Abstract
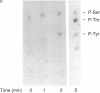
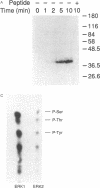
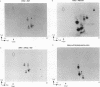
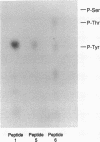
The phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2 (ERK1 and ERK2) in response to insulin in Rat 1 HIRc B cells and in response to nerve growth factor (NGF) in PC12 cells has been examined. ERK1 and ERK2 are phosphorylated on serine in the absence of the stimuli and additionally on tyrosine and threonine residues after exposure to NGF and insulin. NGF stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of ERK1 more rapidly than threonine phosphorylation. Two-dimensional phosphopeptide maps of both ERK1 and ERK2 phosphorylated in intact cells treated with NGF or with insulin display the same three predominant phosphopeptides that comigrate when digests of ERK1 and ERK2 are mixed. As many as five additional phosphopeptides are detected under certain conditions. Autophosphorylated recombinant ERK2 also contains the three tryptic phosphopeptides found in ERKs labeled in intact cells. These experiments demonstrate that ERK1 and ERK2 are phosphorylated on related sites in response to two distinct extracellular signals. The data also support the possibility that autophosphorylation may be involved in the activation of the ERKs.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahn N. G., Krebs E. G. Evidence for an epidermal growth factor-stimulated protein kinase cascade in Swiss 3T3 cells. Activation of serine peptide kinase activity by myelin basic protein kinases in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 15;265(20):11495–11501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blenis J., Erikson R. L. Regulation of protein kinase activities in PC12 pheochromocytoma cells. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3441–3447. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04667.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulton T. G., Cobb M. H. Identification of multiple extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERKs) with antipeptide antibodies. Cell Regul. 1991 May;2(5):357–371. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.5.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulton T. G., Gregory J. S., Cobb M. H. Purification and properties of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1, an insulin-stimulated microtubule-associated protein 2 kinase. Biochemistry. 1991 Jan 8;30(1):278–286. doi: 10.1021/bi00215a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulton T. G., Nye S. H., Robbins D. J., Ip N. Y., Radziejewska E., Morgenbesser S. D., DePinho R. A., Panayotatos N., Cobb M. H., Yancopoulos G. D. ERKs: a family of protein-serine/threonine kinases that are activated and tyrosine phosphorylated in response to insulin and NGF. Cell. 1991 May 17;65(4):663–675. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90098-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulton T. G., Yancopoulos G. D., Gregory J. S., Slaughter C., Moomaw C., Hsu J., Cobb M. H. An insulin-stimulated protein kinase similar to yeast kinases involved in cell cycle control. Science. 1990 Jul 6;249(4964):64–67. doi: 10.1126/science.2164259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cicirelli M. F., Pelech S. L., Krebs E. G. Activation of multiple protein kinases during the burst in protein phosphorylation that precedes the first meiotic cell division in Xenopus oocytes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 5;263(4):2009–2019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobb M. H., Boulton T. G., Robbins D. J. Extracellular signal-regulated kinases: ERKs in progress. Cell Regul. 1991 Dec;2(12):965–978. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.12.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobb M. H., Robbins D. J., Boulton T. G. ERKs, extracellular signal-regulated MAP-2 kinases. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;3(6):1025–1032. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90124-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson R. L. Structure, expression, and regulation of protein kinases involved in the phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6007–6010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotoh Y., Moriyama K., Matsuda S., Okumura E., Kishimoto T., Kawasaki H., Suzuki K., Yahara I., Sakai H., Nishida E. Xenopus M phase MAP kinase: isolation of its cDNA and activation by MPF. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2661–2668. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07809.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotoh Y., Nishida E., Matsuda S., Shiina N., Kosako H., Shiokawa K., Akiyama T., Ohta K., Sakai H. In vitro effects on microtubule dynamics of purified Xenopus M phase-activated MAP kinase. Nature. 1991 Jan 17;349(6306):251–254. doi: 10.1038/349251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotoh Y., Nishida E., Yamashita T., Hoshi M., Kawakami M., Sakai H. Microtubule-associated-protein (MAP) kinase activated by nerve growth factor and epidermal growth factor in PC12 cells. Identity with the mitogen-activated MAP kinase of fibroblastic cells. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Nov 13;193(3):661–669. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19384.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory J. S., Boulton T. G., Sang B. C., Cobb M. H. An insulin-stimulated ribosomal protein S6 kinase from rabbit liver. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18397–18401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gómez N., Tonks N. K., Morrison C., Harmar T., Cohen P. Evidence for communication between nerve growth factor and protein tyrosine phosphorylation. FEBS Lett. 1990 Oct 1;271(1-2):119–122. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80386-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haycock J. W. Phosphorylation of tyrosine hydroxylase in situ at serine 8, 19, 31, and 40. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 15;265(20):11682–11691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Her J. H., Wu J., Rall T. B., Sturgill T. W., Weber M. J. Sequence of pp42/MAP kinase, a serine/threonine kinase regulated by tyrosine phosphorylation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 11;19(13):3743–3743. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.13.3743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshi M., Nishida E., Sakai H. Activation of a Ca2+-inhibitable protein kinase that phosphorylates microtubule-associated protein 2 in vitro by growth factors, phorbol esters, and serum in quiescent cultured human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 15;263(11):5396–5401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan D. R., Martin-Zanca D., Parada L. F. Tyrosine phosphorylation and tyrosine kinase activity of the trk proto-oncogene product induced by NGF. Nature. 1991 Mar 14;350(6314):158–160. doi: 10.1038/350158a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazlauskas A., Cooper J. A. Protein kinase C mediates platelet-derived growth factor-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of p42. J Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;106(4):1395–1402. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.4.1395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher P. A. Nerve growth factor induces protein-tyrosine phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6788–6791. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyasaka T., Chao M. V., Sherline P., Saltiel A. R. Nerve growth factor stimulates a protein kinase in PC-12 cells that phosphorylates microtubule-associated protein-2. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 15;265(8):4730–4735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mutoh T., Rudkin B. B., Koizumi S., Guroff G. Nerve growth factor, a differentiating agent, and epidermal growth factor, a mitogen, increase the activities of different S6 kinases in PC12 cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):15853–15856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne D. M., Rossomando A. J., Martino P., Erickson A. K., Her J. H., Shabanowitz J., Hunt D. F., Weber M. J., Sturgill T. W. Identification of the regulatory phosphorylation sites in pp42/mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAP kinase). EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):885–892. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08021.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray L. B., Sturgill T. W. Characterization of insulin-stimulated microtubule-associated protein kinase. Rapid isolation and stabilization of a novel serine/threonine kinase from 3T3-L1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12721–12727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray L. B., Sturgill T. W. Rapid stimulation by insulin of a serine/threonine kinase in 3T3-L1 adipocytes that phosphorylates microtubule-associated protein 2 in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1502–1506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen O. M., Rubin C. S., Cobb M. H., Smith C. J. Insulin stimulates the phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 in a cell-free system derived from 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):3630–3633. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanghera J. S., Paddon H. B., Bader S. A., Pelech S. L. Purification and characterization of a maturation-activated myelin basic protein kinase from sea star oocytes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):52–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schanen-King C., Nel A., Williams L. K., Landreth G. Nerve growth factor stimulates the tyrosine phosphorylation of MAP2 kinase in PC12 cells. Neuron. 1991 Jun;6(6):915–922. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90232-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seger R., Ahn N. G., Boulton T. G., Yancopoulos G. D., Panayotatos N., Radziejewska E., Ericsson L., Bratlien R. L., Cobb M. H., Krebs E. G. Microtubule-associated protein 2 kinases, ERK1 and ERK2, undergo autophosphorylation on both tyrosine and threonine residues: implications for their mechanism of activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6142–6146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturgill T. W., Ray L. B., Erikson E., Maller J. L. Insulin-stimulated MAP-2 kinase phosphorylates and activates ribosomal protein S6 kinase II. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):715–718. doi: 10.1038/334715a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsao H., Aletta J. M., Greene L. A. Nerve growth factor and fibroblast growth factor selectively activate a protein kinase that phosphorylates high molecular weight microtubule-associated proteins. Detection, partial purification, and characterization in PC12 cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 15;265(26):15471–15480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsao H., Greene L. A. The roles of macromolecular synthesis and phosphorylation in the regulation of a protein kinase activity transiently stimulated by nerve growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 15;266(20):12981–12988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volonté C., Rukenstein A., Loeb D. M., Greene L. A. Differential inhibition of nerve growth factor responses by purine analogues: correlation with inhibition of a nerve growth factor-activated protein kinase. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):2395–2403. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.2395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]