Figure 1. Main elements in the neural pathway from the axons innervating the whisker follicles on a rat’s face (lower left) to the primary somatic sensory cortex (upper right).
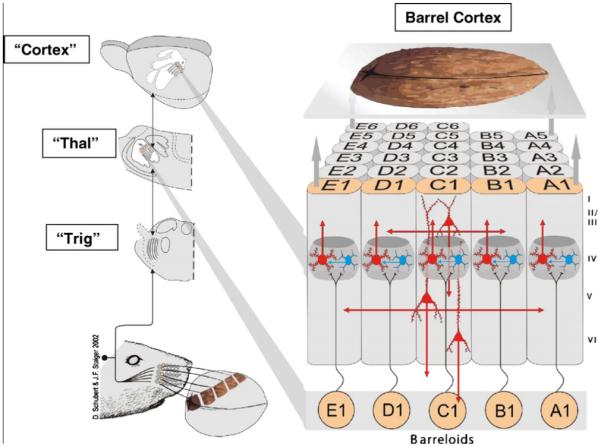
The diagram illustrates the rat palpating a walnut with its whiskers and conceptualizes the walnut being perceived through activity transmitted in the sensory pathway to cortex. The pathway contains a first synapse in the brainstem trigeminal nuclei (“Trig”), a second synapse in the contralateral thalamus (“Thal”) and a third relay from thalamus to primary sensory (SI) cortex (called barrel cortex). There is a separate channel for each whisker on the rat’s face up to and including primary sensory cortex as illustrated on the right, each labeled by a row (from A dorsal to E ventral) and a number starting from posterior and counting anteriorly. The roman numerals to the right of barrel cortex identify the six cortical layers. The results in the present paper were generated by analyzing neurons in the barrel cortex using single cell electrophysiology and biochemical techniques. [Permission was originally obtained from Brain Res. Adapted from D. Schubert and J. F. Staiger, (2002); Woolsey and van der Loos (1970)].
