(2):171–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma J. Y., Shionoya H., Yamada H., Kawabe Y. Production of antibody against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and its serological typing. Jpn J Exp Med. 1971 Feb;41(1):89–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones L. F., Zakanycz J. P., Thomas E. T., Farmer J. J., 3rd Pyocin typing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a simplified method. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Feb;27(2):400–406. doi: 10.1128/am.27.2.400-406.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaharajo K. Changes in serotype of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Jpn J Exp Med. 1973 Jun;43(3):225–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shionoya H., Homma J. Y. Dissociation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Jpn J Exp Med. 1968 Apr;38(2):81–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zierdt C. H., Schmidt P. J. Dissociation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1964 May;87(5):1003–1010. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.5.1003-1010.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


