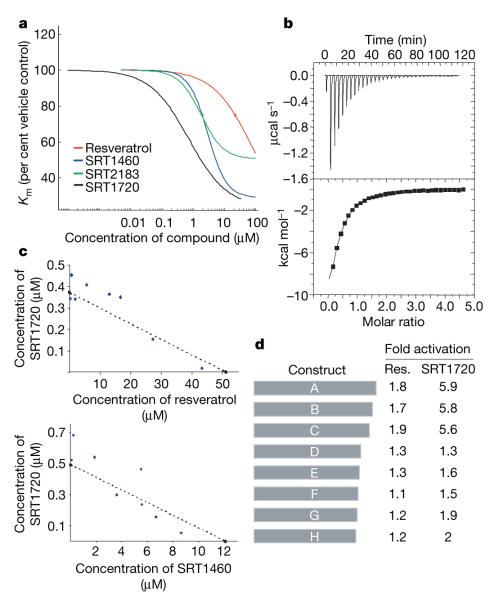
Figure 2. In vitro characterization of activators of human SIRT1.
a, The effect of SIRT1 activators on peptide substrate Km. b, Calorimetric titrations of SIRT1-C—peptide substrate complex with the activator SRT1460. Top panel: heat of binding SRT1460 to enzyme—peptide complex. Bottom panel: integrated fit with a one-site binding model. c, Isobologram analysis of resveratrol versus SRT1720 and SRT1720 versus SRT1460. The experimental data are best fit to the theoretical line of additivity (dashed line). d, SIRT1 N-terminal truncations define the allosteric compound binding site. The ability of resveratrol and SRT1720 to activate SIRT1 was examined against a series of N-terminal deletions in the mass spectrometry assay.