Abstract
Computerized, frequency-pulsed, modulated electron capture gas-liquid chromatography was used to study the acid metabolites produced in vitro in fetal calf serum and in vivo in an animal chamber model. Several strains of Diplostreptococcus agalactiae, Propionibacterium acnes, Staphylococcus aureus, and Streptococcus serogroups A, B, and G were studied. All of these organisms have been reported to be associated with arthritic transudates in humans. Metabolites were detected by this method from derivatized extracts of both spent fetal calf serum and chamber fluids. Since there was little host response to the organisms cultured in the chambers, it is highly probable that the products detected represent metabolites produced in an in vivo type of environment. The metabolic patterns were reproducible and exhibited many similarities in vitro and in vivo. Production of the acids detected was reproducible, and these acids were useful identification markers. The data support published reports (J. B. Brooks, C. C. Alley, and J. A. Liddle, Anal. Chem. 46: 1930-1934, 1974; J. B. Brooks, G. Choudhary, R. B. Craven, D. Edman, C. C. Alley, and J. A. Liddle, J. Clin. Microbiol. 5:625-628, 1977; J. B. Brooks, R. B. Craven, A. R. Melton, and C. C. Alley, in H. H. Johnson and W. B. Newson, ed., Second International Symposium on Rapid Methods and Automation on Microbiology, 1976; J. B. Brooks, R. B. Craven, D. Schlossberg, C. C. Alley, and F. M. Pitts, J. Clin. Microbiol. 8:203-208, 1978; J. B. Brooks, D. S. Kellogg, C. C. Alley, H. B. Short, and H. H. Handsfield, J. Infect. Dis. 129:660-668, 1974) that bacterial metabolites might be detectable in diseased body fluids. The growth characteristics of the organisms in the animal model and fetal calf serum are discussed, and a moderately priced computer for performing data manipulations is evaluated.
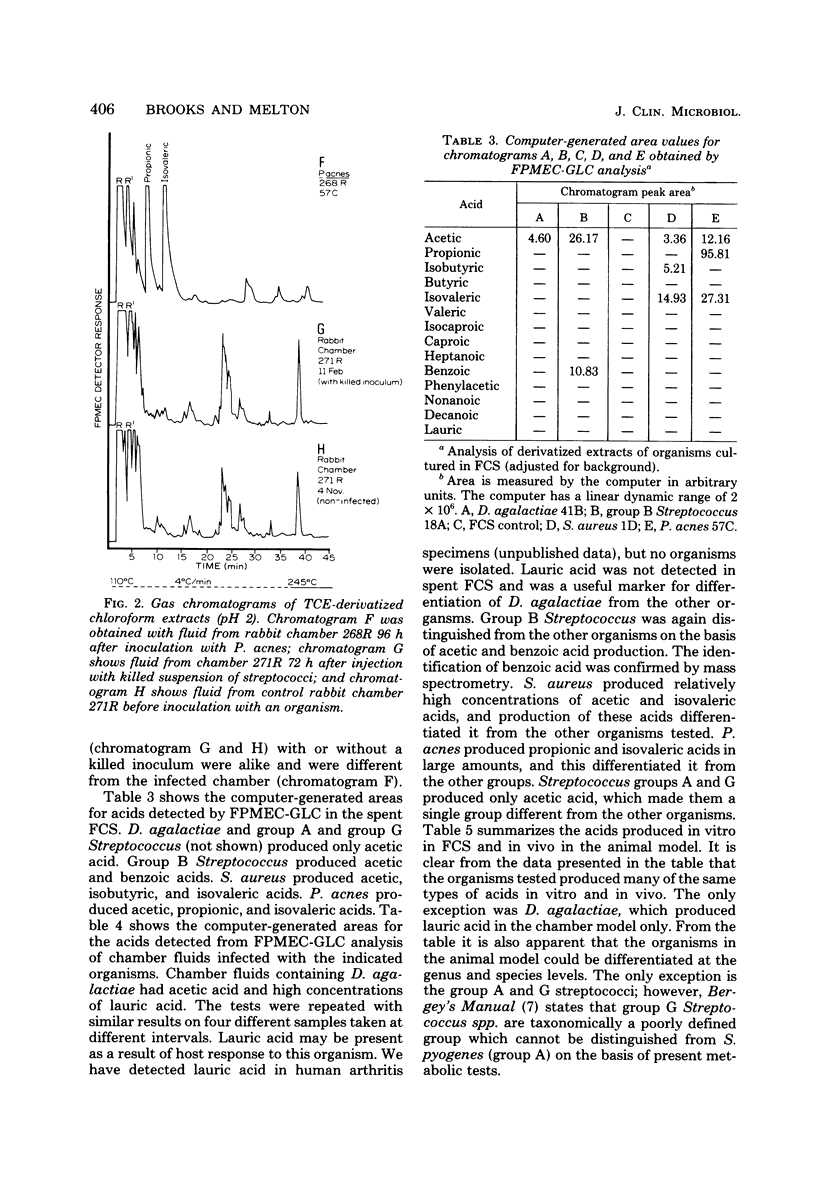
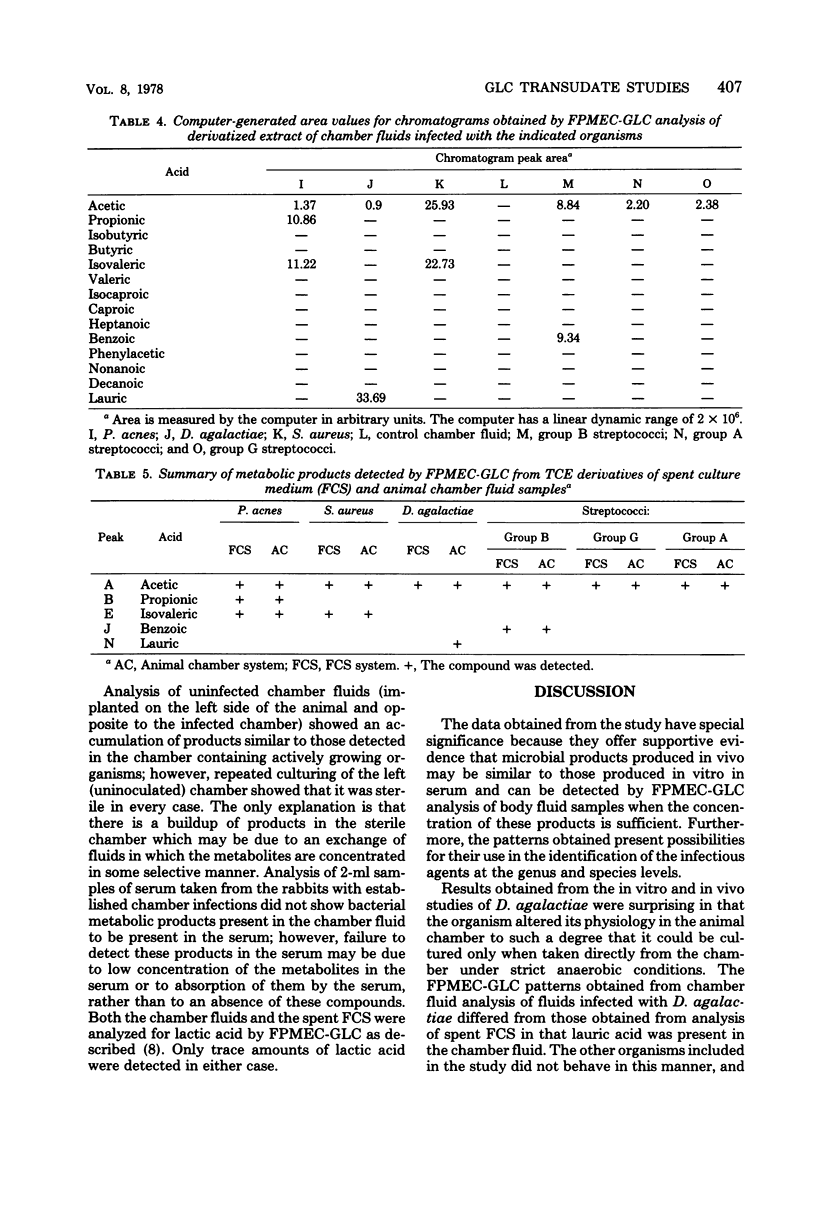
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alley C. C., Brooks J. B., Choudhary G. Electron capture gas-liquid chromatography of short chain acids as their 2,2,2-trichloroethyl esters. Anal Chem. 1976 Feb;48(2):387–390. doi: 10.1021/ac60366a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arko R. J. Implantation and use of a subcutaneous culture chamber in laboratory animals. Lab Anim Sci. 1973 Feb;23(1):105–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arko R. J. Neisseria gonorrhoeae: experimental infection of laboratory animals. Science. 1972 Sep 29;177(4055):1200–1201. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4055.1200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartholomew L. E., Nelson F. R. Corynebacterium acnes in rheumatoid arthritis. I. Isolation and antibody studies. Ann Rheum Dis. 1972 Jan;31(1):22–27. doi: 10.1136/ard.31.1.22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartholomew L. E., Nelson F. R. Corynebacterium acnes in rheumatoid arthritis. II. Identification of antigen in synovial fluid leucocytes. Ann Rheum Dis. 1972 Jan;31(1):28–33. doi: 10.1136/ard.31.1.28. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks J. B., Choudhary G., Craven R. B., Alley C. C., Liddle J. A., Edman D. C., Converse J. D. Electron capture gas chromatography detection and mass spectrum identification of 3-(2'-ketohexyl)indoline in spinal fluids of patients with tuberculous meningitis. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Jun;5(6):625–628. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.6.625-628.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks J. B., Craven R. B., Schlossberg D., Alley C. C., Pitts F. M. Possible use of frequency-pulse-modulated electron capture gas-liquid chromatography to identify septic and aseptic causes of pleural effusions. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Aug;8(2):203–208. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.2.203-208.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks J. B. Detection of bacterial metabolites in spent culture media and body fluids by electron capture gas-liquid chromatography. Adv Chromatogr. 1977;15:1–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks J. B., Kellogg D. S., Alley C. C., Short H. B., Handsfield H. H., Huff B. Gas chromatography as a potential means of diagnosing arthritis. I. Differentiation between staphylococcal, streptococcal, gonococcal, and traumatic arthritis. J Infect Dis. 1974 Jun;129(6):660–668. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.6.660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craven R. B., Brooks J. B., Edman D. C., Converse J. D., Greenlee J., Schlossberg D., Furlow T., Gwaltney J. M., Jr, Miner W. F. Rapid diagnosis of lymphocytic meningitis by frequency-pulsed electron capture gas-liquid chromatography: differentiation of tuberculous, cryptococcal, and viral meningitis. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Jul;6(1):27–32. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.1.27-32.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H. Amino acid metabolism in mammalian cell cultures. Science. 1959 Aug 21;130(3373):432–437. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3373.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Facklam R. R., Padula J. F., Thacker L. G., Wortham E. C., Sconyers B. J. Presumptive identification of group A, B, and D streptococci. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Jan;27(1):107–113. doi: 10.1128/am.27.1.107-113.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse C. D., Brooks J. B., Kellogg D. S., Jr Electron capture gas chromatographic detection of acethylmethylcarbinol produced by neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Jan;3(1):34–41. doi: 10.1128/jcm.3.1.34-41.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANTZ L. A., RANDALL E. Use of autoclaved extracts of hemolytic streptococci for serological grouping. Stanford Med Bull. 1955 May;13(2):290–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svartz N. The primary cause of rheumatoid arthritis is an infection--the infectious agent exists in milk. Acta Med Scand. 1972 Sep;192(3):231–239. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1972.tb04807.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


