Abstract
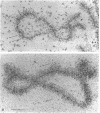
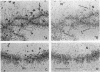
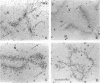
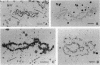
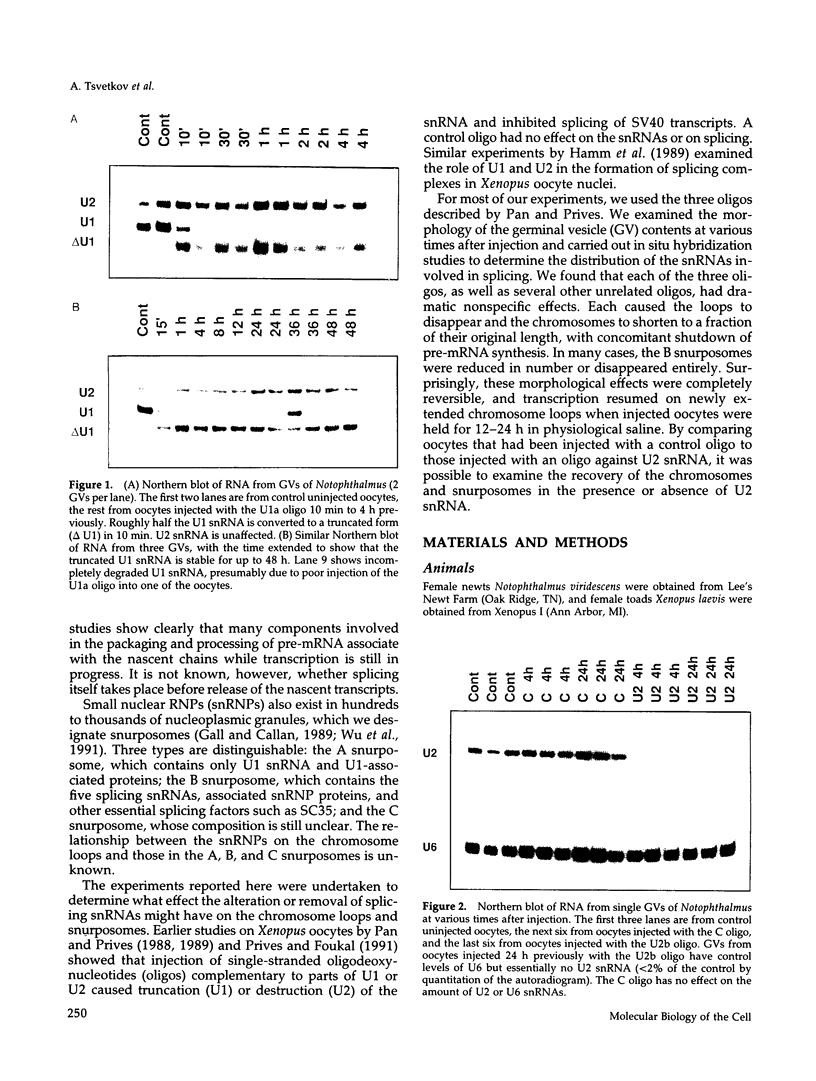
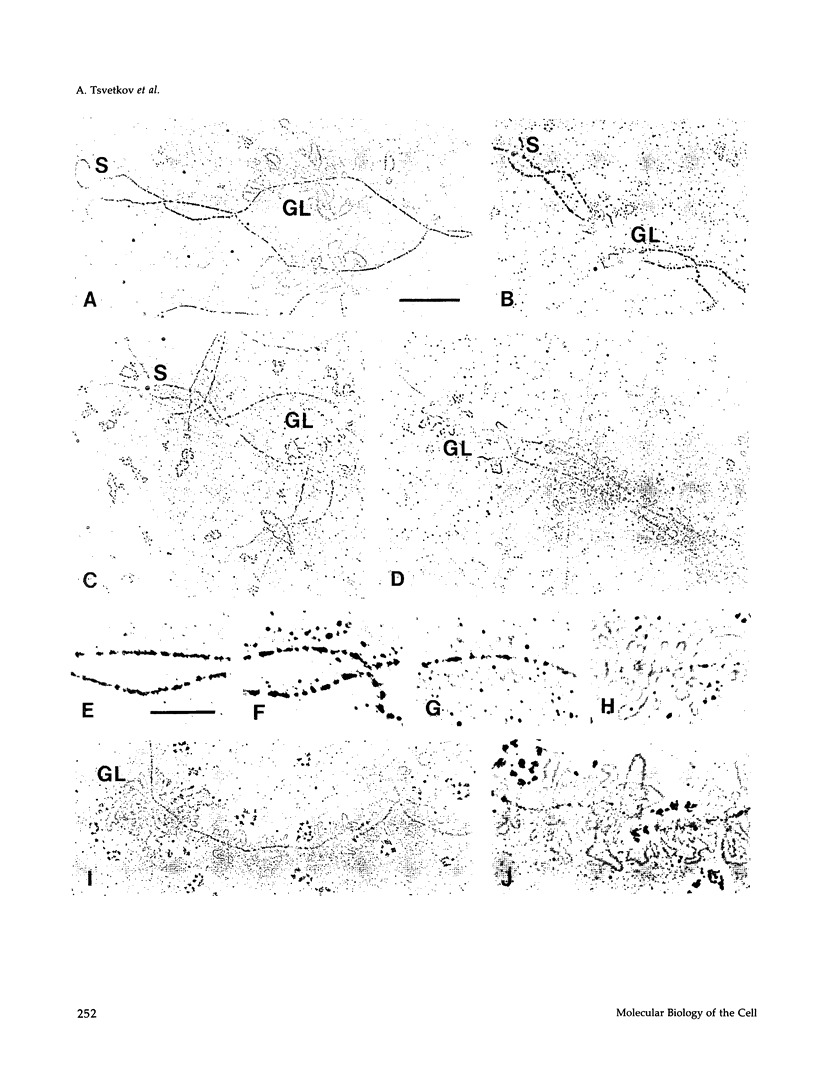
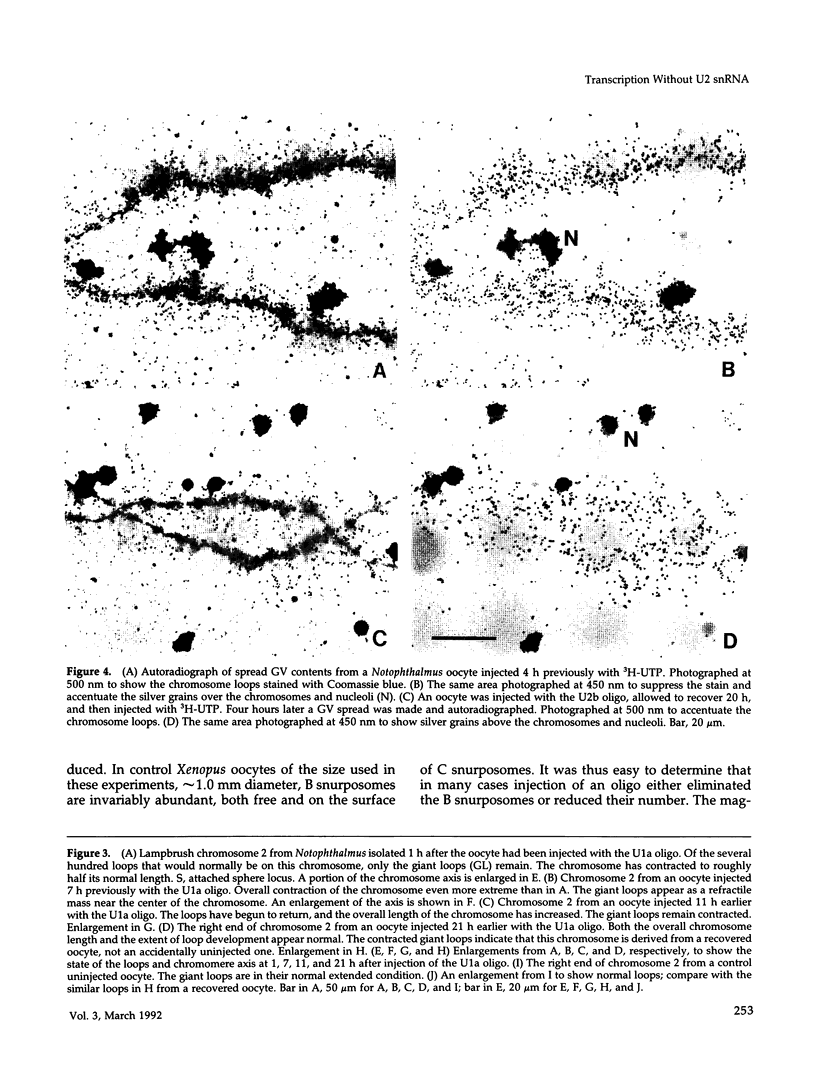
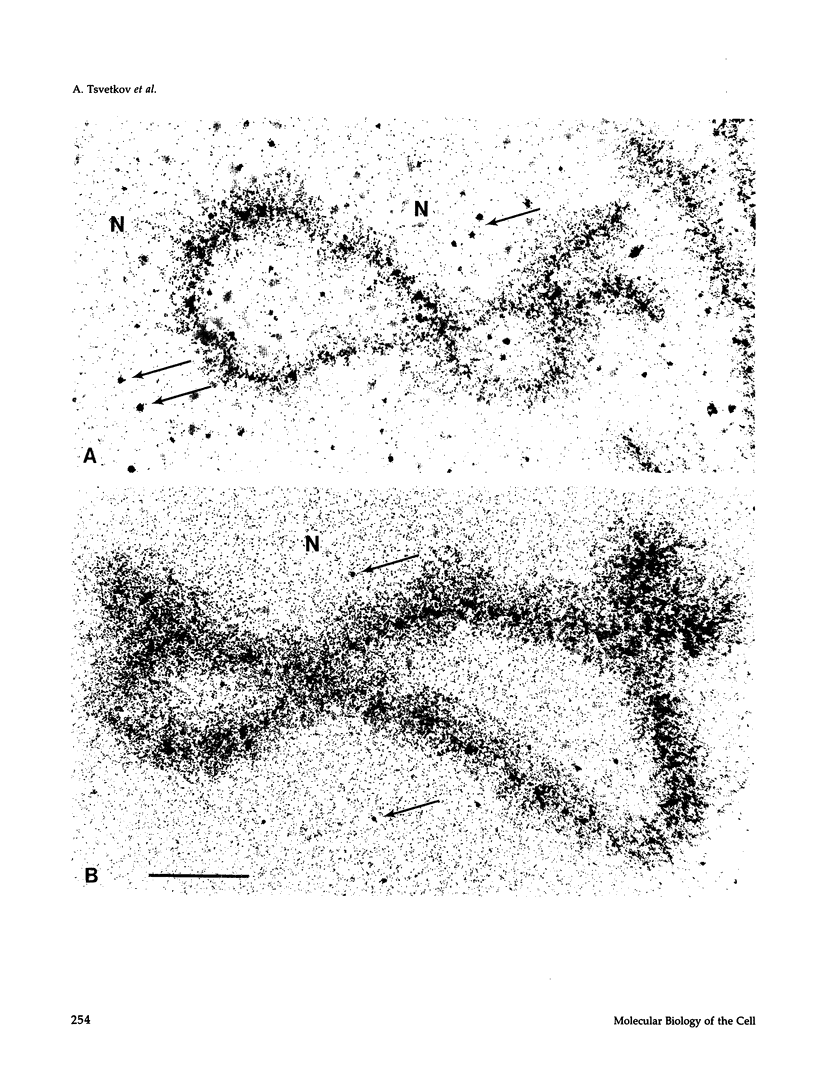
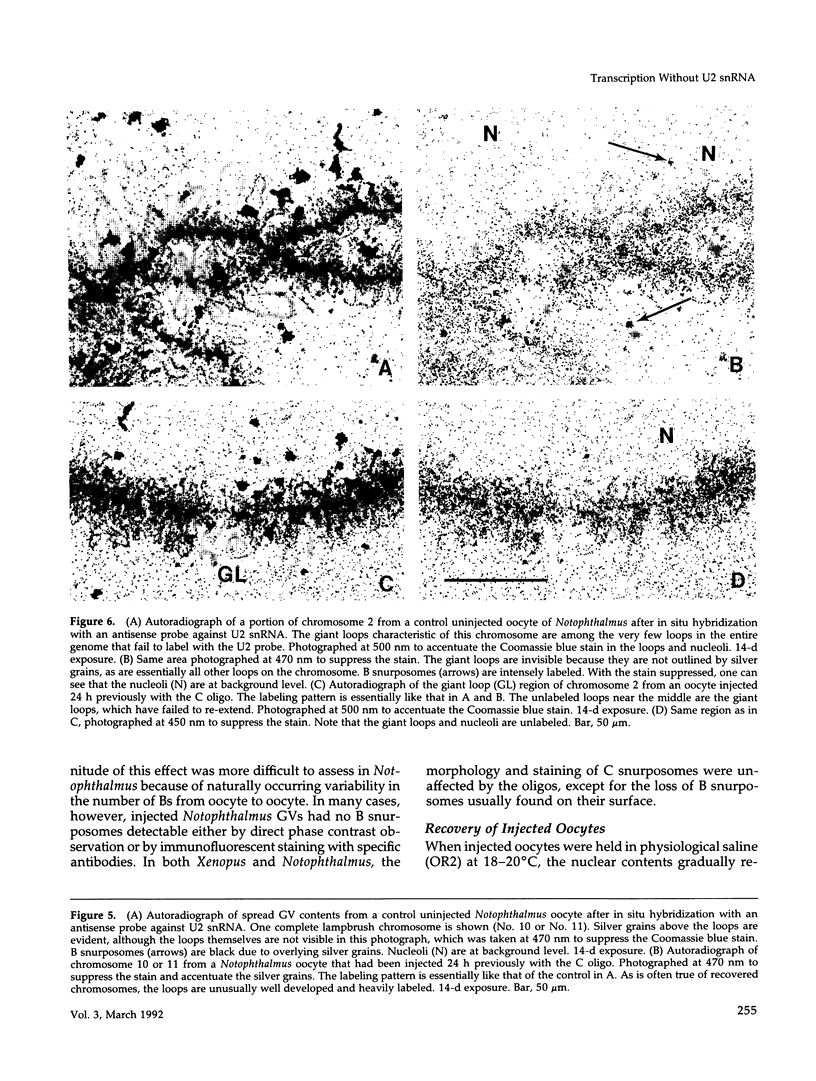
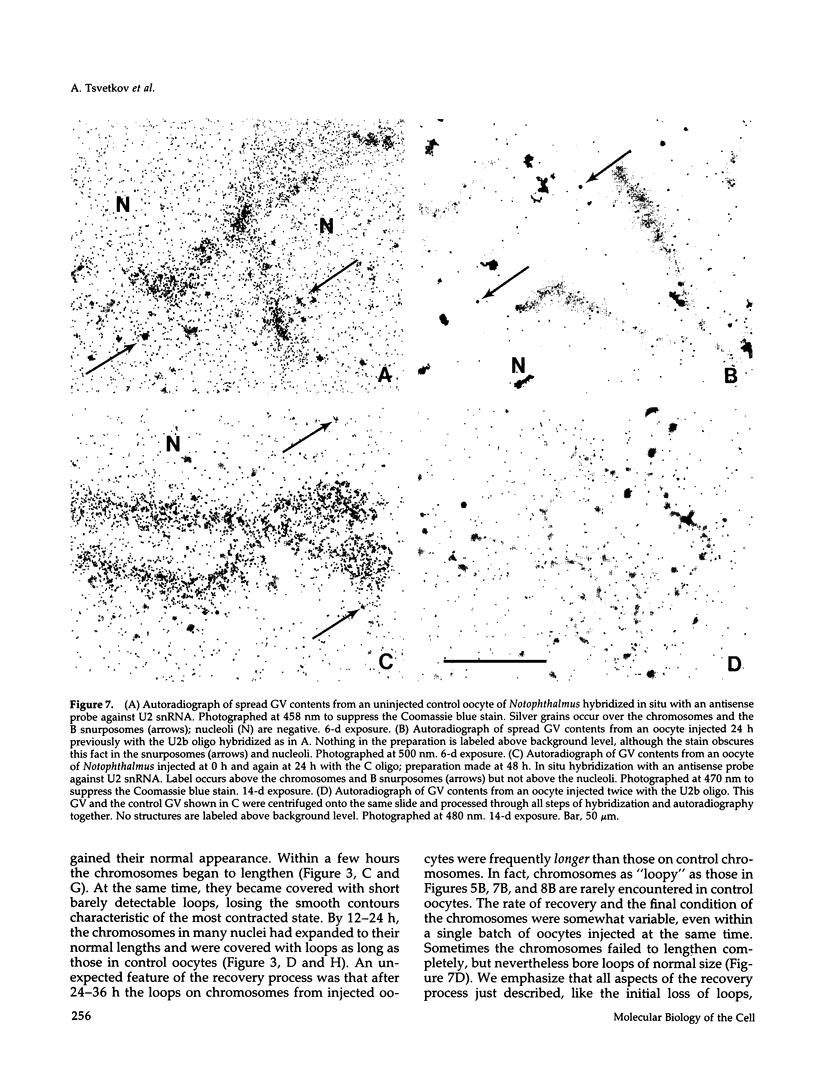
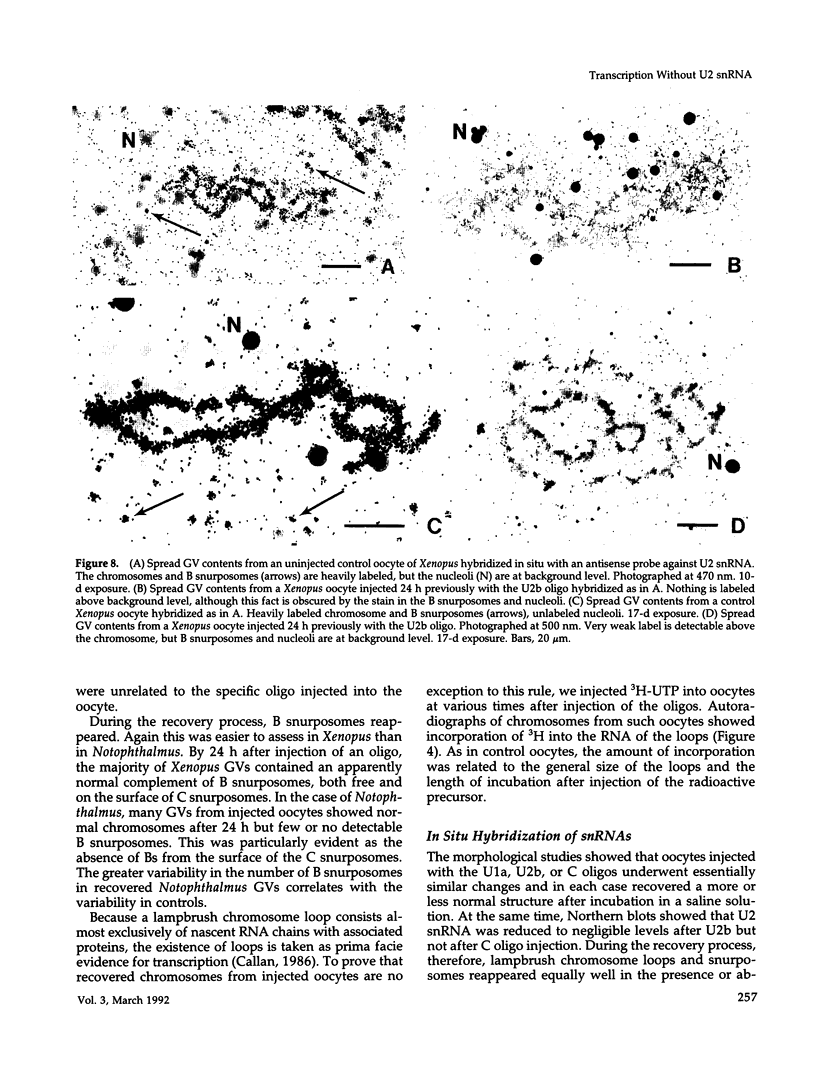
The five small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs) involved in splicing occur on the loops of amphibian lampbrush chromosomes and in hundreds to thousands of extrachromosomal granules called B snurposomes. To assess the role of these snRNAs during transcription and to explore possible relationships between the loops and B snurposomes, we injected single-stranded antisense oligodeoxynucleotides (oligos) against U1 and U2 snRNA into toad and newt oocytes. As shown before, antisense U1 and U2 oligos caused truncation of U1 and complete destruction of U2 snRNAs, respectively. However, injection of any oligo, regardless of sequence, brought on dramatic cytological changes, including shortening of the chromosomes and retraction of the lateral loops, with concomitant shutdown of polymerase II transcription, as well as disappearance of some or all of the B snurposomes. When injected oocytes were incubated for 12 h or longer in physiological saline, these changes were reversible; that is, the chromosomes lengthened, transcription (detected by 3H-UTP incorporation) resumed on newly extended lateral loops, and B snurposomes reappeared. In situ hybridization showed that loops and B snurposomes had negligible amounts of U2 snRNA after recovery from injection of the anti-U2 oligo, whereas these structures had normal levels of U2 snRNA after recovery from a control oligo. Thus, the morphological integrity of B snurposomes and lampbrush chromosome loops is not dependent on the presence of U2 snRNA. Because transcription occurs in the absence of U2 snRNA, we conclude that splicing is not required for transcription on lampbrush chromosome loops.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angelier N., Bonnanfant-Jais M. L., Herberts C., Lautredou N., Moreau N., N'Da E., Penrad-Mobayed M., Rodriguez-Martin M. L., Sourrouille P. Chromosomes of amphibian oocytes as a model for gene expression: significance of lampbrush loops. Int J Dev Biol. 1990 Mar;34(1):69–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beyer A. L., Osheim Y. N. Splice site selection, rate of splicing, and alternative splicing on nascent transcripts. Genes Dev. 1988 Jun;2(6):754–765. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.6.754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bittner M., Kupferer P., Morris C. F. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins and nucleic acids from slab gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl cellulose or nitrocellulose sheets. Anal Biochem. 1980 Mar 1;102(2):459–471. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90182-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callan H. G., Gall J. G. Association of RNA with the B and C snurposomes of Xenopus oocyte nuclei. Chromosoma. 1991 Nov;101(2):69–82. doi: 10.1007/BF00357056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cazenave C., Chevrier M., Nguyen T. T., Hélène C. Rate of degradation of [alpha]- and [beta]-oligodeoxynucleotides in Xenopus oocytes. Implications for anti-messenger strategies. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 23;15(24):10507–10521. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.24.10507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin D. J., Green G. A., Zon G., Szoka F. C., Jr, Straubinger R. M. Rapid nuclear accumulation of injected oligodeoxyribonucleotides. New Biol. 1990 Dec;2(12):1091–1100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman A. Antisense strategies in cell and developmental biology. J Cell Sci. 1990 Nov;97(Pt 3):399–409. doi: 10.1242/jcs.97.3.399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMario P. J., Bromley S. E., Gall J. G. DNA-binding proteins on lampbrush chromosome loops. Chromosoma. 1989 May;97(6):413–420. doi: 10.1007/BF00295024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fakan S., Leser G., Martin T. E. Immunoelectron microscope visualization of nuclear ribonucleoprotein antigens within spread transcription complexes. J Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;103(4):1153–1157. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.4.1153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flannery A. V., Hill R. S. The effect of heat shock on the morphology of amphibian lampbrush chromosomes. Exp Cell Res. 1988 Jul;177(1):9–18. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(88)90020-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. D., Maniatis T. Factor required for mammalian spliceosome assembly is localized to discrete regions in the nucleus. Nature. 1990 Feb 1;343(6257):437–441. doi: 10.1038/343437a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gall J. G., Callan H. G. The sphere organelle contains small nuclear ribonucleoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6635–6639. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gall J. G., Murphy C., Callan H. G., Wu Z. A. Lampbrush chromosomes. Methods Cell Biol. 1991;36:149–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guthrie C., Patterson B. Spliceosomal snRNAs. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:387–419. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.002131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamm J., Dathan N. A., Mattaj I. W. Functional analysis of mutant Xenopus U2 snRNAs. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):159–169. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90878-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IZAWA M., ALLEFREY V. G., MIRSKY A. E. The relationship between RNA synthesis and loop structure in lampbrush chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Apr;49:544–551. doi: 10.1073/pnas.49.4.544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay B. K. Xenopus laevis: Practical uses in cell and molecular biology. Injections of oocytes and embryos. Methods Cell Biol. 1991;36:663–669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar A., Williams K. R., Szer W. Purification and domain structure of core hnRNP proteins A1 and A2 and their relationship to single-stranded DNA-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):11266–11273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacroix J. C., Azzouz R., Boucher D., Abbadie C., Pyne C. K., Charlemagne J. Monoclonal antibodies to lampbrush chromosome antigens of Pleurodeles waltlii. Chromosoma. 1985;92(1):69–80. doi: 10.1007/BF00327246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loones M. T. In vivo effects of gamma-irradiation on the functional architecture of the lampbrush chromosomes in Pleurodeles (Amphibia, Urodela). Chromosoma. 1979 Aug;73(3):357–368. doi: 10.1007/BF00288697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancino G., Nardi I., Corvaja N., Fiume L., Marinozzi V. Effects of alpha-amanitin on Triturus lampbrush chromosomes. Exp Cell Res. 1971 Jan;64(1):237–239. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(71)90218-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Reed R. The role of small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles in pre-mRNA splicing. Nature. 1987 Feb 19;325(6106):673–678. doi: 10.1038/325673a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreau N., Angelier N., Bonnanfant-Jais M. L., Gounon P., Kubisz P. Association of nucleoplasmin with transcription products as revealed by immunolocalization in the amphibian oocyte. J Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;103(3):683–690. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.3.683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osheim Y. N., Miller O. L., Jr, Beyer A. L. RNP particles at splice junction sequences on Drosophila chorion transcripts. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):143–151. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90019-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan Z. Q., Prives C. Assembly of functional U1 and U2 human-amphibian hybrid snRNPs in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Science. 1988 Sep 9;241(4871):1328–1331. doi: 10.1126/science.2970672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan Z. Q., Prives C. U2 snRNA sequences that bind U2-specific proteins are dispensable for the function of U2 snRNP in splicing. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12A):1887–1898. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12a.1887. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piñol-Roma S., Choi Y. D., Matunis M. J., Dreyfuss G. Immunopurification of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles reveals an assortment of RNA-binding proteins. Genes Dev. 1988 Feb;2(2):215–227. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.2.215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piñol-Roma S., Swanson M. S., Gall J. G., Dreyfuss G. A novel heterogeneous nuclear RNP protein with a unique distribution on nascent transcripts. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):2575–2587. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.2575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prives C., Foukai D. Use of oligonucleotides for antisense experiments in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Methods Cell Biol. 1991;36:185–210. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riva S., Morandi C., Tsoulfas P., Pandolfo M., Biamonti G., Merrill B., Williams K. R., Multhaup G., Beyreuther K., Werr H. Mammalian single-stranded DNA binding protein UP I is derived from the hnRNP core protein A1. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2267–2273. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04494.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Martin M. L., Herberts C., Moreau N., Angelier N. Effects of in vivo heat treatment on lampbrush chromosome structure in amphibian oocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1989 Dec;185(2):546–550. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(89)90324-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth M. B., Gall J. G. Monoclonal antibodies that recognize transcription unit proteins on newt lampbrush chromosomes. J Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;105(3):1047–1054. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.3.1047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruby S. W., Abelson J. Pre-mRNA splicing in yeast. Trends Genet. 1991 Mar;7(3):79–85. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90276-V. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sass H., Pederson T. Transcription-dependent localization of U1 and U2 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins at major sites of gene activity in polytene chromosomes. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 25;180(4):911–926. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90263-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheer U., Hinssen H., Franke W. W., Jockusch B. M. Microinjection of actin-binding proteins and actin antibodies demonstrates involvement of nuclear actin in transcription of lampbrush chromosomes. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):111–122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90196-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz L. D., Kay B. K., Gall J. G. In vitro RNA synthesis in oocyte nuclei of the newt Notophthalmus. Chromosoma. 1981;82(2):171–187. doi: 10.1007/BF00286102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott S. E., Sommerville J. Location of nuclear proteins on the chromosomes of newt oocytes. Nature. 1974 Aug 23;250(5468):680–682. doi: 10.1038/250680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. C., Bement W. M., Dersch M. A., Dworkin-Rastl E., Dworkin M. B., Capco D. G. Nonspecific effects of oligodeoxynucleotide injection in Xenopus oocytes: a reevaluation of previous D7 mRNA ablation experiments. Development. 1990 Nov;110(3):769–779. doi: 10.1242/dev.110.3.769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snow M. H., Callan H. G. Evidence for a polarized movement of the lateral loops of newt lampbrush chromosomes during oogenesis. J Cell Sci. 1969 Jul;5(1):1–25. doi: 10.1242/jcs.5.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. A., Jared D. W., Dumont J. N., Sega M. W. Protein incorporation by isolated amphibian oocytes. 3. Optimum incubation conditions. J Exp Zool. 1973 Jun;184(3):321–333. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401840305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wassarman P. M., Hollinger T. G., Smith L. D. Ribonuclease H activity in germinal vesicles of oocytes from Rana pipiens. Exp Cell Res. 1974 Dec;89(2):410–412. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90809-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu Z. A., Murphy C., Callan H. G., Gall J. G. Small nuclear ribonucleoproteins and heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins in the amphibian germinal vesicle: loops, spheres, and snurposomes. J Cell Biol. 1991 May;113(3):465–483. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.3.465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]