Abstract
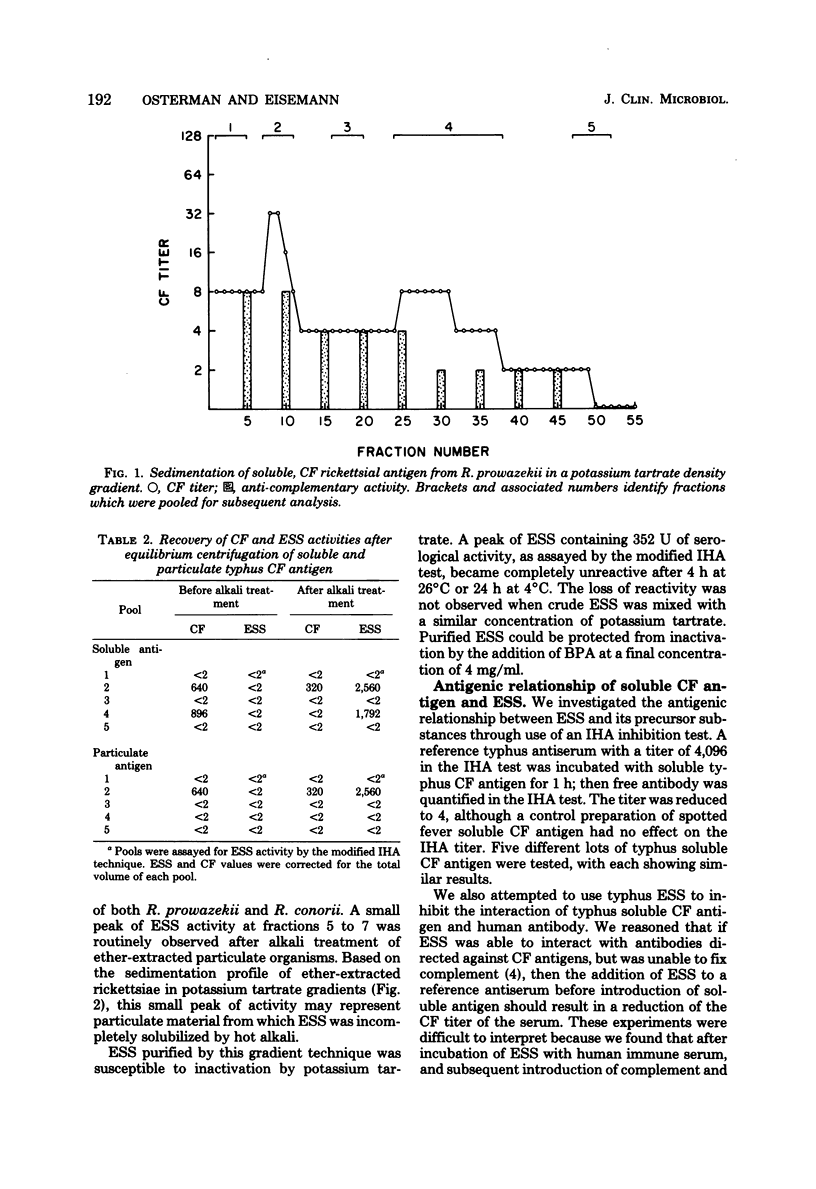
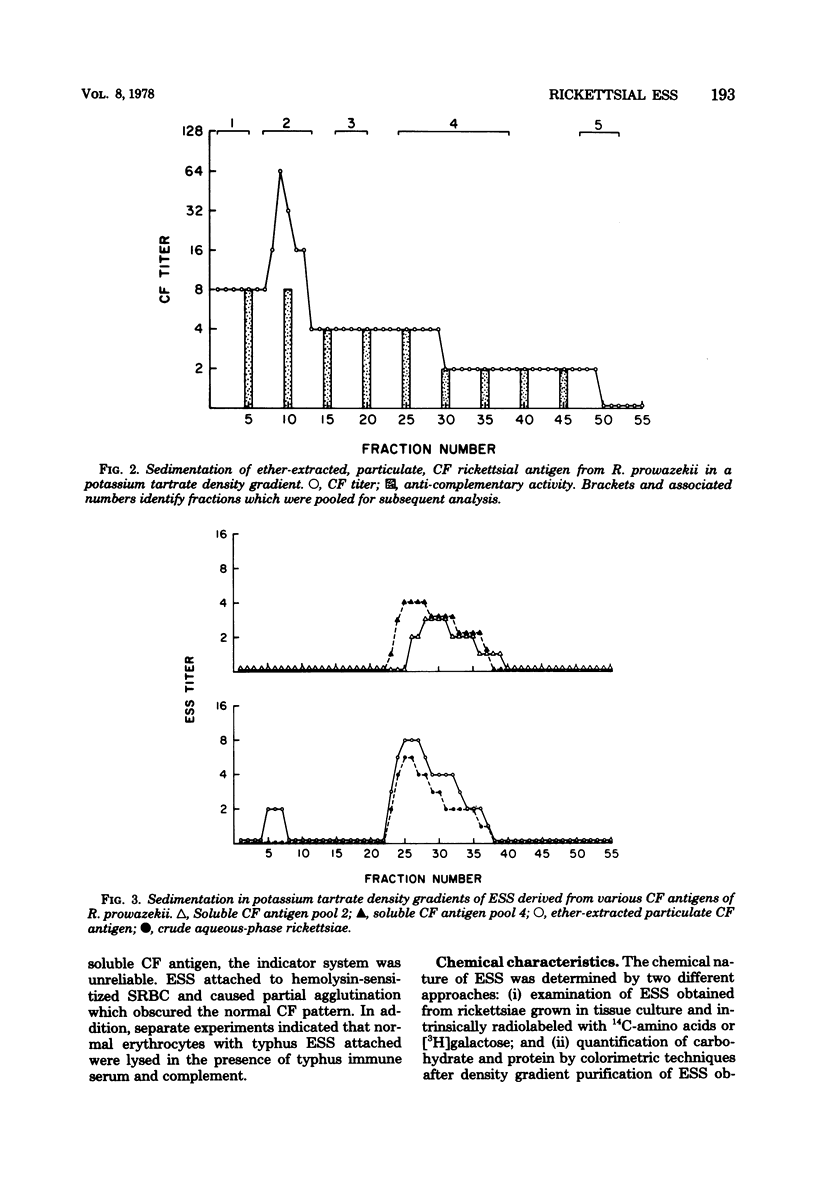
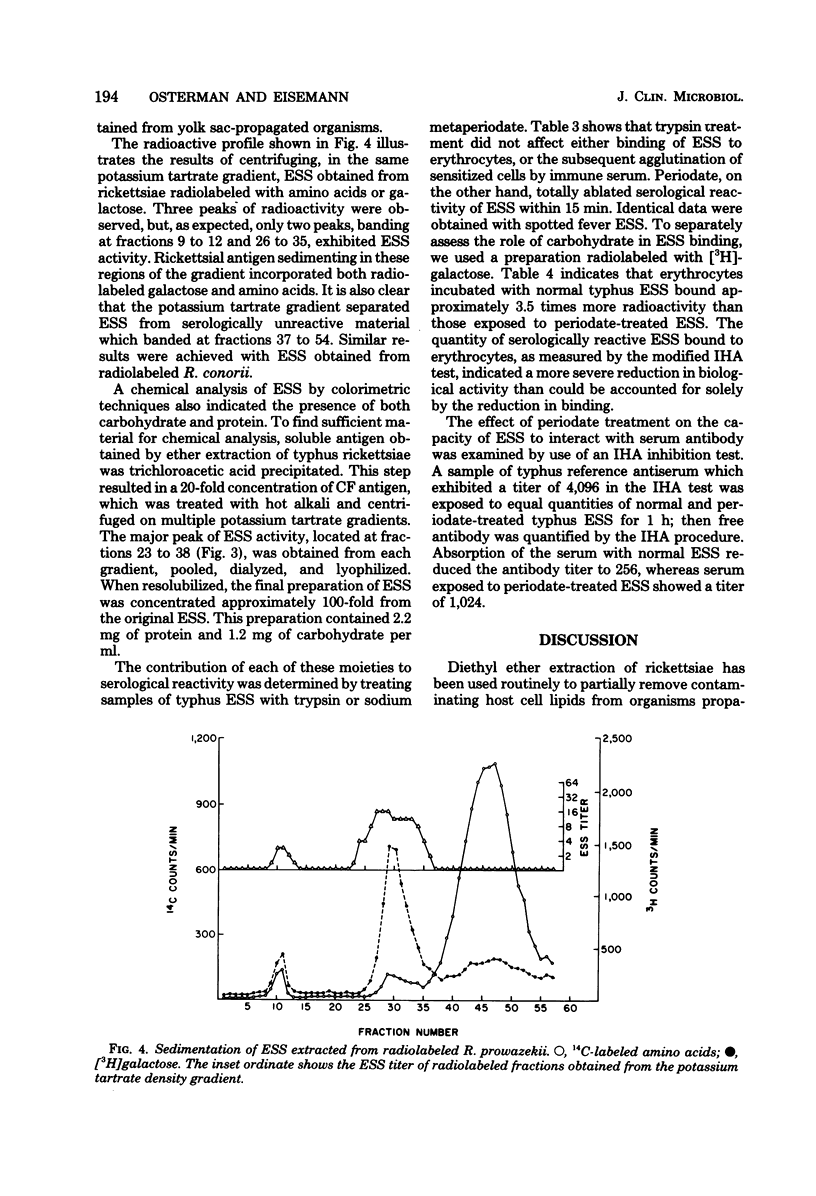
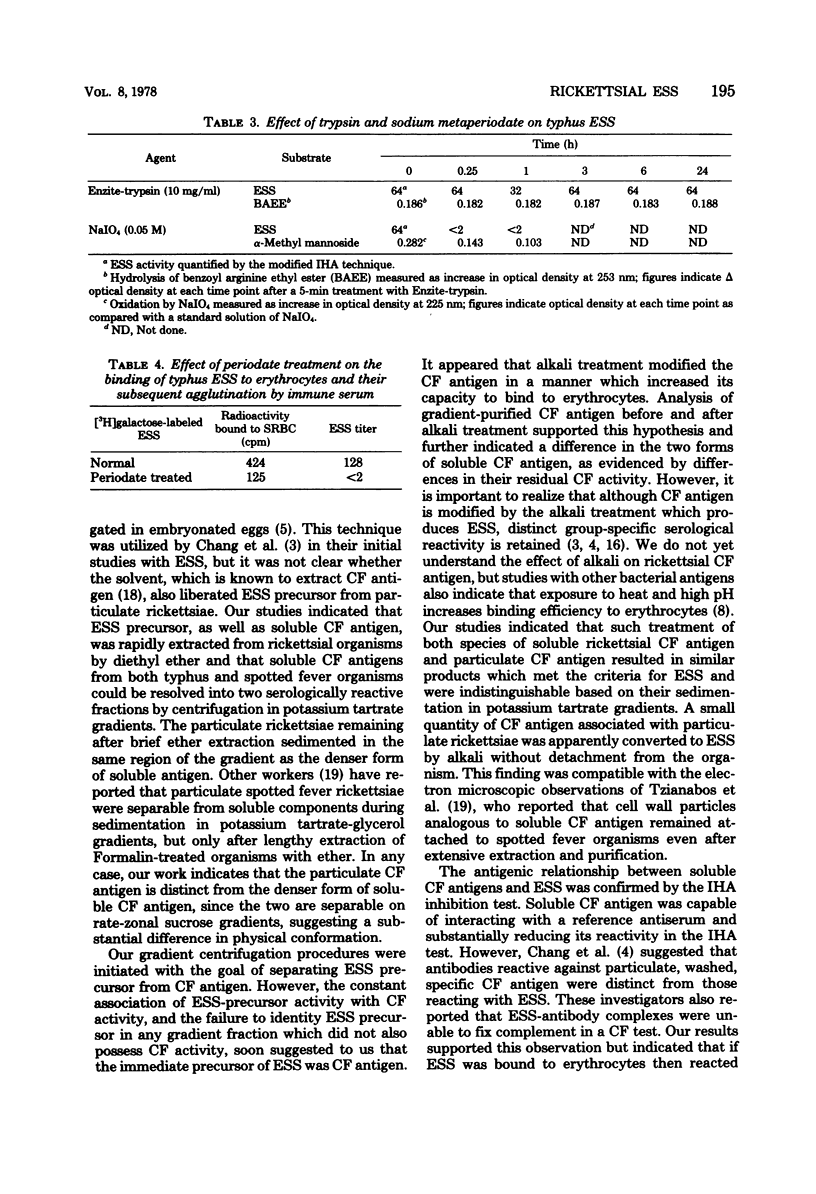
The erythrocyte-sensitizing substances (ESS) of Rickettsia prowazekii and R. conorii were characterized by biological and chemical criteria. ESS could be derived from either soluble or particulate complement-fixing antigens obtained by ether extraction of rickettsiae. The soluble complement-fixing antigen exhibited two peaks of serological activity in potassium tartrate density gradients. The particulate complement-fixing antigen coincided with the more dense peak but was distinguishable by its sedimentation in rate-zonal sucrose gradients. ESS was obtained from each of the complement-fixing-reactive gradient peaks by extraction with hot alkali and was quantified by a modified indirect hemagglutination test. These ESS preparations sedimented similarly in potassium tartrate gradients and were shown to contain protein and carbohydrate, both by colorimetric tests and by incorporation of radioactive precursors. The serological activity of ESS was unaffected by trypsin, but both antigenicity and erythrocyte-binding capacity were reduced after exposure to sodium metaperiodate. Highly purified ESS was rapidly inactivated by potassium tartrate and required stabilization with bovine plasma albumin.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anacker R. L., Gerloff R. K., Thomas L. A., Mann R. E., Bickel W. D. Immunological properties of Rickettsia rickettsii purified by zonal centrifugation. Infect Immun. 1975 Jun;11(6):1203–1209. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.6.1203-1209.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANG R. S., MURRAY E. S., SNYDER J. C. Erythrocyte-sensitizing substances from Rickettsiae of the Rocky Mountain spotted fever group. J Immunol. 1954 Jul;73(1):8–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANG S. M. A serologically-active erythrocyte-sensitizing substance from typhus rickettsiae. I. Isolation and titration. J Immunol. 1953 Mar;70(3):212–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANG S. M., SNYDER J. C., MURRAY E. S. A serologically active erythrocyte sensitizing substance from typhus rickettsiae. II. Serological properties. J Immunol. 1953 Mar;70(3):215–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisemann C. S., Osterman J. V. Proteins of typhus and spotted fever group rickettsiae. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):155–162. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.155-162.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENT J. F., FIFE E. H., Jr Precise standardization of reagents for complement fixation. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1963 Jan;12:103–116. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1963.12.103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philip R. N., Casper E. A., MacCormack J. N., Sexton D., Thomas L. A., Anacker R. L., Burgdorfer W., Vick S. A comparison of serologic methods for diagnosis of Rocky Mountain spotted fever. Am J Epidemiol. 1977 Jan;105(1):56–67. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAECHTER M., TOUSIMIS A. J., COHN Z. A., ROSEN H., CAMPBELL J., HAHN F. E. Morphological, chemical, and serological studies of the cell walls of Rickettsia mooseri. J Bacteriol. 1957 Dec;74(6):822–829. doi: 10.1128/jb.74.6.822-829.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWERT G. W., TAKENAKA Y. A spectrophotometric determination of trypsin and chymotrypsin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1955 Apr;16(4):570–575. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(55)90280-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEVER J. L. Application of a microtechnique to viral serological investigations. J Immunol. 1962 Mar;88:320–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirai A., Dietel J. W., Osterman J. V. Indirect hemagglutination test for human antibody to typhus and spotted fever group rickettsiae. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Nov;2(5):430–437. doi: 10.1128/jcm.2.5.430-437.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzianabos T., Palmer E. L., Obijeski J. F., Martin M. L. Origin and structure of the group-specific, complement-fixing antigen of Rickettsia rickettsii. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Sep;28(3):481–488. doi: 10.1128/am.28.3.481-488.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. H., Jr, Wisseman C. L., Jr Studies of Rickettsia mooseri cell walls. II. Immunologic properties. J Immunol. 1967 Jun;98(6):1224–1230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


