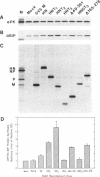
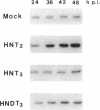
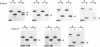Abstract
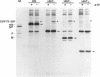
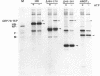
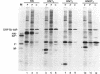
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-localized chaperone protein, GRP78-BiP, is involved in the folding and oligomerization of secreted and membrane proteins, including the simian virus 5 hemagglutinin-neuraminidase (HN) glycoprotein. To understand this interaction better, we have constructed a series of HN mutants in which specific portions of the extracytoplasmic domain have been deleted. Analysis of these mutant polypeptides expressed in CV-1 cells have indicated that GRP78-BiP binds to selective sequences in HN and that there exists more than a single site of interaction. Mutant polypeptides have been characterized that are competent and incompetent for association with GRP78-BiP. These mutants have been used to show that the induction of GRP78-BiP synthesis due to the presence of nonnative protein molecules in the ER is dependent on GRP78-BiP complex formation with its substrates. These studies have implications for the function of the GRP78-BiP protein and the mechanism by which the gene is regulated.
Full text
PDF


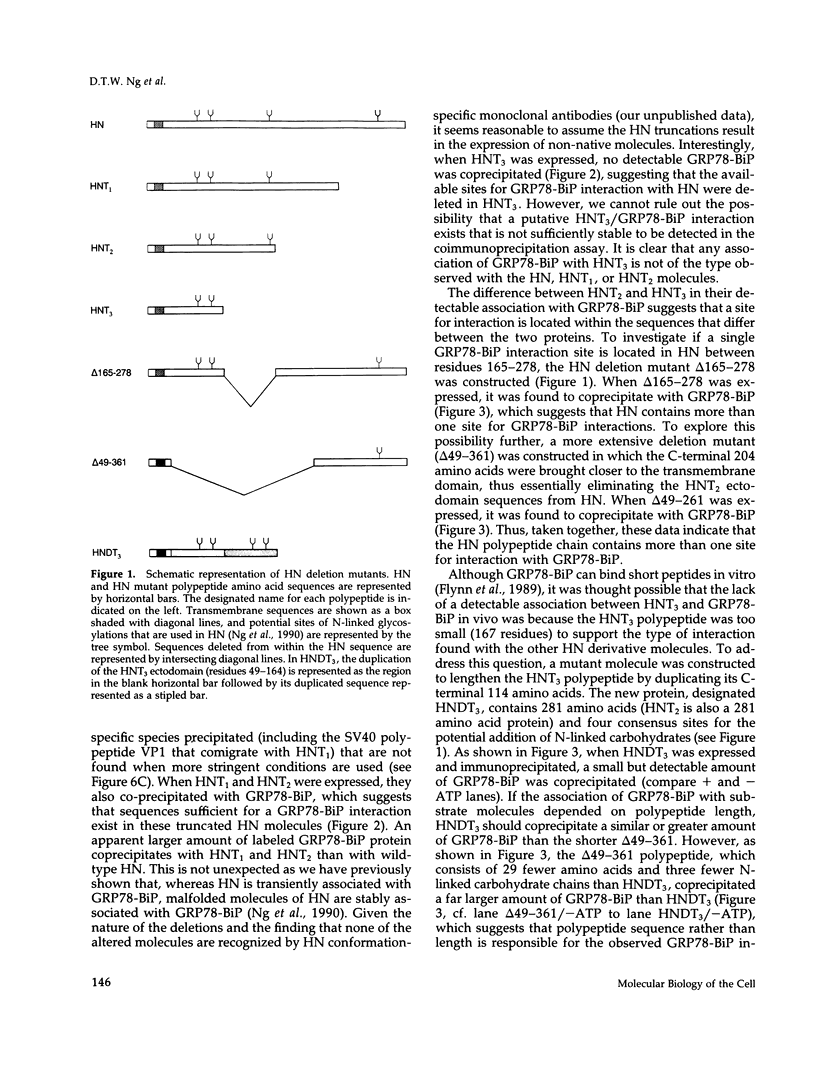




Images in this article
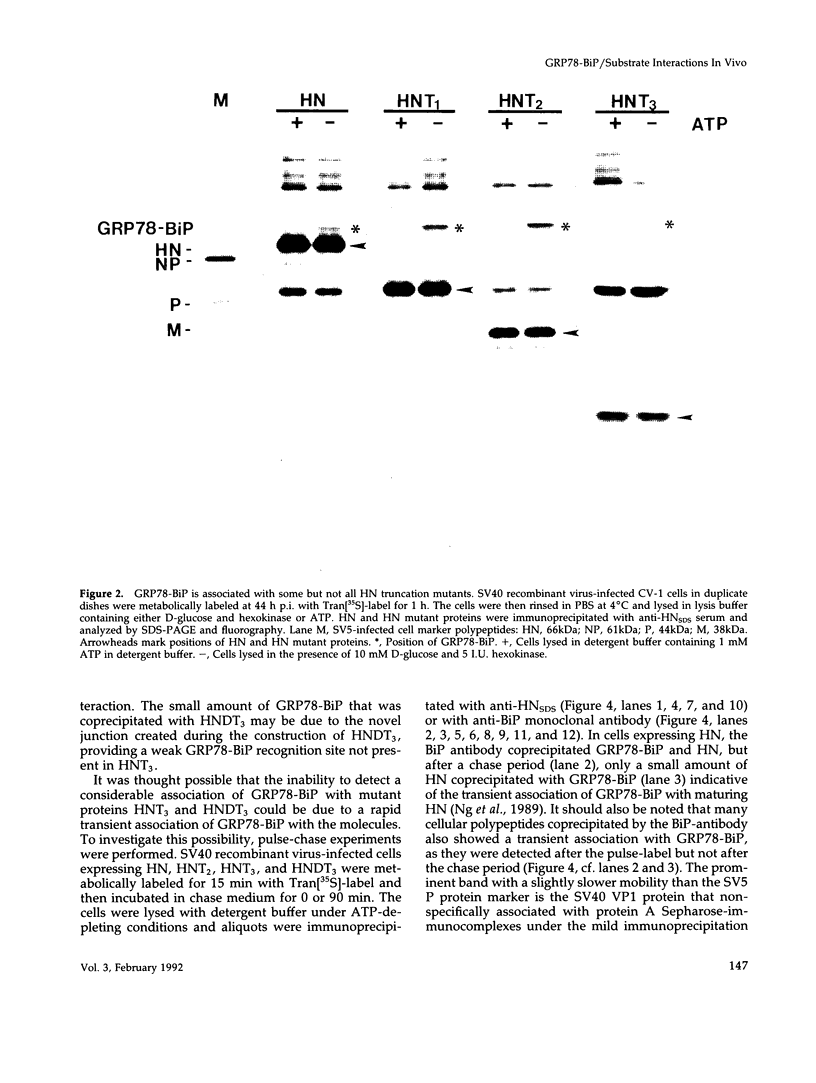
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bole D. G., Hendershot L. M., Kearney J. F. Posttranslational association of immunoglobulin heavy chain binding protein with nascent heavy chains in nonsecreting and secreting hybridomas. J Cell Biol. 1986 May;102(5):1558–1566. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.5.1558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulleid N. J., Freedman R. B. Defective co-translational formation of disulphide bonds in protein disulphide-isomerase-deficient microsomes. Nature. 1988 Oct 13;335(6191):649–651. doi: 10.1038/335649a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang S. C., Wooden S. K., Nakaki T., Kim Y. K., Lin A. Y., Kung L., Attenello J. W., Lee A. S. Rat gene encoding the 78-kDa glucose-regulated protein GRP78: its regulatory sequences and the effect of protein glycosylation on its expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):680–684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng M. Y., Hartl F. U., Horwich A. L. The mitochondrial chaperonin hsp60 is required for its own assembly. Nature. 1990 Nov 29;348(6300):455–458. doi: 10.1038/348455a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng M. Y., Hartl F. U., Martin J., Pollock R. A., Kalousek F., Neupert W., Hallberg E. M., Hallberg R. L., Horwich A. L. Mitochondrial heat-shock protein hsp60 is essential for assembly of proteins imported into yeast mitochondria. Nature. 1989 Feb 16;337(6208):620–625. doi: 10.1038/337620a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins P. L., Hightower L. E., Ball L. A. Transcription and translation of Newcastle disease virus mRNA's in vitro. J Virol. 1978 Oct;28(1):324–336. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.1.324-336.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland C. S., Doms R. W., Bolzau E. M., Webster R. G., Helenius A. Assembly of influenza hemagglutinin trimers and its role in intracellular transport. J Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;103(4):1179–1191. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.4.1179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doms R. W., Ruusala A., Machamer C., Helenius J., Helenius A., Rose J. K. Differential effects of mutations in three domains on folding, quaternary structure, and intracellular transport of vesicular stomatitis virus G protein. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;107(1):89–99. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.1.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorner A. J., Bole D. G., Kaufman R. J. The relationship of N-linked glycosylation and heavy chain-binding protein association with the secretion of glycoproteins. J Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;105(6 Pt 1):2665–2674. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.6.2665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorner A. J., Wasley L. C., Kaufman R. J. Increased synthesis of secreted proteins induces expression of glucose-regulated proteins in butyrate-treated Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 5;264(34):20602–20607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond I. A., Lee A. S., Resendez E., Jr, Steinhardt R. A. Depletion of intracellular calcium stores by calcium ionophore A23187 induces the genes for glucose-regulated proteins in hamster fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12801–12805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis R. J., Hemmingsen S. M. Molecular chaperones: proteins essential for the biogenesis of some macromolecular structures. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Aug;14(8):339–342. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90168-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flynn G. C., Chappell T. G., Rothman J. E. Peptide binding and release by proteins implicated as catalysts of protein assembly. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):385–390. doi: 10.1126/science.2756425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher P., Henneberry J., Wilson I., Sambrook J., Gething M. J. Addition of carbohydrate side chains at novel sites on influenza virus hemagglutinin can modulate the folding, transport, and activity of the molecule. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 1):2059–2073. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., McCammon K., Sambrook J. Expression of wild-type and mutant forms of influenza hemagglutinin: the role of folding in intracellular transport. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):939–950. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90076-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., Sambrook J. Transport and assembly processes in the endoplasmic reticulum. Semin Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;1(1):65–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson R., Schlesinger S., Kornfeld S. The nonglycosylated glycoprotein of vesicular stomatitis virus is temperature-sensitive and undergoes intracellular aggregation at elevated temperatures. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 10;254(9):3600–3607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas I. G., Wabl M. Immunoglobulin heavy chain binding protein. Nature. 1983 Nov 24;306(5941):387–389. doi: 10.1038/306387a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardwick K. G., Lewis M. J., Semenza J., Dean N., Pelham H. R. ERD1, a yeast gene required for the retention of luminal endoplasmic reticulum proteins, affects glycoprotein processing in the Golgi apparatus. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):623–630. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08154.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendershot L. M. Immunoglobulin heavy chain and binding protein complexes are dissociated in vivo by light chain addition. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):829–837. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendershot L. M., Kearney J. F. A role for human heavy chain binding protein in the developmental regulation of immunoglobin transport. Mol Immunol. 1988 Jun;25(6):585–595. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(88)90081-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendershot L. M., Ting J., Lee A. S. Identity of the immunoglobulin heavy-chain-binding protein with the 78,000-dalton glucose-regulated protein and the role of posttranslational modifications in its binding function. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4250–4256. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendershot L., Bole D., Köhler G., Kearney J. F. Assembly and secretion of heavy chains that do not associate posttranslationally with immunoglobulin heavy chain-binding protein. J Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;104(3):761–767. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.3.761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiebert S. W., Lamb R. A. Cell surface expression of glycosylated, nonglycosylated, and truncated forms of a cytoplasmic protein pyruvate kinase. J Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;107(3):865–876. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.3.865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiebert S. W., Paterson R. G., Lamb R. A. Hemagglutinin-neuraminidase protein of the paramyxovirus simian virus 5: nucleotide sequence of the mRNA predicts an N-terminal membrane anchor. J Virol. 1985 Apr;54(1):1–6. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.1.1-6.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurtley S. M., Bole D. G., Hoover-Litty H., Helenius A., Copeland C. S. Interactions of misfolded influenza virus hemagglutinin with binding protein (BiP). J Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;108(6):2117–2126. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.6.2117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurtley S. M., Helenius A. Protein oligomerization in the endoplasmic reticulum. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1989;5:277–307. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.05.110189.001425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassenbrock C. K., Garcia P. D., Walter P., Kelly R. B. Heavy-chain binding protein recognizes aberrant polypeptides translocated in vitro. Nature. 1988 May 5;333(6168):90–93. doi: 10.1038/333090a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld R., Kornfeld S. Assembly of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:631–664. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozutsumi Y., Segal M., Normington K., Gething M. J., Sambrook J. The presence of malfolded proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum signals the induction of glucose-regulated proteins. Nature. 1988 Mar 31;332(6163):462–464. doi: 10.1038/332462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb R. A., Choppin P. W. Synthesis of influenza virus proteins in infected cells: translation of viral polypeptides, including three P polypeptides, from RNA produced by primary transcription. Virology. 1976 Oct 15;74(2):504–519. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90356-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb R. A., Etkind P. R., Choppin P. W. Evidence for a ninth influenza viral polypeptide. Virology. 1978 Nov;91(1):60–78. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90355-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodish H. F. Transport of secretory and membrane glycoproteins from the rough endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi. A rate-limiting step in protein maturation and secretion. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 15;263(5):2107–2110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machamer C. E., Doms R. W., Bole D. G., Helenius A., Rose J. K. Heavy chain binding protein recognizes incompletely disulfide-bonded forms of vesicular stomatitis virus G protein. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6879–6883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machamer C. E., Rose J. K. Influence of new glycosylation sites on expression of the vesicular stomatitis virus G protein at the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5948–5954. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machamer C. E., Rose J. K. Vesicular stomatitis virus G proteins with altered glycosylation sites display temperature-sensitive intracellular transport and are subject to aberrant intermolecular disulfide bonding. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5955–5960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro S., Pelham H. R. An Hsp70-like protein in the ER: identity with the 78 kd glucose-regulated protein and immunoglobulin heavy chain binding protein. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):291–300. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90746-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng D. T., Hiebert S. W., Lamb R. A. Different roles of individual N-linked oligosaccharide chains in folding, assembly, and transport of the simian virus 5 hemagglutinin-neuraminidase. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):1989–2001. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng D. T., Randall R. E., Lamb R. A. Intracellular maturation and transport of the SV5 type II glycoprotein hemagglutinin-neuraminidase: specific and transient association with GRP78-BiP in the endoplasmic reticulum and extensive internalization from the cell surface. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 2):3273–3289. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.3273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks G. D., Lamb R. A. Defective assembly and intracellular transport of mutant paramyxovirus hemagglutinin-neuraminidase proteins containing altered cytoplasmic domains. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3605–3616. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3605-3616.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson R. G., Hiebert S. W., Lamb R. A. Expression at the cell surface of biologically active fusion and hemagglutinin/neuraminidase proteins of the paramyxovirus simian virus 5 from cloned cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7520–7524. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. Control of protein exit from the endoplasmic reticulum. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1989;5:1–23. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.05.110189.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. Speculations on the functions of the major heat shock and glucose-regulated proteins. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):959–961. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90693-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peluso R. W., Lamb R. A., Choppin P. W. Infection with paramyxoviruses stimulates synthesis of cellular polypeptides that are also stimulated in cells transformed by Rous sarcoma virus or deprived of glucose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6120–6124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollok B. A., Anker R., Eldridge P., Hendershot L., Levitt D. Molecular basis of the cell-surface expression of immunoglobulin mu chain without light chain in human B lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9199–9203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pouysségur J., Shiu R. P., Pastan I. Induction of two transformation-sensitive membrane polypeptides in normal fibroblasts by a block in glycoprotein synthesis or glucose deprivation. Cell. 1977 Aug;11(4):941–947. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90305-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E. Polypeptide chain binding proteins: catalysts of protein folding and related processes in cells. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):591–601. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90005-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roux L. Selective and transient association of Sendai virus HN glycoprotein with BiP. Virology. 1990 Mar;175(1):161–166. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90196-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheshberadaran H., Lamb R. A. Simian virus 5 membrane protein maturation: expression in virus-infected cells and from a eukaryotic vector. Virology. 1991 Aug;183(2):803–809. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)91015-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiu R. P., Pouyssegur J., Pastan I. Glucose depletion accounts for the induction of two transformation-sensitive membrane proteinsin Rous sarcoma virus-transformed chick embryo fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3840–3844. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skowyra D., Georgopoulos C., Zylicz M. The E. coli dnaK gene product, the hsp70 homolog, can reactivate heat-inactivated RNA polymerase in an ATP hydrolysis-dependent manner. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):939–944. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90268-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckle M. Y., Sugano S., Hampe A., Vashistha A., Pellman D., Hanafusa H. 78-kilodalton glucose-regulated protein is induced in Rous sarcoma virus-transformed cells independently of glucose deprivation. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;8(7):2675–2680. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.7.2675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watowich S. S., Morimoto R. I. Complex regulation of heat shock- and glucose-responsive genes in human cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):393–405. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watowich S. S., Morimoto R. I., Lamb R. A. Flux of the paramyxovirus hemagglutinin-neuraminidase glycoprotein through the endoplasmic reticulum activates transcription of the GRP78-BiP gene. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3590–3597. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3590-3597.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiest D. L., Burkhardt J. K., Hester S., Hortsch M., Meyer D. I., Argon Y. Membrane biogenesis during B cell differentiation: most endoplasmic reticulum proteins are expressed coordinately. J Cell Biol. 1990 May;110(5):1501–1511. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.5.1501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu B., Hunt C., Morimoto R. Structure and expression of the human gene encoding major heat shock protein HSP70. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;5(2):330–341. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.2.330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]