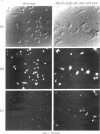
Abstract
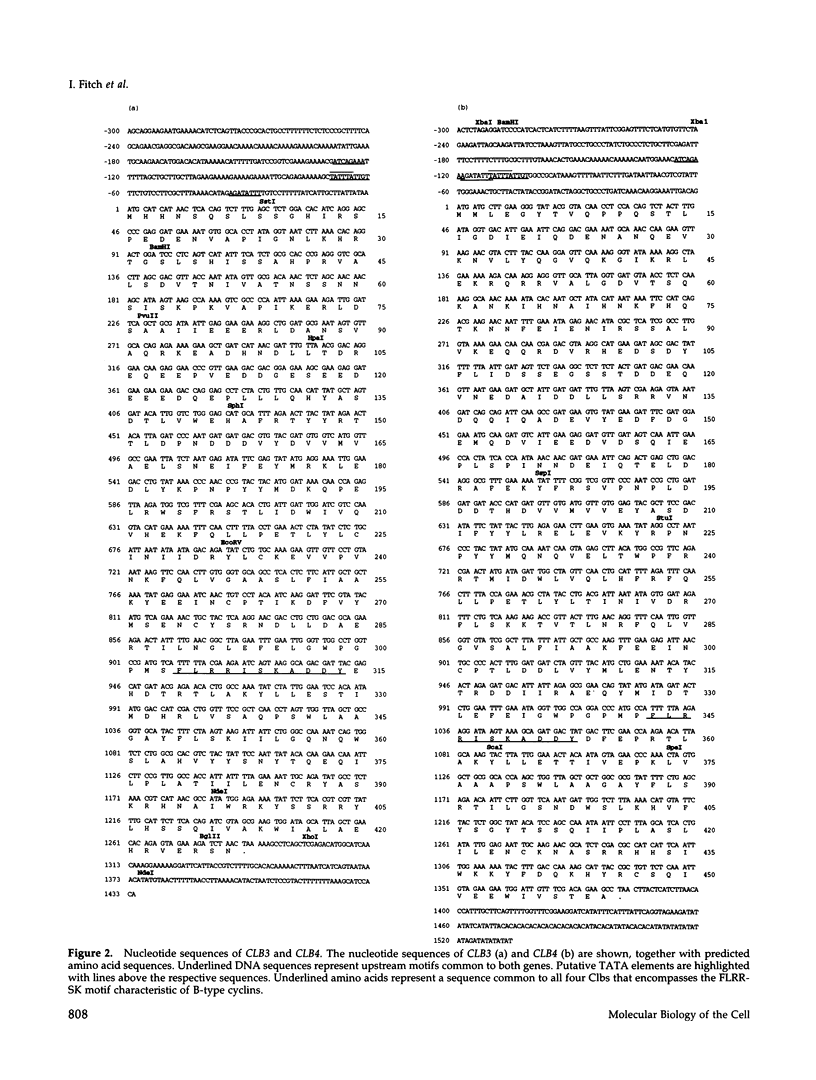
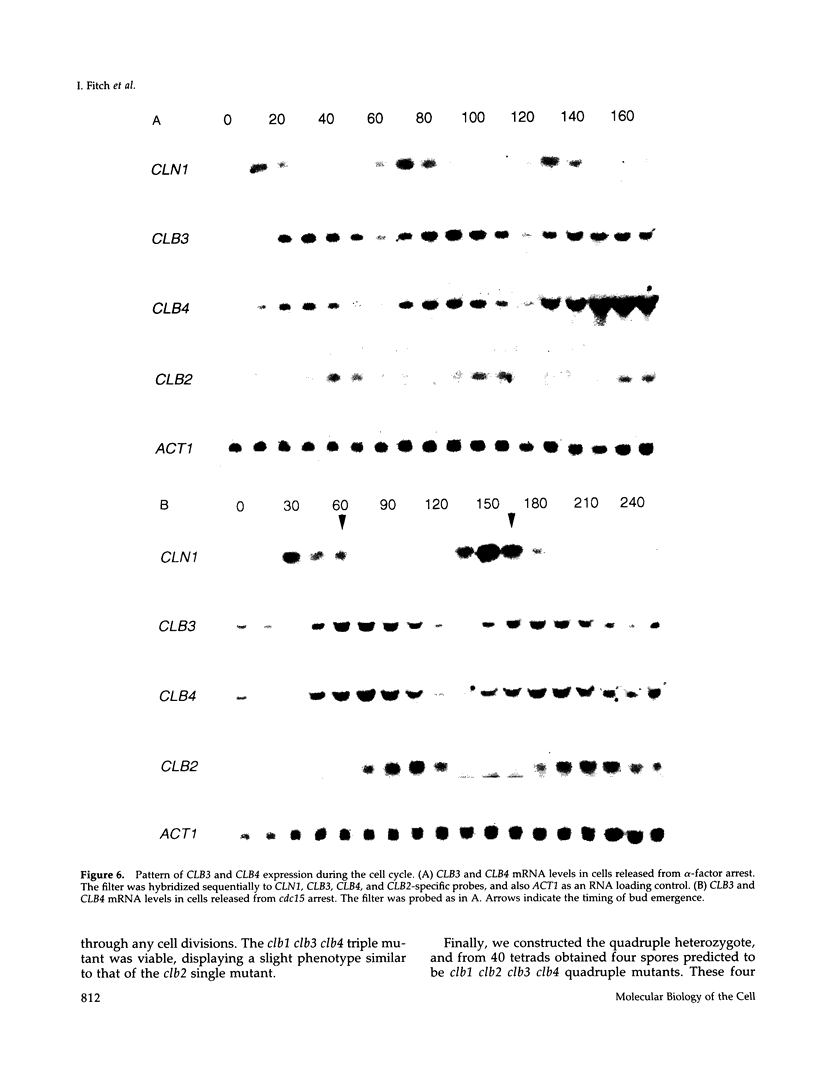
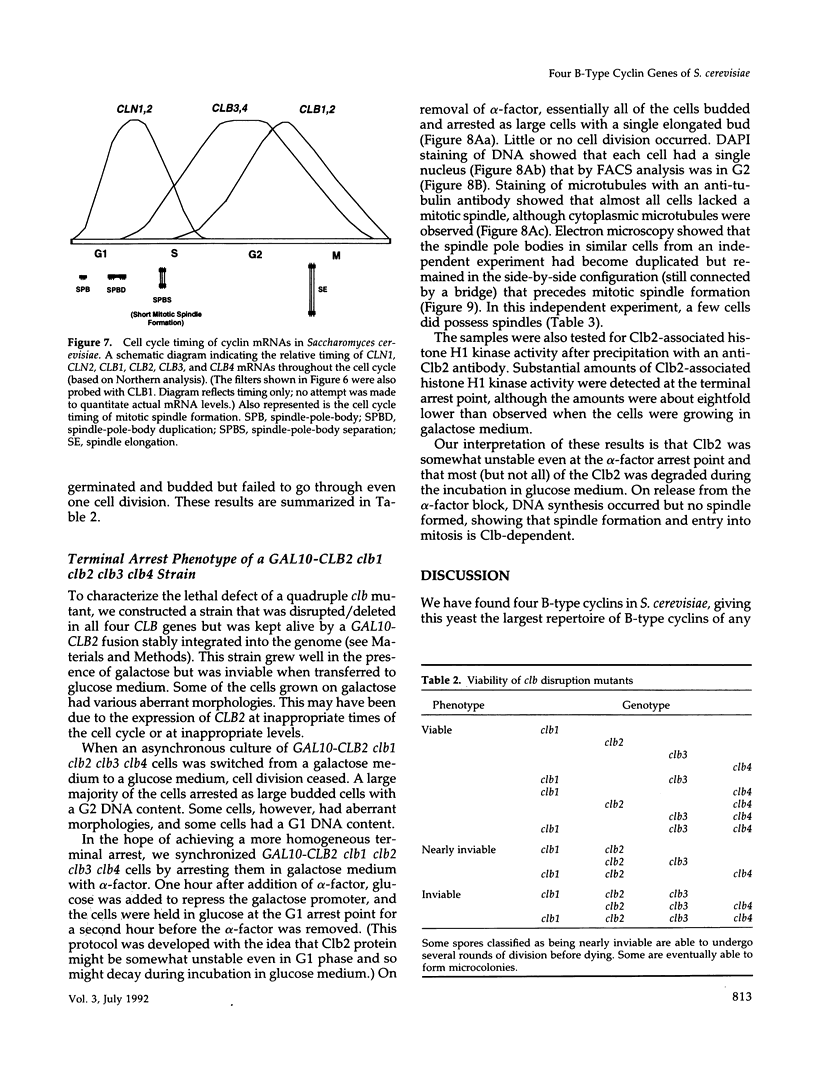
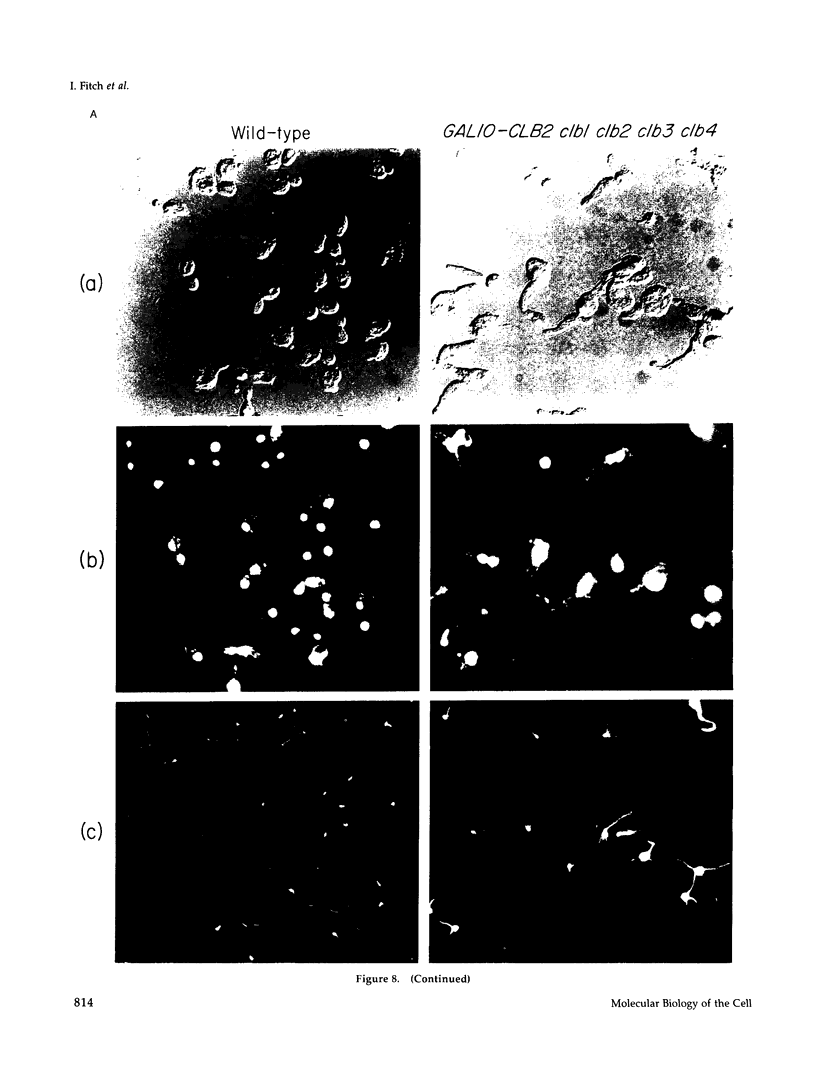
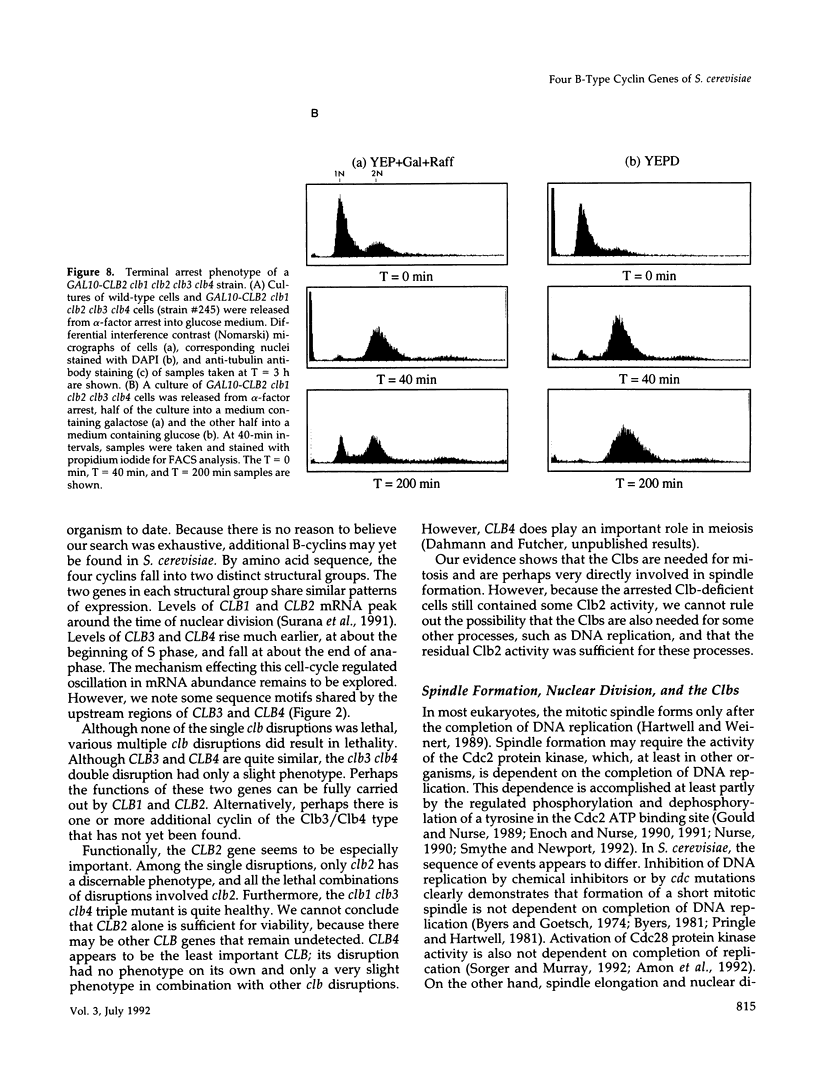
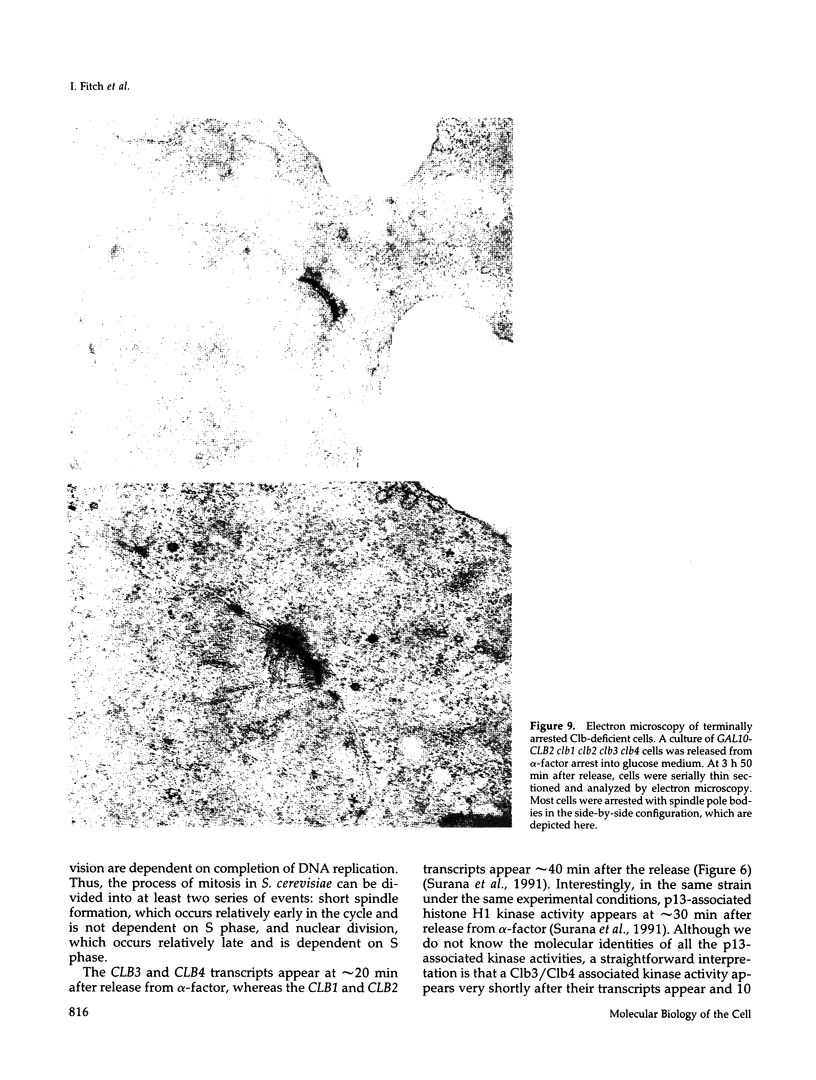
The previously described CLB1 and CLB2 genes encode a closely related pair of B-type cyclins. Here we present the sequences of another related pair of B-type cyclin genes, which we term CLB3 and CLB4. Although CLB1 and CLB2 mRNAs rise in abundance at the time of nuclear division, CLB3 and CLB4 are turned on earlier, rising early in S phase and declining near the end of nuclear division. When all possible single and multiple deletion mutants were constructed, some multiple mutations were lethal, whereas all single mutants were viable. All lethal combinations included the clb2 deletion, whereas the clb1 clb3 clb4 triple mutant was viable, suggesting a key role for CLB2. The inviable multiple clb mutants appeared to have a defect in mitosis. Conditional clb mutants arrested as large budded cells with a G2 DNA content but without any mitotic spindle. Electron microscopy showed that the spindle pole bodies had duplicated but not separated, and no spindle had formed. This suggests that the Clb/Cdc28 kinase may have a relatively direct role in spindle formation. The two groups of Clbs may have distinct roles in spindle formation and elongation.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amon A., Surana U., Muroff I., Nasmyth K. Regulation of p34CDC28 tyrosine phosphorylation is not required for entry into mitosis in S. cerevisiae. Nature. 1992 Jan 23;355(6358):368–371. doi: 10.1038/355368a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booher R. N., Alfa C. E., Hyams J. S., Beach D. H. The fission yeast cdc2/cdc13/suc1 protein kinase: regulation of catalytic activity and nuclear localization. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):485–497. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90429-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booher R., Beach D. Involvement of cdc13+ in mitotic control in Schizosaccharomyces pombe: possible interaction of the gene product with microtubules. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2321–2327. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03075.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bueno A., Richardson H., Reed S. I., Russell P. A fission yeast B-type cyclin functioning early in the cell cycle. Cell. 1991 Jul 12;66(1):149–159. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90147-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers B., Goetsch L. Duplication of spindle plaques and integration of the yeast cell cycle. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:123–131. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers B., Goetsch L. Preparation of yeast cells for thin-section electron microscopy. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:602–608. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94044-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colasanti J., Tyers M., Sundaresan V. Isolation and characterization of cDNA clones encoding a functional p34cdc2 homologue from Zea mays. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3377–3381. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cyclin in fission yeast. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):738–740. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)90933-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G., Beach D. Activation of cdc2 protein kinase during mitosis in human cells: cell cycle-dependent phosphorylation and subunit rearrangement. Cell. 1988 Jul 1;54(1):17–26. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90175-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G., Luca F., Westendorf J., Brizuela L., Ruderman J., Beach D. Cdc2 protein kinase is complexed with both cyclin A and B: evidence for proteolytic inactivation of MPF. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):829–838. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90687-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enoch T., Nurse P. Coupling M phase and S phase: controls maintaining the dependence of mitosis on chromosome replication. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):921–923. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90542-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enoch T., Nurse P. Mutation of fission yeast cell cycle control genes abolishes dependence of mitosis on DNA replication. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):665–673. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90669-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Rosenthal E. T., Youngblom J., Distel D., Hunt T. Cyclin: a protein specified by maternal mRNA in sea urchin eggs that is destroyed at each cleavage division. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):389–396. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90420-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallant P., Nigg E. A. Cyclin B2 undergoes cell cycle-dependent nuclear translocation and, when expressed as a non-destructible mutant, causes mitotic arrest in HeLa cells. J Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;117(1):213–224. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.1.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier J., Minshull J., Lohka M., Glotzer M., Hunt T., Maller J. L. Cyclin is a component of maturation-promoting factor from Xenopus. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):487–494. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90599-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghiara J. B., Richardson H. E., Sugimoto K., Henze M., Lew D. J., Wittenberg C., Reed S. I. A cyclin B homolog in S. cerevisiae: chronic activation of the Cdc28 protein kinase by cyclin prevents exit from mitosis. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):163–174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90417-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glotzer M., Murray A. W., Kirschner M. W. Cyclin is degraded by the ubiquitin pathway. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):132–138. doi: 10.1038/349132a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Nurse P. Tyrosine phosphorylation of the fission yeast cdc2+ protein kinase regulates entry into mitosis. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):39–45. doi: 10.1038/342039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadwiger J. A., Wittenberg C., Richardson H. E., de Barros Lopes M., Reed S. I. A family of cyclin homologs that control the G1 phase in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6255–6259. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagan I., Hayles J., Nurse P. Cloning and sequencing of the cyclin-related cdc13+ gene and a cytological study of its role in fission yeast mitosis. J Cell Sci. 1988 Dec;91(Pt 4):587–595. doi: 10.1242/jcs.91.4.587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H., Weinert T. A. Checkpoints: controls that ensure the order of cell cycle events. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):629–634. doi: 10.1126/science.2683079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hata S., Kouchi H., Suzuka I., Ishii T. Isolation and characterization of cDNA clones for plant cyclins. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2681–2688. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07811.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Pines J. Cyclins and cancer. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1071–1074. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90028-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez J., Alphey L., Nurse P., Glover D. M. Complementation of fission yeast cdc2ts and cdc25ts mutants identifies two cell cycle genes from Drosophila: a cdc2 homologue and string. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3565–3571. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07567.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston M., Davis R. W. Sequences that regulate the divergent GAL1-GAL10 promoter in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1440–1448. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. S., Prakash L. Yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae selectable markers in pUC18 polylinkers. Yeast. 1990 Sep-Oct;6(5):363–366. doi: 10.1002/yea.320060502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. G., Nurse P. Complementation used to clone a human homologue of the fission yeast cell cycle control gene cdc2. Nature. 1987 May 7;327(6117):31–35. doi: 10.1038/327031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner C. F., O'Farrell P. H. Drosophila cdc2 homologs: a functional homolog is coexpressed with a cognate variant. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3573–3581. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07568.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner C. F., O'Farrell P. H. The roles of Drosophila cyclins A and B in mitotic control. Cell. 1990 May 4;61(3):535–547. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90535-m. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minshull J., Blow J. J., Hunt T. Translation of cyclin mRNA is necessary for extracts of activated xenopus eggs to enter mitosis. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):947–956. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90628-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash R., Tokiwa G., Anand S., Erickson K., Futcher A. B. The WHI1+ gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae tethers cell division to cell size and is a cyclin homolog. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4335–4346. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03332.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurse P. Universal control mechanism regulating onset of M-phase. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):503–508. doi: 10.1038/344503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piggott J. R., Rai R., Carter B. L. A bifunctional gene product involved in two phases of the yeast cell cycle. Nature. 1982 Jul 22;298(5872):391–393. doi: 10.1038/298391a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J., Hunt T. Molecular cloning and characterization of the mRNA for cyclin from sea urchin eggs. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):2987–2995. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02604.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J., Hunter T. Isolation of a human cyclin cDNA: evidence for cyclin mRNA and protein regulation in the cell cycle and for interaction with p34cdc2. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):833–846. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90936-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. I., Wittenberg C. Mitotic role for the Cdc28 protein kinase of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5697–5701. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson H. E., Wittenberg C., Cross F., Reed S. I. An essential G1 function for cyclin-like proteins in yeast. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1127–1133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90768-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitou N., Nei M. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol. 1987 Jul;4(4):406–425. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smythe C., Newport J. W. Coupling of mitosis to the completion of S phase in Xenopus occurs via modulation of the tyrosine kinase that phosphorylates p34cdc2. Cell. 1992 Feb 21;68(4):787–797. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90153-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorger P. K., Murray A. W. S-phase feedback control in budding yeast independent of tyrosine phosphorylation of p34cdc28. Nature. 1992 Jan 23;355(6358):365–368. doi: 10.1038/355365a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surana U., Robitsch H., Price C., Schuster T., Fitch I., Futcher A. B., Nasmyth K. The role of CDC28 and cyclins during mitosis in the budding yeast S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):145–161. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90416-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenson K. I., Farrell K. M., Ruderman J. V. The clam embryo protein cyclin A induces entry into M phase and the resumption of meiosis in Xenopus oocytes. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):861–870. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90801-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tachibana K., Ishiura M., Uchida T., Kishimoto T. The starfish egg mRNA responsible for meiosis reinitiation encodes cyclin. Dev Biol. 1990 Aug;140(2):241–252. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(90)90074-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong Y., Connolly T., Futcher B., Beach D. Human D-type cyclin. Cell. 1991 May 17;65(4):691–699. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90100-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Loon A. E., Colas P., Goedemans H. J., Néant I., Dalbon P., Guerrier P. The role of cyclins in the maturation of Patella vulgata oocytes. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3343–3349. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04898.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]