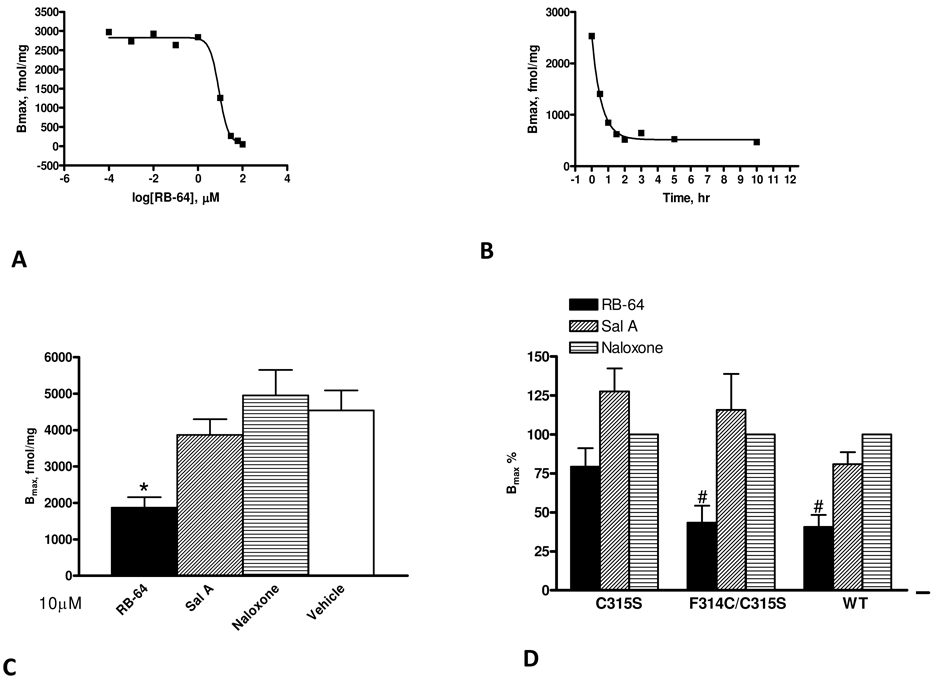
Figure 3. RB-64 induces wash-resistant inhibition of KOR binding at C315.
(A) Dose-response curve for RB-64 for wash-resistant inhibition of binding at 4 °C (2 h) yielding an EC50 of 1.2 µM. (B) Time-course study at 4 °C with a maximally-effective dose of RB-64 (10 µM) yielding t1/2 = 0.4 h. (C) Cells expressing KOR were exposed for 10 µM/3 h to RB-64, salvinorin A, naloxone and vehicle (DMSO only). After incubation, the cell membranes were extensively washed (at least three times); the residual binding was determined by [3H]diprenorphine saturation binding. Data presented are Bmax values for 2–4 independent experiments. (D) Bmax values of various mutants after being labeled with RB-64, salvinorin A and naloxone. Bmax values were expressed as a percentage of vehicle control. Each bar represents the mean ± SEM for two to four independent experiments. An asterisk (*) indicates that RB-64 labeling was significantly different (p < 0.01) from the reference (vehicle) by ANOVA. A hash mark (#) indicates that RB-64 labeling was significantly different (p < 0.05) than that of naloxone by ANOVA.