Abstract
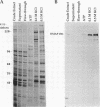
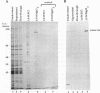
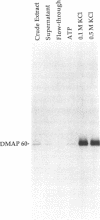
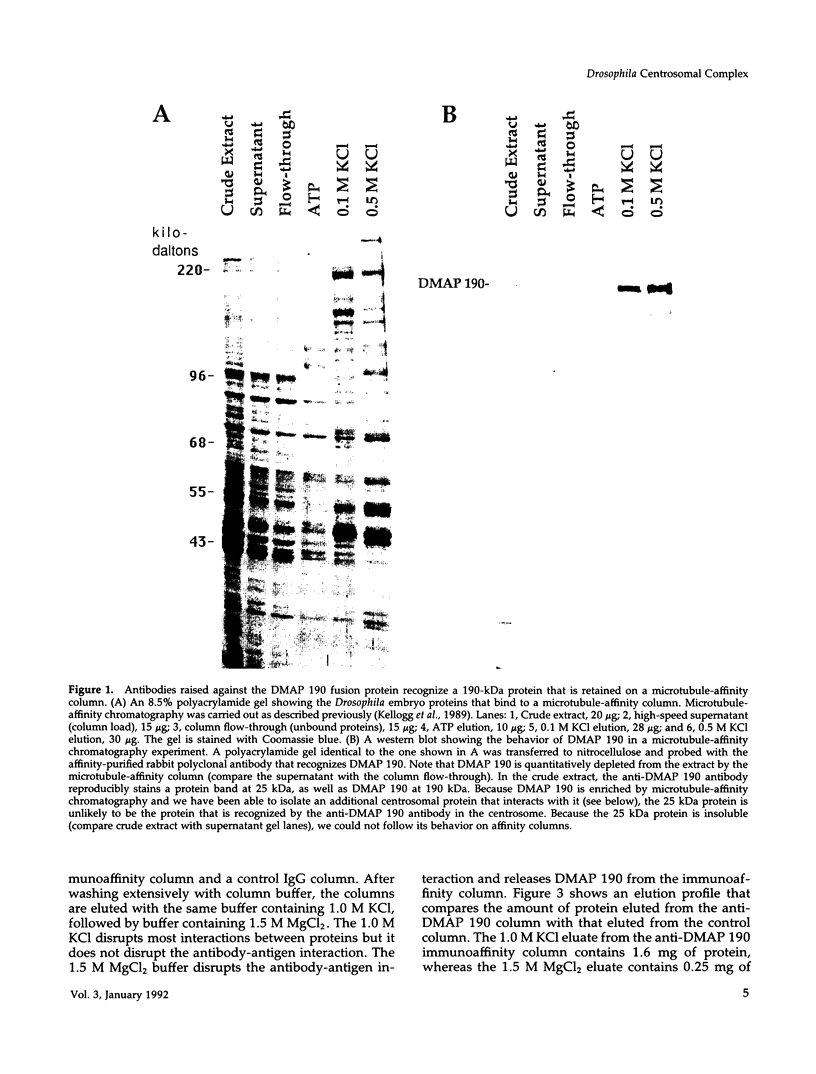
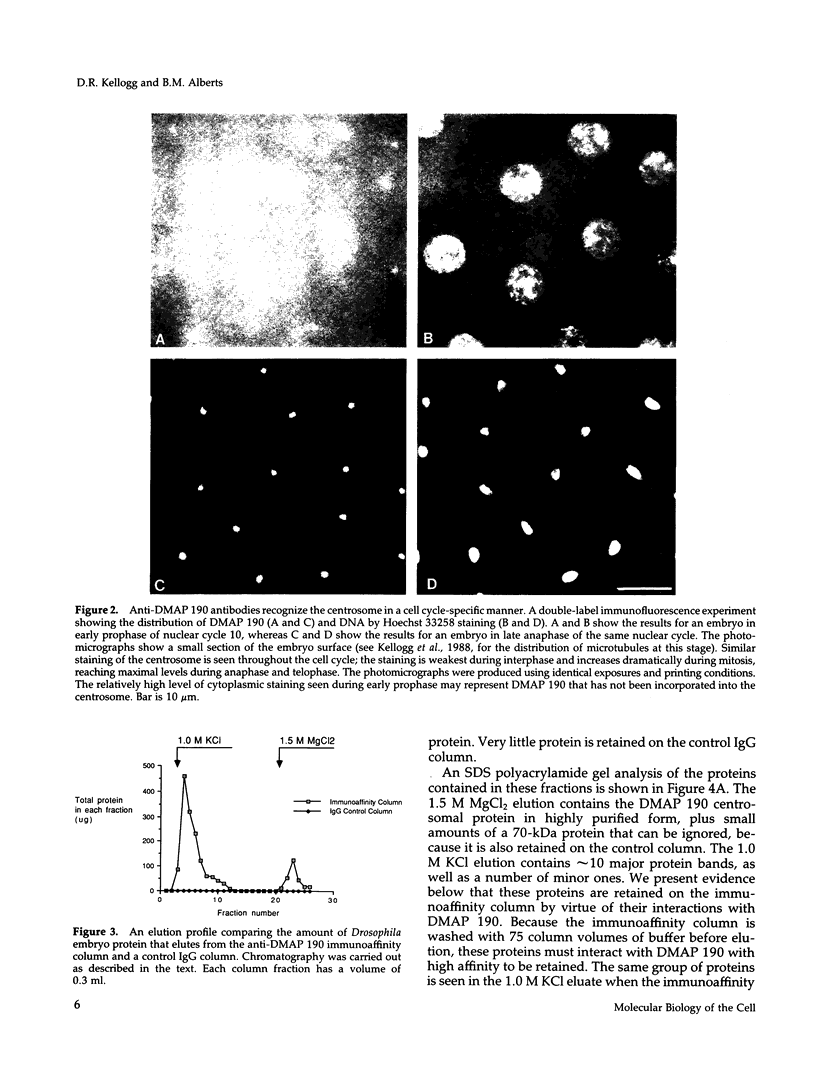
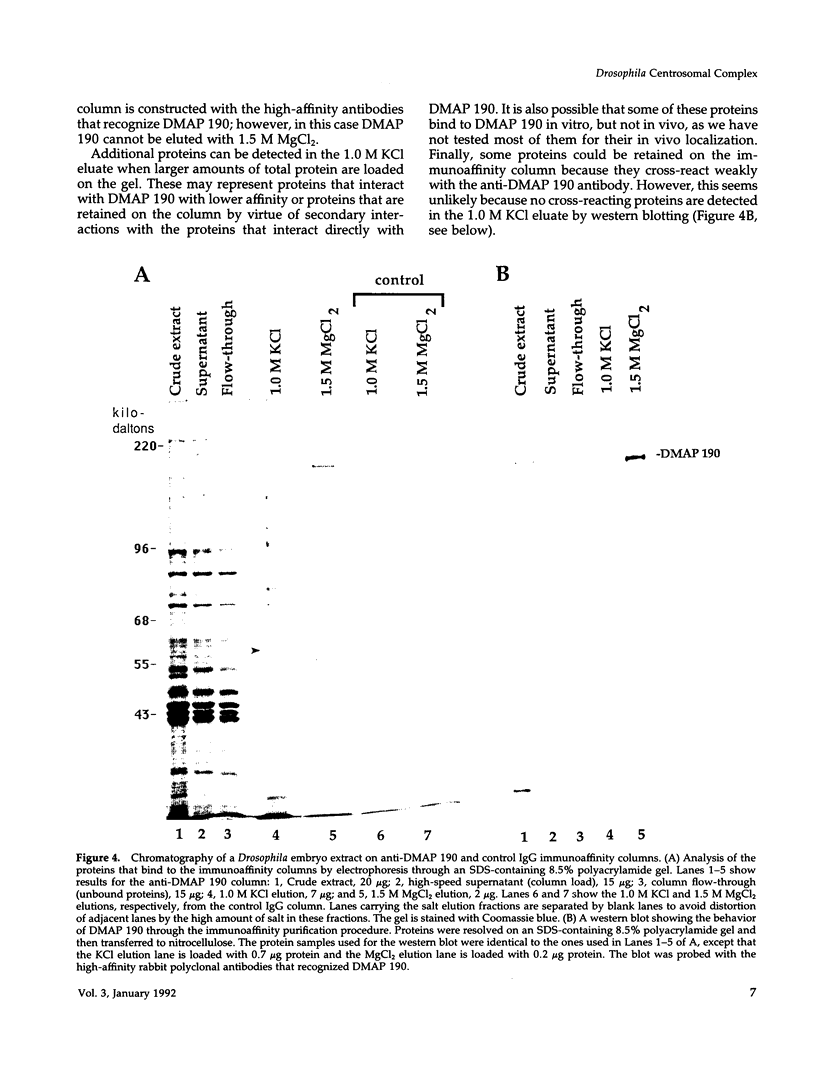
A 190-kDa centrosomal protein interacts with microtubules when Drosophila embryo extracts are passed over microtubule-affinity columns. We have obtained a partial cDNA clone that encodes this protein. Using a fusion protein produced from the clone, we have developed a novel immunoaffinity chromatography procedure that allows both the 190-kDa protein and a complex of proteins that associates with it to be isolated in in a single step. For this procedure, the fusion protein is used as an antigen to prepare rabbit polyclonal antibodies, and those antibodies that recognize the 190-kDa protein with low affinity are selectively purified on a column containing immobilized antigen. These low-affinity antibodies are then used to construct an immunoaffinity column. When Drosophila embryo extracts are passed over this column, the 190-kDa protein is quantitatively retained and can be eluted in nearly pure form under nondenaturing conditions with 1.5 M MgCl2, pH 7.6. The immunoaffinity column is washed with 1.0 M KCl just before the elution with 1.5 M MgCl2. This wash elutes 10 major proteins, as well as a number of minor ones. We present evidence that these KCl-eluted proteins represent additional centrosomal components that interact with the 190-kDa protein to form a multiprotein complex within the cell.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkley B. R. Microtubule organizing centers. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:145–172. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.001045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang L. M., Bollum F. J. Molecular biology of terminal transferase. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1986;21(1):27–52. doi: 10.3109/10409238609113608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang L. M., Rafter E., Augl C., Bollum F. J. Purification of a DNA polymerase-DNA primase complex from calf thymus glands. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14679–14687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch M., Glover D. M., Saumweber H. Nuclear antigens follow different pathways into daughter nuclei during mitosis in early Drosophila embryos. J Cell Sci. 1986 Jun;82:155–172. doi: 10.1242/jcs.82.1.155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gard D. L., Hafezi S., Zhang T., Doxsey S. J. Centrosome duplication continues in cycloheximide-treated Xenopus blastulae in the absence of a detectable cell cycle. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;110(6):2033–2042. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.6.2033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishimi Y., Claude A., Bullock P., Hurwitz J. Complete enzymatic synthesis of DNA containing the SV40 origin of replication. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 25;263(36):19723–19733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellogg D. R., Field C. M., Alberts B. M. Identification of microtubule-associated proteins in the centrosome, spindle, and kinetochore of the early Drosophila embryo. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):2977–2991. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.2977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellogg D. R., Mitchison T. J., Alberts B. M. Behaviour of microtubules and actin filaments in living Drosophila embryos. Development. 1988 Aug;103(4):675–686. doi: 10.1242/dev.103.4.675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K. G., Alberts B. M. F-actin affinity chromatography: technique for isolating previously unidentified actin-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):4808–4812. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.4808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyland M. E., Loeb L. A. On the fidelity of DNA replication. Isolation of high fidelity DNA polymerase-primase complexes by immunoaffinity chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10824–10830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simanis V., Lane D. P. An immunoaffinity purification procedure for SV40 large T antigen. Virology. 1985 Jul 15;144(1):88–100. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90308-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sluder G., Miller F. J., Cole R., Rieder C. L. Protein synthesis and the cell cycle: centrosome reproduction in sea urchin eggs is not under translational control. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;110(6):2025–2032. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.6.2025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vorobjev I. A., Nadezhdina E. S. The centrosome and its role in the organization of microtubules. Int Rev Cytol. 1987;106:227–293. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61714-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitfield W. G., Millar S. E., Saumweber H., Frasch M., Glover D. M. Cloning of a gene encoding an antigen associated with the centrosome in Drosophila. J Cell Sci. 1988 Apr;89(Pt 4):467–480. doi: 10.1242/jcs.89.4.467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]