Abstract
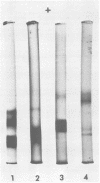
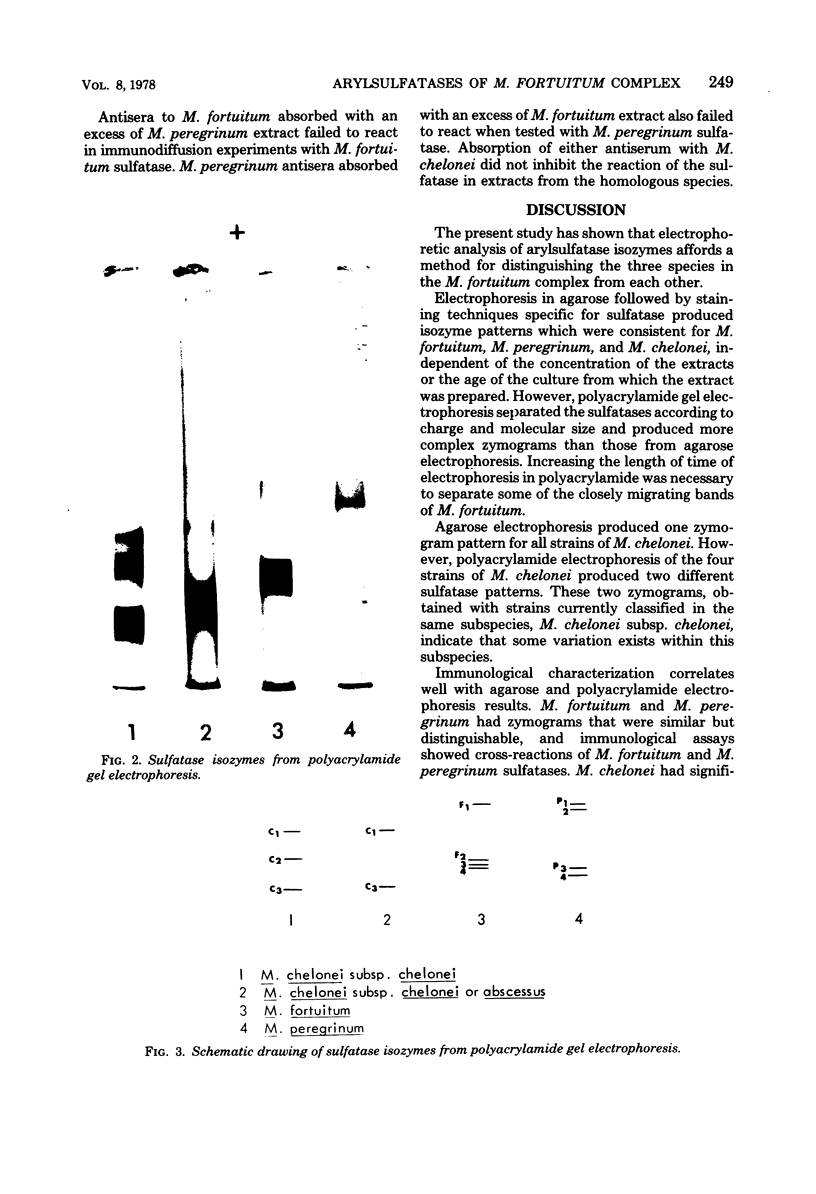
The arylsulfatase isozymes of Mycobacterium fortuitum, M. peregrinum, M. chelonei subsp. chelonei, and M. chelonei subsp. abscessus were examined to determine the isozymal and immunological relationship among the members of the M. fortuitum complex. Cell extracts were subjected to electrophoresis on agarose and polyacrylamide gel, and arylsulfatase activity was localized using beta-naphthyl sulfate as substrate. Unique zymograms were produced for M. fortuitum, M. peregrinum, and M. chelonei which were characteristic for each species. The immunological relationship among the sulfatases was assayed by using immunodiffusion and immunoelectrophoresis followed by sulfatase staining for the enzyme. One of the isozymes of M. fortuitum and M. peregrinum cross-reacted, showing immunological identity. Antisera to sulfatases of M. fortuitum and M. peregrinum did not react with sulfatases of M. chelonei. The characterization of sulfatase isozymes in extracts of organisms in the M. fortuitum complex suggests the division of the M. fortuitum complex into two species, M. fortuitum and M. chelonei, with subspecies designations.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels T. M., Affronti L. F. Immunoelectrophoretic analysis of antigenic constituents of Seibert fractions of mycobacterial culture filtrates. Identification with the proposed United States-Japan reference nomenclature. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1973 Nov;108(5):1244–1248. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1973.108.5.1244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins P. A., Marks J., Schaefer W. B. Lipid chromatography and seroagglutination in the classification of rapidly growing mycobacteria. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1971 Feb;103(2):179–187. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1971.103.2.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubica G. P., Baess I., Gordon R. E., Jenkins P. A., Kwapinski J. B., McDurmont C., Pattyn S. R., Saito H., Silcox V., Stanford J. L. A co-operative numerical analysis of rapidly growing mycobacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Nov;73(1):55–70. doi: 10.1099/00221287-73-1-55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubica G. P. Differential identification of mycobacteria. VII. Key features for identification of clinically significant mycobacteria. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1973 Jan;107(1):9–21. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1973.107.1.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama Y., Takeya K. Esterase zymogram method for classifying mycobacteria. Nature. 1967 Feb 4;213(5075):504–504. doi: 10.1038/213504a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OUCHTERLONY O. Diffusion-in-gel methods for immunological analysis. II. Prog Allergy. 1962;6:30–154. doi: 10.1159/000313795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REGGIARDO Z. ANTIGENIC RELATIONSHIPS AMONG MYCOBACTERIA BY AGGLUTINATION AND AGGLUTININ-ABSORPTION REACTIONS. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1964 Nov;90:800–803. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1964.90.5.800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer W. B. Serologic identification and classification of the atypical mycobacteria by their agglutination. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1965 Dec;92(6):85–93. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1965.92.6P2.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanford J. L., Gunthorpe W. J. Serological and bacteriological investigation of Mycobacterium ranae (fortuitum). J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):375–383. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.375-383.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanford J. L., Pattyn S. R., Portaels F., Gunthorpe W. J. Studies on Mycobacterium chelonei. J Med Microbiol. 1972 May;5(2):177–182. doi: 10.1099/00222615-5-2-177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukamura M. Differentiation between Mycobacterium abscessus and Mycobacterium borstelense. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1970 Mar;101(3):426–428. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1970.101.3.426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright G. L., Jr, Roberts D. B. Two-dimensional immunoelectrophoresis of mycobacterial antigens. Comparison with a reference system. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1974 Feb;109(2):306–310. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1974.109.2.306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]